
SolarWinds Traceroute is an essential network diagnostic utility that allows IT professionals to quickly trace the path packets take across a network to identify potential issues, bottlenecks, and optimize performance. As part of SolarWinds’ comprehensive suite of network management solutions, this tool provides valuable insights into network routing by displaying the route and measuring the time taken by each hop. This helps in pinpointing network slowdowns or failures, enabling users to address network problems more efficiently.
What sets SolarWinds Traceroute apart is its ability to perform traceroute operations with minimal configuration and its integration with other SolarWinds network management tools. It’s designed to be easy to use, even for those who are not network specialists, yet it provides detailed data essential for in-depth network troubleshooting. With SolarWinds, users can also access historical data, which helps in identifying recurring issues over time and tracking improvements made to the network.
In this review, we will dive into the key features and functionalities of SolarWinds Traceroute, analyzing how it can benefit network administrators, IT teams, and businesses in improving their network infrastructure. We will explore how it works, what makes it reliable for diagnosing routing problems, and why it should be considered an important part of any network professional’s toolkit.
Finally, we have a surprise: SolarWinds has two Traceroute tools for you:
We are going to review both of these.
The first of these is a sophisticated tool with a Graphical User Interface (GUI). The second is a free text-based utility. All SolarWinds products are written to run on the Windows Server environment and both of these tools are meant to run on that operating system.
SolarWinds Traceroute
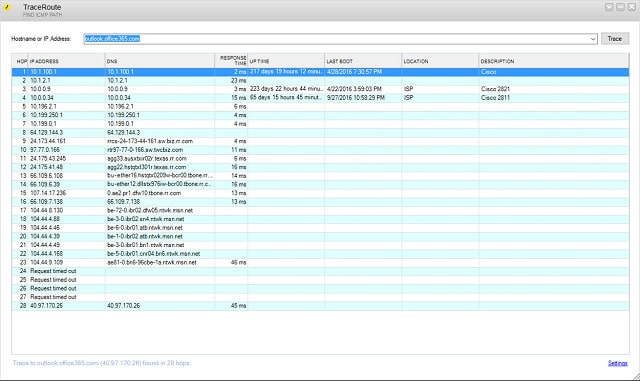
The SolarWinds Traceroute implementation puts a GUI front-end on the Traceroute utility. The implementation of the trace is a little more sophisticated than the command line Traceroute that you are used to because it is implemented with TCP rather than UDP. The utility also adds fields reporting on router status and make. These pieces of information are gleaned through the SNMP messaging system. However, not all routers will allow outsiders to query this information, so those columns are more likely to be populated by in-house equipment rather than by routers on the internet.
Pros:
- Easy to use, doesn’t include any unnecessary ‘fluff’
- Includes a suite of other helpful tools, specifically designed for network administrators and on-site technicians
- Aids in device discovery and testing
- Can help verify DNS and DHCP functionality for different devices
- Can easily export or import results from previous scans
Cons:
- Could benefit from a longer 30-day trial time
SolarWinds Traceroute is not available as a standalone purchase. It is part of the Engineer’s Toolset, which is a bundle of more than 60 network administration tools. This pack includes a network performance monitor and an address management system. The inclusion of the SolarWinds Traceroute facility in this bundle gives you a tool to make quick checks on the health of the links on your network. The inclusion of SNMP fields in the output of this Traceroute implementation implies that this tool is intended for use on large private networks rather than as a method of examining routes across the internet. You can get the Engineer’s Toolset on a 14-day free trial
Traceroute NG

Unlike SolarWinds Traceroute, you can download Traceroute NG individually. This free tool is an advancement on the standard command-line Traceroute that you probably use now. It opens an environment, rather than outputting to the command line and it has a rudimentary menu. However, this is a text-based environment, and it doesn’t recognize mouse actions. The “NG” in the name for this tool stands for “next generation,” which expresses that this tool is a step up from the classic Traceroute.
Another advantage of Traceroute NG over standard Traceroute is that it gives you an option of running TCP or ICMP (UDP) tests. The error reporting derives from ICMP, but the inclusion of TCP packets will make transmission time reporting more accurately reflect the journey of your TCP connections. Traceroute NG can be set to update continuously and it will highlight any path changes, giving you a notification when any downstream problems have resulted in rerouting. This tool is suitable for testing internet connections as well as network link statuses.
Pros:
- Lightweight tool allows you to run it on virtually any network off of any machine
- Supports both IPv4 and IPv6, making it flexible or larger networks utilizing more modern protocols
- Acts as a troubleshooting tool to detect packet loss, jitter, and latency
- Offers simple visual representations of network traffic
- Is completely free
Cons:
- Advanced features such as alerting and network monitoring are not supported but can be found in their flagship tool SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor
SolarWinds offers Traceroute NG as a free download.
About Traceroute
Traceroute is a well-known networking function that shows the likeliest path that connections to a stated destination will follow. The technique sends out a series of UDP packets that are all addressed to the same destination. The facility uses the “time to live” field in the packet header to stop each packet at a router in the path. The TTL field specifies the maximum number of routers that the packet should pass through. Each router that receives the packet decreases the TTL number by one. If a router receives a packet with a TTL of zero, it drops the packet and reports back to the sender in ICMP format that the transmission failed.
