Trellix is a relatively new security software brand and it produces a SIEM. However, you will find that tool difficult to find because Trellix calls its SIEM the Enterprise Security Manager. We will explore the platform and its components later, but first we will look at what a SIEM is and how we can identify a package as a SIEM even when the producer doesn’t give the tool that name.
What does SIEM do?
SIEM stands for Security Information and Event Management. It is a combination of two threat detection strategies. Host-based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDSs) look through log files for signs of anomalous activity. Security Information Management (SIM) is a HIDS. Network-based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDSs) watch network traffic to look for intrusions. Security Event Management (SEM) is a NIDS strategy. SIEM is the combination of SIM and SEM.
The advantage of SEM is that it works on live data. However, network monitors only operate on one point of the network and watch all passing traffic. If the contents of each traveling packet are encrypted, all the SEM system has to work on is the packet header data. SEM isn’t able to compare events in different locations on the network and on separate devices.
SIM is able to see patterns of activity across devices. However, SIM methodologies produce better results with more source data. As the input information for SIM is written to logs, the best SIM results come with the passage of time. A big problem of SIM is that it detects intrusion in retrospect – it isn’t immediate.
SIEM combines the strengths of SIM and SEM. Even SIEM, with its varied techniques, isn’t able to block intrusion. This is the second line of defense and is intended to flush out malicious activities that have managed to slip past edge and boundary defenses.
McAfee and Trellix
McAfee was created in 1987 as McAfee Associates. The company became Intel Security Group in 2014 and then McAfee, LLC in 2017. McAfee was the first producer of commercial antivirus software and gained early successes, making the business an attractive takeover target. Eccentric founder, John McAfee withdrew from the company in 1994, selling all of his shares. After a series of takeovers, the company was bought by Intel in 2014. McAfee was then spun out back into an independent company in 2017 with Intel still maintaining a large shareholding.
As hacker activities become more sophisticated, the traditional antivirus model became unable to fully protect an IT system. The concept of “intrusion” in an IT system involves a hacker gaining entry into a network and establishing a long-term occupation, which is termed an “Advanced Persistent Threat (APT).”
McAfee has invested in machine learning software that uses AI techniques to identify anomalous activity without needing to refer to a database of activity signatures.
The Trellix brand was created in March 2021 by the private equity firm, Symphony Technology Group (STG). The main purpose of the brand was to market the products that STG acquired by buying McAfee Enterprise. This did not include the entire McAfee company – the brand continues as a producer of security tools for home use.
Trellix later acquired FireEye, which added more corporate security tools to the Trellix stable. However, the SIEM tool that we are examining here came from McAfee.
Trellix Enterprise Security Manager
Trellix Enterprise Security Manager (ESM) is a platform of tools that combine to acquire live activity data, scan it for threats, and implement responses either through alerts and notifications or through active automated remediation.
Enterprise Security Manager is a comprehensive security management platform that helps organizations strengthen their cybersecurity posture by providing centralized visibility and control over security operations. ESM aggregates security data from a wide range of sources, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, endpoint security tools, and more, to provide a unified view of security incidents and activities.
The platform’s centralized approach helps security teams quickly identify, investigate, and respond to potential threats across their entire network infrastructure. One of the key strengths of Trellix ESM is its advanced analytics and correlation capabilities.
ESM uses real-time event correlation to identify patterns of suspicious behavior and generate actionable insights, enabling security teams to prioritize and respond to critical incidents. It also supports automated workflows, helping to streamline incident response processes and reduce response times. The platform’s customizable dashboards and reporting features offer detailed visibility into security events and vulnerabilities, which aids in decision-making and compliance reporting.
Trellix ESM can connect to other security solutions, providing a scalable and flexible solution that adapts to evolving security needs. It supports advanced threat detection, vulnerability management, and incident management, making it a valuable tool for organizations looking to protect sensitive data and ensure operational continuity. Trellix Enterprise Security Manager is an essential platform for proactive threat management and enhancing organizational cybersecurity resilience.
Trellix Enterprise Security Manager modules
ESM is actually a platform of modules rather than a single product. This doesn’t have too much influence on the price because when you buy the ESM, you get the whole package. However, the modularity of the platform is both a blessing and a curse. The system allws you to configure each element in the SIEM toolkit individually, which provides you with more control to tailor the package to be more suitable for your enterprise. However, that also means setting up ther SIEM is a lot of work.
The modules on the ESM platform are:
- Event Receiver
- Advanced Correlation Engine
- Enterprise Log Manager
- Enterprise Log Search
- Application Data Monitor
- Direct Attached Storage
- Global Threat Intelligence
You can read about each of these modules in the following sections.
