Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are two tools that network administrators use to identify cyber-attacks. IDS and IPS tools are both used to discover online threats but there is a distinct difference in how they operate and what they do.
IDS vs IPS: What’s the difference?
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are both critical security technologies used to detect and respond to unauthorized activities within a network. While they share similarities, they differ significantly in their core functions and how they handle security threats.
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is designed to monitor network traffic and detect any suspicious activity or potential security threats. IDS works by analyzing inbound and outbound network traffic against known attack signatures or patterns. When it detects any irregularities or threats, such as an attempted malware attack or unauthorized access, it alerts administrators to take action. However, IDS is a passive system—it only detects and alerts on threats but does not intervene in the traffic itself. This makes it more suitable for environments where a passive approach to monitoring is desired.
On the other hand, an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) not only detects malicious activity but also actively prevents or blocks potential threats in real-time. IPS works similarly to IDS in that it analyzes network traffic, but it goes a step further by taking immediate action, such as blocking suspicious traffic or severing malicious connections. This proactive approach helps prevent attacks before they can cause damage, making IPS a more comprehensive security solution for environments that require active threat mitigation.
In summary, the key difference between IDS and IPS is that IDS is focused on detection and alerting, while IPS goes beyond detection by actively preventing threats. Many modern security systems combine both IDS and IPS features to provide a comprehensive solution to network security challenges.
What is an IDS and what does it do?
The IDS monitors network traffic and sends an alert to the user when it identifies suspicious traffic. After receiving the alert the user can take action to find the root cause and remedy it. To detect bad traffic, IDS solutions come in two variations: a Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) and a Host Intrusion Detection System (HIDS).
A NIDS monitors network traffic for security threats through sensors, which are placed throughout the network. A HIDS monitors traffic on the device or system where it is installed. Both of these formats use two main methods of threat detection; signature-based and anomaly-based (we will look at these in more detail further below).
A signature-based IDS uses a list of known attack behaviors to identify new attacks. When network activity matches or resembles an attack from the list the user receives a notification.
The signature-based approach is effective but it has the limitation of only recognizing attacks that match the existing database. As a result, it is poor at detecting Day One attacks.
An anomaly-based IDS uses a baseline model of behavior to detect anomalous activity on the network. Many vendors are using AI and machine learning to help these systems detect abnormal behavior. These systems are extremely effective but can be prone to false positives depending on the vendor you buy from. The top vendors focus on maintaining a low false-positive rate.
What is an IPS? and what does it do?
An IPS (also known as an intrusion detection prevention system or IDPS) is a software platform that analyses network traffic content to detect and respond to exploits. The IPS sits behind the firewall and uses anomaly detection or signature-based detection to identify network threats.
An IPS uses anomaly detection and signature-based detection similar to an IDS. With signature-based detection, the platform scans for patterns that indicate vulnerabilities or exploitation attempts.
Likewise, anomaly detection analyses network traffic and identifies performance anomalies. When the system detects an anomaly it will follow up with an automated response.
These solutions also come with automated responses such as blocking the traffic source address, dropping malicious packets, and sending alerts to the user. Fundamentally, an IPS solution isn’t just a diagnostic tool that identifies network security threats but a platform that can respond to them as well.
Threat Detection methods used by IDS and IPS
Two common detection methods used by IDS and IPS tools alike are signature-based detection and anomaly-based detection. Security vendors combine these two forms of detection methods to provide broader protection against online threats. In this section, we’re going to look at these detection methods in further detail.
Signature-based Detection
IDS and IPS solutions that use signature-based detection look for attack signatures, activity, and malicious code that match the profile of known attacks. Attacks are detected by examining data patterns, packet headers, source addresses, and destinations.
Signature-based detection is excellent at identifying established, less sophisticated attacks. However, detecting based on signatures is ineffective at detecting zero-day attacks, which don’t match other established attack signatures.
Anomaly Detection
To detect more sophisticated threats, vendors have turned to machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI). IDS and IPS tools with anomaly detection can detect malicious behavior in data organically rather than referring to past attacks.