In a Traceroute test, a computer sends out a packet with a TTL of 1 and this provokes the first router in the path to drop the packet and report back. The next packet that goes out to the same destination has a TTL of 2, so the second router in the path will drop the packet and report back. The Traceroute routine will continue sending out packets with progressively higher TTL values until it receives back delivery confirmation from the destination.
All of the failure messages that Traceroute receives back get compiled into a list of the routers in the path to the destination. Another piece of information that a Traceroute probe can derive is the time it took for a packet to reach each router in the path and for that router to reply with an error message. By this simple method, a network administrator can detect where links are slowing down a connection. Traceroute actually sends multiple packets for each hop and so the results reported back show the average speeds and will also register any packet loss on the test.
See also: Best traceroute Tools and tracert Software plus Guide
Traceroute limitations
Traceroute can’t analyze what happened on a previous connection and it can’t set the routes that future connections will take. Each router in a path makes its own calculations on which of its neighboring devices it should forward a packet to. This decision is based on a database of the quickest routes to reach a particular destination. Damaged or overloaded routers downstream will alter those calculations. However, notifications of router problems take time to propagate around the internet, so the most efficient path will eventually be recalculated by a router once information of downstream problems are received. Routers closer to the point of failure will receive that information sooner and so they will forward packets to a different router, which may not be in the shortest path.
The fact that route calculations change constantly means that the report from Traceroute might not reflect the exact route that a previous connection took. It is particularly useful if it can be used in parallel with an enduring problematic connection. In such a case, the network administrator will get back a report on the same route that the slow connection is following. Traceroute NG can be set to run constantly, which will give you a live status on the path of an essential link and you will be able to see when that route changes due to device failure on the originally preferred route.
See also: Best Traceroute Alternatives
Traceroute interface types
Seasoned network administrators are accustomed to using command line utilities when investigating performance problems. The output format of standard Traceroute is very easy to follow as the fields for each record are, within one or two characters, always the same width, so an accumulation of records, displays on the screen in a table-like format.
Traceroute NG opens up an environment, so it operates a little like a Windows GUI facility. However, it is not responsive to the mouse and a limited menu structure is implemented through keystrokes. Traceroute NG pads each field in the output resulting in the appearance of a perfect table. This format is very easy to follow and the free tool may give you all the information you need to make a quick test on connection performance.
The use of a graphical user interface for SolarWinds Traceroute lines up the fields in each record into a perfect table. It adds color and commands are implemented by buttons rather than typed text. Some network administrators find that this type of interface enables them to execute a trace quicker than a command line utility where typing errors can delay the successful execution of Traceroute. In both SolarWinds Traceroute and Traceroute NG, output can be saved to a file. With SolarWinds Traceroute, saving output to a file is achieved with a mouse pointer and menu options, in Traceroute NG the save function is available on a keyboard-driven menu.
Traceroute options
Which Traceroute implementation is better, SolarWinds Traceroute or Traceroute NG? Both provide advancements on the standard Traceroute command. Ultimately, your choice of tool will come down to your own personal preferences, habits, and working style. The fact that Traceroute NG is free means that you have nothing to lose by downloading it and installing it. If you have zero budget for network administration tools, then this utility is going to be your only option.
SolarWinds Traceroute is part of a very big package of more than 60 networking tools, so, if you are in the market for a range of network administration tools, then the Engineer’s Toolset represents very good value for money, and SolarWinds Traceroute is in that bundle so you will own it whether you choose to use it or not. SolarWinds offers a 14-day free trial of the Engineer’s Toolset.
Image: Europe network from PXHere. Public domain
Traceroute FAQs
What is the difference between Traceroute and tracert?
Traceroute is the name of a utility. This is implemented by a command that can be issued at the command line of a computer. On Linux and macOS, that command is traceroute; on Windows, the command is tracert.
What is better than Tracert?
Seasoned IT administrators swear by Ping and Tracert as quick checks on system availability and performance. However, these commands have to be issued manually and the results are not pleasing to the eye. Graphical systems are easier to work with and there are many network monitors that operate constantly, checking the performance of every device on the network. These tools are much better than Traceroute. Check out the SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor for an example
What two tools are similar to Traceroute?
Ping is the main rival to Traceroute. Ping only reports on the speed of a connection to a target, while Traceroute gives the connection speed to each router on the path to that location. Pathping is a Ping adaptation that operates in the same way as Traceroute, giving a report on all nodes in a route.
Can I Traceroute a port?
Traceroute doesn’t offer the ability to trace the route to a specific port. On Linux and Unix, use tcptraceroute. This utility is available on macOS through the homebrew package. Type brew install tcptraceroute to activate it. A version is available for Windows. This is called TraceTCP. You also need to install WinPcap in order to run it.
How do I run a traceroute in Windows 10?
To run Traceroute in Windows 10:
- Go to the Start menu search field and type in cmd.
- Click on Open in the results page.
- At the command prompt type tracert to see the format for the command.
- Enter tracert followed by an IP address or domain name to run a traceroute.



