Perl is a powerful and flexible programming language widely used for network programming due to its ease of use, extensive library support, and strong text processing capabilities. Whether you’re developing network applications, automating tasks, or building system administration scripts, Perl provides robust tools that help streamline these processes.
One of Perl’s most important contributions to network programming is its ability to handle both client-side and server-side tasks, making it ideal for creating network protocols, socket-based applications, and communication between different systems across a network. For network administrators, developers, and IT professionals, understanding Perl’s network programming features can dramatically improve productivity and reduce development time.
Perl provides a rich set of built-in modules for network-related tasks, such as working with sockets, handling HTTP requests, and managing DNS queries. These modules make it easier to interact with networks, perform troubleshooting, and even create network-based applications. However, the sheer number of functions and syntax options available in Perl can be overwhelming, especially for beginners or those who need quick access to specific programming commands.
This cheat sheet serves as a valuable resource for those working with Perl in network programming. Whether you’re new to Perl or need a refresher, this guide will help you navigate the key functions, modules, and syntax used in network programming.
From socket programming and HTTP requests to DNS lookups and networking protocols, this cheat sheet will provide you with the essential tools to effectively use Perl for a wide range of network-related tasks.
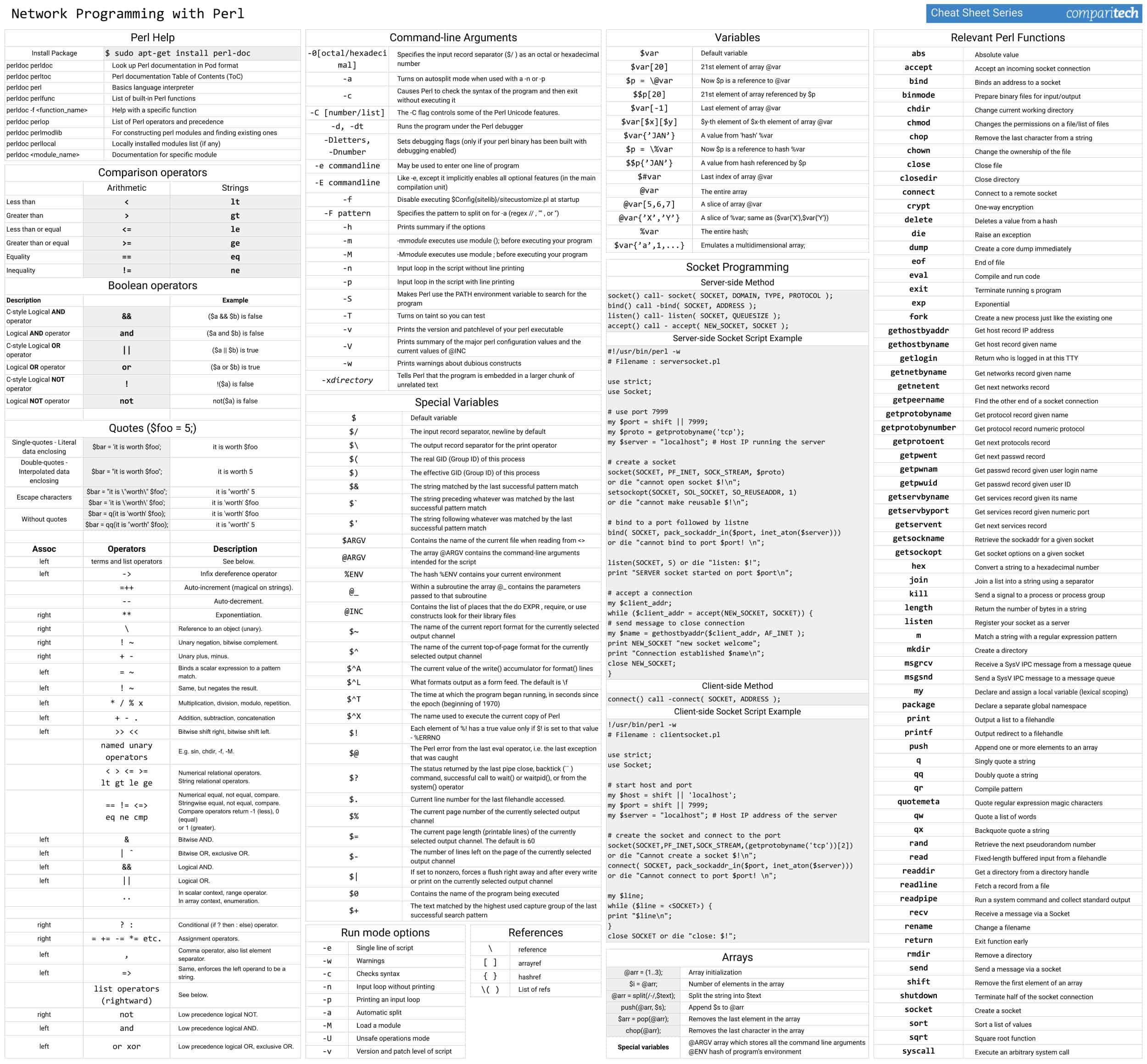
All the tables provided in the cheat sheets are also presented in tables below which are easy to copy and paste.