These solutions can detect the malicious nature of new attacks it hasn’t seen before. Anomaly detection systems vary widely between vendors depending on the techniques they use to detect anomalies.
Why are IDS and IPS solutions important?
IDS and IPS solutions are meaningful because they can identify cyberattacks that can damage a company’s information assets. The consequences of a cyber attack can be dramatic. The average cost of a malware attack on a company is $2.4 million. IS and IPS tools provide you with the means to detect cyber attacks.
Both IDS and IPS can detect vulnerability exploits, Denial of Service (DOS) attacks, and brute force attacks that cybercriminals use to put organizations out of action. Therefore each has a place in the cybersecurity strategy of most organizations.
Which is better?
Which tool is better primarily depends on your needs. Both IDS and IPS solutions excel in different areas, but there is a strong argument that IPS is a much more comprehensive cybersecurity solution. Many companies are replacing IDS solutions in favor of the automated features that come with an IPS.
The reason why many companies are transitioning to IPS is that IDS solutions are good at raising the alarm during an attack but they can’t stop an attack. Instead, the user has to remediate the incident manually.
On the other hand, an IPS can identify and block the attack in real-time. The user can configure automated actions and rules to execute automatically during a security incident. For example, if a source is sending malicious traffic to your network then the program can block the offending source IP address or reset the connection to thwart the attack.
Detecting intrusions is very useful but preventing them is often better, which gives IPS solutions a distinct edge. The automated responses of an ISP offer a more effective way to manage threats than manually remediating security events after receiving an alert.
However, if you want to detect attacks then the visual focus of an IDS is likely to be a better fit. The lack of automated features makes it difficult to respond to real-time events (even with the assistant of a security analyst). The real-time response capabilities of an IPS make it a priority for organizations that want to speed up incident remediation and stay secure.
IDS tool example
Though IDS solutions are the same in principle, there is a substantial difference in the end-user experience offered across the products. Fundamentally the key differentiator between these products is the level of visibility (quality/depth of visual displays) and the configurability of the alerts system. In this section, we’re going to look at an example of an IDS tool.
IPS solutions / IPS tool example
IPS solutions also vary significantly from vendor to vendor. The types of threat intelligence and automated response capabilities depend on the quality of the vendor. In this section, we’re going to look at an example of an IPS solution.
Intrusion Prevention with Trend Micro
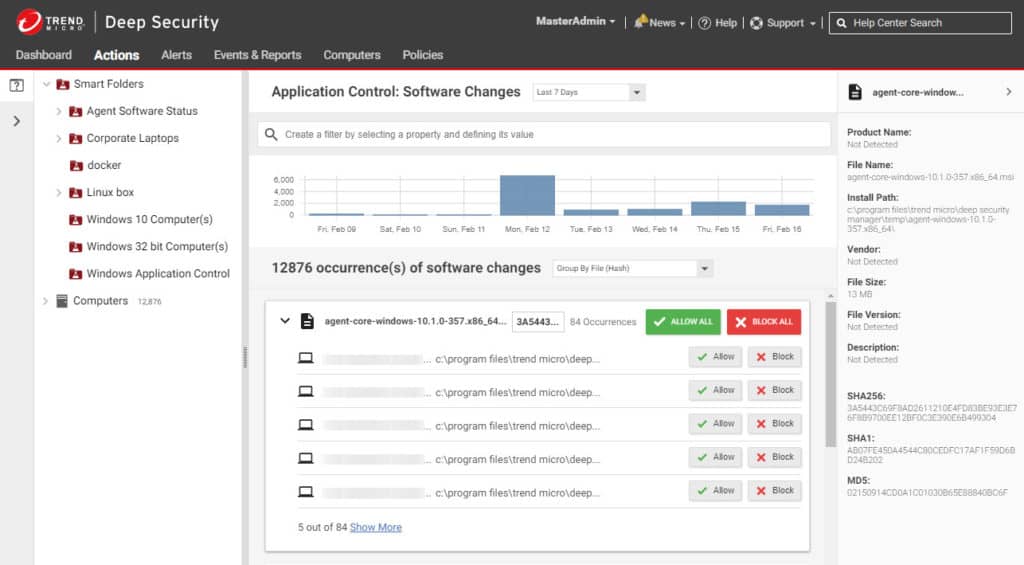
Trend Micro is an IPS solution that can detect and automatically remediate cyber-attacks in real-time. The software uses deep packet inspection, advanced malware analysis, URL reputation, and threat reputation to detect and block attacks. To detect more emerging threats and zero-day attacks, Trend Micro uses machine learning.