Event Receiver
The Event Receiver is a split system for log collection. An agent resides on each monitored device. It is able to store collected data locally in case the network is unavailable. The central collection system communicates with all agents to receive data from them.
The central controller acts as a log server. It reformats received data into a standard layout, enabling all records to be stored together. Related events are marked so that they can be grouped by analytical searches in the future. This is called a log correlation.
Advanced Correlation Engine
The Advanced Correlation Engine (ACE) builds on the work of the Event Receiver. It searches through past log records to see whether newly filed log messages pertaining to an event that is already in progress and has been identified by earlier messages.
The ACE marks new records so that they can be tied together with older log messages. The identified message group doesn’t link similar records; rather it uses a rule system that spots indicators of the same event that manifests itself through different actions in different locations.
Enterprise Log Manager
The Enterprise Log Manager (ELM) is a log file manager and its purpose is to provide the mandatory log file management facilities required by security standards. It creates log files for incoming log messages both as a source of data for the Security Event Manager and for data security standards reporting.
While standards require raw logs to be saved and be accessible, the Security Event Manager is only interested in certain records that highlight unusual activities, so some log messages will be duplicated and stored in different formats. ELM can be configured to use either local or remote storage facilities. The ELM is an optional module in the SIEM system. The Enterprise Security Manager is able to function without the presence of the Enterprise Log Manager.
Enterprise Log Search
Enterprise Log Search (ELS) is based on Elasticsearch. It is a component of the SIEM system but it is also able to work as a standalone utility. This search facility can operate on the files composed by McAfee Advanced Correlation Engine and the Enterprise Log Manager too examine records of events and identify possible intrusion or data theft. The ELS is integrated into the console of the Enterprise Security Manager and is intended for ad-hoc queries and analysis.
Application Data Monitor
The Application Data Monitor (ADM) provides the SEM part of SIEM. This tool operates on live data and watches all traffic around the network. The monitor is able to look into emails and PDFs, searching for embedded Trojans and dangerous programs.
The monitor operates at the application layer, so it is able to spot attacks that hackers split across packets, hoping to fool traditional network monitors. The service operates on a SPAN port, duplicating data flows rather than sitting inline. This removes the danger of introducing lag on the network.
As well as looking for incoming attack attempts, the ADM searches outgoing traffic for data loss events and unauthorized communications. All discoveries are audited in compliance with data protection standards.
Direct Attached Storage
Direct Attached Storage serves the Enterprise Security Manager and the Enterprise Log Manager, providing a RAID controller, mirrored cache, and IO multi-pathing.
Global Threat Intelligence for ESM
The Global Threat Intelligence (GTI) feed is a core service that supports all of its security products. The GTI is made available in a format suitable for the Enterprise Security Manager.
Trellix Enterprise Security Manager Deployment
Enterprise Security Manager is a cloud-based SaaS product. You sign up for the service at the Trellix website and then get access to your own account page where you can set up the service. The dashboard for the SIEM system is hosted in the cloud, so you will always access the console through a Web browser. During the onboarding process, you will identify your site and target URLs for servers. The tool will then download agents onto your system.
The package includes a series of receivers, so there will be quite a lot of work you need to do on the data generating functions of your system. You need to forward logs to the platform. So, there is a combination of push and pull functions to get data into your ESM implementation. The package can also connect to third party tools for output and remediation.
You can learn more about Enterprise Security Manager by requesting a demo.
Dashboard
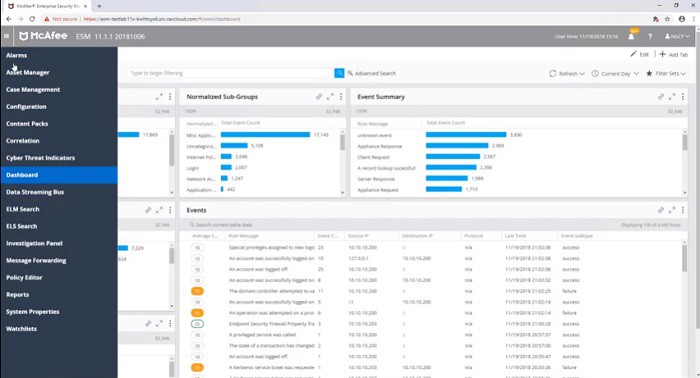
The console of the ESM is accessed through a standard web browser whither it is being deployed as a cloud service or as an appliance. The screens of the service occupy the full width of the browser window and don’t reserve space for a menu. The menu slides in from the left on-demand at the press of a button in the title bar of each screen. Unfortunately, Trellix doesn’t publish screenshots of Enterprise Security Manager’s dashboard since its takeover, so we show here some images of the dashboard under the McAfee brand.
The main screen of the system shows a list of recent events. Other options that can be accessed off the main menu include a log file explorer and the Elasticsearch utility that operates on log files.