The Perl Network Programming Cheat Sheet covers:
- Perl help
- Comparison operators
- Command-line arguments
- Special variables
- Run mode options
- References
- Variables
- Arrays
- Socket programming with Server-side & Client-side examples
- Relevant Perl functions
View or Download the Cheat Sheet JPG image
Right-click on the image below to save the JPG file (2500 width x 2320 height in pixels), or click here to open it in a new browser tab. Once the image opens in a new window, you may need to click on the image to zoom in and view the full-sized jpeg.
View or Download the cheat sheet PDF file
Download the cheat sheet PDF file here. When it opens in a new browser tab, simply right click on the PDF and navigate to the download menu.
What’s included in this cheat sheet
The following categories and items have been included in the cheat sheet:
Perl help
Install Package | $ sudo apt-get install perl-doc |
|---|---|
perldoc perldoc | Look up Perl documentation in Pod format |
perldoc perltoc | Perl documentation Table of Contents (ToC) |
perldoc perl | Basics language interpreter |
perldoc perlfunc | List of built-in Perl functions |
perldoc -f | Help with a specific function |
perldoc perlop | List of Perl operators and precedence |
perldoc perlmodlib | For constructing perl modules and finding existing ones |
perldoc perllocal | Locally installed modules list (if any) |
perldoc | Documentation for specific module |
Comparison operators
Arithmetic | Strings | |
|---|---|---|
Less than | < | lt |
Greater than | > | gt |
Less than or equal | <= | le |
Greater than or equal | >= | ge |
Equality | == | eq |
Inequality | != | ne |
Boolean operators |
||
|---|---|---|
Description | Example | |
C-style Logical AND operator | && | ($a && $b) is false |
Logical AND operator | and | ($a and $b) is false |
C-style Logical OR operator | || | ($a || $b) is true |
Logical OR operator | or | ($a or $b) is true |
C-style Logical NOT operator | ! | !($a) is false |
Logical NOT operator | not | not($a) is false |
Quotes ($foo = 5;) |
||
|---|---|---|
Single-quotes - Literal data enclosing | $bar = 'it is worth $foo'; | it is worth $foo |
Double-quotes - Interpolated data enclosing | $bar = "it is worth $foo"; | it is worth 5 |
Escape characters | $bar = "it is \"worth\" $foo"; | it is "worth" 5 |
Without quotes | $bar = q(it is 'worth' $foo); | it is 'worth' $foo |
Assoc | Operators | Description |
|---|---|---|
left | terms and list operators | See below. |
left | -> | Infix dereference operator |
=++ | Auto-increment (magical on strings). |
|
-- | Auto-decrement. |
|
right | ** | Exponentiation. |
right | \ | Reference to an object (unary). |
right | ! ~ | Unary negation, bitwise complement. |
right | + - | Unary plus, minus. |
left | = ~ | Binds a scalar expression to a pattern match. |
left | ! ~ | Same, but negates the result. |
left | * / % x | Multiplication, division, modulo, repetition. |
left | + - . | Addition, subtraction, concatenation |
left | >> << | Bitwise shift right, bitwise shift left. |
named unary operators | E.g. sin, chdir, -f, -M. |
|
< > <= >= lt gt le ge | Numerical relational operators. String relational operators. |
|
== != <=> eq ne cmp | Numerical equal, not equal, compare. Stringwise equal, not equal, compare. Compare operators return -1 (less), 0 (equal) or 1 (greater). |
|
left | & | Bitwise AND. |
left | | ˆ | Bitwise OR, exclusive OR. |
left | && | Logical AND. |
left | || | Logical OR. |
.. | In scalar context, range operator. In array context, enumeration. |
|
right | ? : | Conditional (if ? then : else) operator. |
right | = += -= *= etc. | Assignment operators. |
left | , | Comma operator, also list element separator. |
left | => | Same, enforces the left operand to be a string. |
list operators (rightward) | See below. |
|
right | not | Low precedence logical NOT. |
left | and | Low precedence logical AND. |
left | or xor | Low precedence logical OR, exclusive OR. |
Command-line Arguments
-0[octal/hexadecimal] | Specifies the input record separator ($/ ) as an octal or hexadecimal number |
-a | Turns on autosplit mode when used with a -n or -p |
-c | Causes Perl to check the syntax of the program and then exit without executing it |
-C [number/list] | The -C flag controls some of the Perl Unicode features. |
-d, -dt | Runs the program under the Perl debugger |
-Dletters, -Dnumber | Sets debugging flags (only if your perl binary has been built with debugging enabled) |
-e commandline | May be used to enter one line of program |
-E commandline | Like -e, except it implicitly enables all optional features (in the main compilation unit) |
-f | Disable executing $Config{sitelib}/sitecustomize.pl at startup |
-F pattern | Specifies the pattern to split on for -a (regex // , "" , or '') |
-h | Prints summary if the options |
-m | -mmodule executes use module (); before executing your program |
-M | -Mmodule executes use module ; before executing your program |
-n | Input loop in the script without line printing |
-p | Input loop in the script with line printing |
-S | Makes Perl use the PATH environment variable to search for the program |
-T | Turns on taint so you can test |
-v | Prints the version and patchlevel of your perl executable |
-V | Prints summary of the major perl configuration values and the current values of @INC |
-w | Prints warnings about dubious constructs |
-xdirectory | Tells Perl that the program is embedded in a larger chunk of unrelated text |
Special Variables
$ | Default variable |
$/ | The input record separator, newline by default |
$\ | The output record separator for the print operator |
$( | The real GID (Group ID) of this process |
$) | The effective GID (Group ID) of this process |
$& | The string matched by the last successful pattern match |
$` | The string preceding whatever was matched by the last successful pattern match |
$' | The string following whatever was matched by the last successful pattern match |
$ARGV | Contains the name of the current file when reading from <> |
@ARGV | The array @ARGV contains the command-line arguments intended for the script |
%ENV | The hash %ENV contains your current environment |
@_ | Within a subroutine the array @_ contains the parameters passed to that subroutine |
@INC | Contains the list of places that the do EXPR , require, or use constructs look for their library files |
$~ | The name of the current report format for the currently selected output channel |
$^ | The name of the current top-of-page format for the currently selected output channel |
$^A | The current value of the write() accumulator for format() lines |
$^L | What formats output as a form feed. The default is \f |
$^T | The time at which the program began running, in seconds since the epoch (beginning of 1970) |
$^X | The name used to execute the current copy of Perl |
$! | Each element of %! has a true value only if $! is set to that value - %ERRNO |
$@ | The Perl error from the last eval operator, i.e. the last exception that was caught |
$? | The status returned by the last pipe close, backtick (`` ) command, successful call to wait() or waitpid(), or from the system() operator |
$. | Current line number for the last filehandle accessed. |
$% | The current page number of the currently selected output channel |
$= | The current page length (printable lines) of the currently selected output channel. The default is 60 |
$- | The number of lines left on the page of the currently selected output channel |
$| | If set to nonzero, forces a flush right away and after every write or print on the currently selected output channel |
$0 | Contains the name of the program being executed |
$+ | The text matched by the highest used capture group of the last successful search pattern |
Run mode options
-e | Single line of script |
-w | Warnings |
-c | Checks syntax |
-n | Input loop without printing |
-p | Printing an input loop |
-a | Automatic split |
-M | Load a module |
-U | Unsafe operations mode |
-v | Version and patch level of script |
References
\ | reference |
[ ] | arrayref |
{ } | hashref |
\( ) | List of refs |
Variables
$var | Default variable |
$var[20] | 21st element of array @var |
$p = \@var | Now $p is a reference to @var |
$$p[20] | 21st element of array referenced by $p |
$var[-1] | Last element of array @var |
$var[$x][$y] | $y-th element of $x-th element of array @var |
$var{’JAN’} | A value from ‘hash’ %var |
$p = \%var | Now $p is a reference to hash %var |
$$p{’JAN’} | A value from hash referenced by $p |
$#var | Last index of array @var |
@var | The entire array |
@var[5,6,7] | A slice of array @var |
@var{’X’,’Y’} | A slice of %var; same as ($var{’X’},$var{’Y’}) |
%var | The entire hash; |
$var{’a’,1,...} | Emulates a multidimensional array; |
Arrays
@arr = (1..3); | Array initialization |
$i = @arr; | Number of elements in the array |
@arr = split(/-/,$text); | Split the string into $text |
push(@arr, $s); | Append $s to @arr |
$arr = pop(@arr); | Removes the last element in the array |
chop(@arr); | Removes the last character in the array |
Special variables | @ARGV array which stores all the command line arguments @ENV hash of program’s environment |