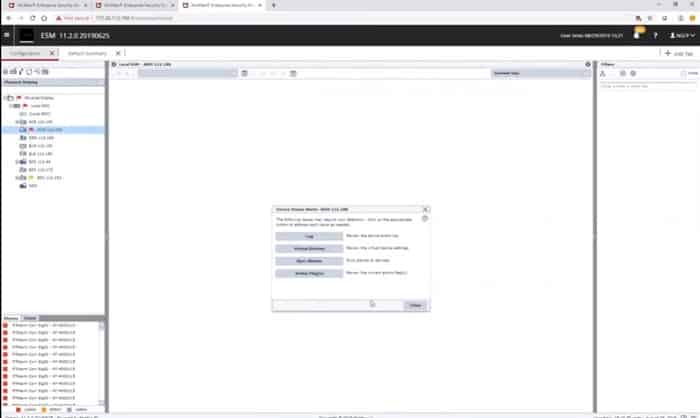
Without the menu in place, it is possible to see the left-panel of the main screen, which lists all monitored devices. A small flag on one of the entries in that list indicates that an event has been detected at that location or that action needs to be taken in order to check on the settings or resources for that device.
Clicking on the flagged device brings up a box of buttons that give access to facilities within the ESM that can resolve the alert that is being shown for that device.
Alternatives to Trellix Enterprise Security Manager
Trellix ESM is one of the best SIEM products on the market. It integrates virus detection and blocks malware download attempts as well as looking for unauthorized human activity. The service includes data loss prevention and suspicious outbound communications. The threat intelligence feed supplied by Trellix’s central labs is one of the most highly regarded in the world.
You can read more about SIEM systems and the best services available on the market today in the best SIEM tools post. However, if you don’t want to read through another article about SIEM, you can see a brief description of other SIEM systems that are worth a try.
Here is our list of the best Trellix ESM alternatives:
- ManageEngine EventLog Analyzer (FREE TRIAL) A partial SIEM offering SIM functions that can be partnered with the Log360 tool to get a feed of live network data in order to create a full SIEM. It installs on Windows and Linux. Start a 30-day free trial.
- Datadog Security Monitoring A cloud-based service that requires the installation of agents on site. The security monitoring log manager and SIEM that is a module of a system monitoring package with alerts.
- Fortinet FortiSIEM A comprehensive cloud-based SIEM system that requires agents to be installed on-site. It includes automated response actions to shut down detected malicious activity.
- CrowdStrike Falcon Insight A combination of a cloud-based SIEM and endpoint detection and response modules that are installed on each device. This system receives an intelligence feed to enhance threat hunting through log records and activity reports and the EDR units implement user and entity behavior analytics to spot anomalies and block zero-day attacks.
- Rapid7 InsightIDR A cloud-based security service that deploys agents on each protected endpoint. The agents ensure protection continuity should the network become unavailable. This service integrates an automated response mechanism.
- OSSEC A free open-source host-based intrusion detection system. It only covers the SIM part of SIEM but can be expanded to cover live network data by bouncing a live feed through files. It installs on Windows, macOS, Linux, and Unix.
- LogRhythm NextGen SIEM Platform It takes live traffic statistics and log messages as input. It applies AI-based machine learning to reduce false positives. It has excellent user guides. This software package installs on Windows and Linux.
- SolarWinds Security Event Manager This tool combines log sources and live data inputs to detect anomalies. The product is part of a suite of infrastructure monitoring tools produced by SolarWinds. This software installs on Windows Server.
- AT&T Cybersecurity AlienVault Unified Security Management A highly regarded and comprehensive independently-developed security system that is now an asset of AT&T. It runs on Windows and macOS.
- Splunk Enterprise Security It combines network monitoring and log management to provide a SIEM tool with data analysis utilities. On-premises software installs on Windows and Linux.
Trellix Enterprise Security Manager FAQs
How long are raw logs stored in Trellix ESM?
The data retention period for raw log data in Trellix ESM is up to you. The length of time that uncompressed logs are kept can be 365 days, 90 days, or 30 days and it is a big influence on the price that you pay for the service.
How do you add a data source in Trellix Enterprise Security Manager?
In order to add a data source to the Trellix ESM system, you need to open the dashboard for the Enterprise Security Manager (ESM). You need to set up an Event Receiver and then configure it. Access to this setup system is via a button in the dashboard that looks like a circular arrow pointing into its center. This is the Get Events and Flows icon and once you enter that system, the process of adding a data source and downloading a collector is guided.
How do you do a packet capture in Trellix Enterprise Security Manager?
Trellix Enterprise Security Manager doesn’t have a native tool for packet capture. Instead, you need to issue a tcpdump command in a terminal session and direct the output to a file.