Socket Programming with Server-side & Client-side examples
Server-side Method |
|
socket() call- socket( SOCKET, DOMAIN, TYPE, PROTOCOL ); |
|
Server-side Socket Script Example |
|
#!/usr/bin/perl -w |
|
Client-side Method |
|
connect() call -connect( SOCKET, ADDRESS ); |
|
Client-side Socket Script Example |
|
!/usr/bin/perl -w |
Relevant Perl Functions
abs | Absolute value |
accept | Accept an incoming socket connection |
bind | Binds an address to a socket |
binmode | Prepare binary files for input/output |
chdir | Change current working directory |
chmod | Changes the permissions on a file/list of files |
chop | Remove the last character from a string |
chown | Change the ownership of the file |
close | Close file |
closedir | Close directory |
connect | Connect to a remote socket |
crypt | One-way encryption |
delete | Deletes a value from a hash |
die | Raise an exception |
dump | Create a core dump immediately |
eof | End of file |
eval | Compile and run code |
exit | Terminate running s program |
exp | Exponential |
fork | Create a new process just like the existing one |
gethostbyaddr | Get host record IP address |
gethostbyname | Get host record given name |
getlogin | Return who is logged in at this TTY |
getnetbyname | Get networks record given name |
getnetent | Get next networks record |
getpeername | FInd the other end of a socket connection |
getprotobyname | Get protocol record given name |
getprotobynumber | Get protocol record numeric protocol |
getprotoent | Get next protocols record |
getpwent | Get next passwd record |
getpwnam | Get passwd record given user login name |
getpwuid | Get passwd record given user ID |
getservbyname | Get services record given its name |
getservbyport | Get services record given numeric port |
getservent | Get next services record |
getsockname | Retrieve the sockaddr for a given socket |
getsockopt | Get socket options on a given socket |
hex | Convert a string to a hexadecimal number |
join | Join a list into a string using a separator |
kill | Send a signal to a process or process group |
length | Return the number of bytes in a string |
listen | Register your socket as a server |
m | Match a string with a regular expression pattern |
mkdir | Create a directory |
msgrcv | Receive a SysV IPC message from a message queue |
msgsnd | Send a SysV IPC message to a message queue |
my | Declare and assign a local variable (lexical scoping) |
package | Declare a separate global namespace |
Output a list to a filehandle |
|
printf | Output redirect to a filehandle |
push | Append one or more elements to an array |
q | Singly quote a string |
Doubly quote a string |
|
qr | Compile pattern |
quotemeta | Quote regular expression magic characters |
qw | Quote a list of words |
qx | Backquote quote a string |
rand | Retrieve the next pseudorandom number |
read | Fixed-length buffered input from a filehandle |
readdir | Get a directory from a directory handle |
readline | Fetch a record from a file |
readpipe | Run a system command and collect standard output |
recv | Receive a message via a Socket |
rename | Change a filename |
return | Exit function early |
rmdir | Remove a directory |
send | Send a message via a socket |
shift | Remove the first element of an array |
shutdown | Terminate half of the socket connection |
socket | Create a socket |
sort | Sort a list of values |
sqrt | Square root function |
syscall | Execute an arbitrary system call |
Perl network programming FAQs
Is Perl good for networking?
Perl shares a lot of characteristics with C and it includes daemon handling procedures, such as port binding and session management that enables the system to be used for network programming. Like the function library system of C, Perl can be extended by imported modules. This means that Perl can be infinitely extended with new functions or libraries of previously developed utilities.
Is Perl programming still used?
Perl is still widely used because there is a large programmer community with skills in Perl, which is always a good sign that a programming language is going to continue to be used for a long time. There are a large number of libraries of functions that are available for Perl that make the programming language suitable for a wide range of tasks.
Is Perl an Internet language?
Perl is useful for network programming and as the Internet is a network, Perl is also good for Internet programming. The useful features of Perl that make it great for Internet and Web programming are its ability to manage connections, handle files, and build interfaces.