Why do we recommend it?
Trend Micro provides a link between the detection of threats and actions that can be implemented to block them. The responses to detected threats are not usually implemented by the Trend Micro system itself. Rather, the tool advises other systems, such as access rights managers and firewalls.
Unlike an IDS the platform doesn’t just discover attacks but responds by blocking exploits, with sandbox analysis and deploys virtual patches to eliminate vulnerabilities quickly.
Trend Micro has out-of-the-box configurations that are automatically updated to protect against the latest threats. The user can also manage security policies through the Security Management System.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is efficient because it interfaces with the system security tools that you already use. It is a good option for mid-sized and large businesses because it is able to keep an eye on all assets simultaneously, which no human could manage. The package also includes a threat intelligence feed.
IPS software like Trend Micro not only discovers security issues but also gives users the security tools to address them. You can find pricing information by requesting a quote from the company.
Intrusion Detection with SolarWinds Security Event Manager
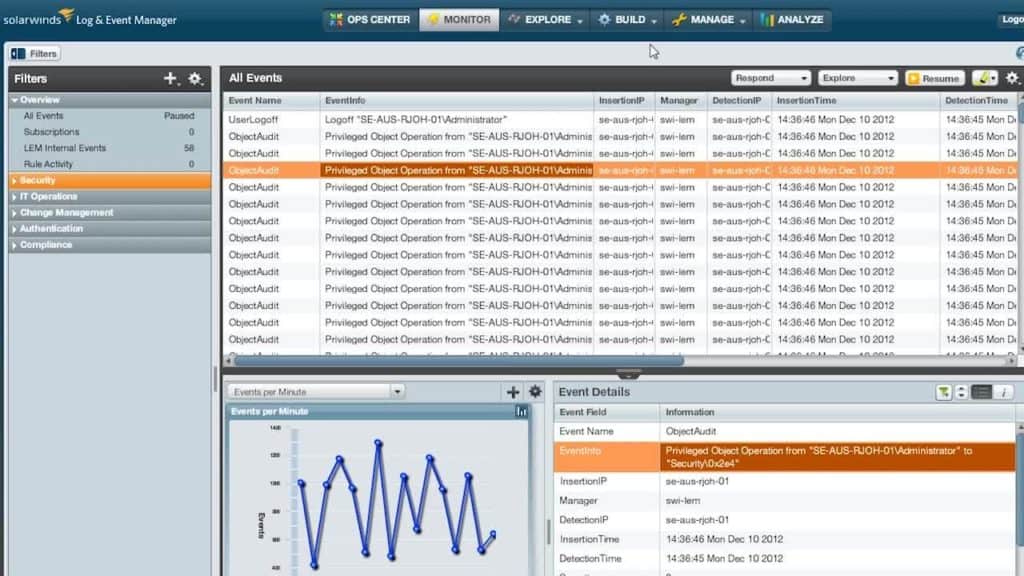
SolarWinds Security Event Manager is an intrusion detection software platform and SIEM solution that collects lots of data from NIDS to identify malicious traffic. Once the tool detects suspicious activity it sends the user an alert. Alert conditions can be managed through the Rule section, where the user configures what events or activities will trigger an alert.
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Security Event Manager is a host-based intrusion detection system that can have live network data fed into it to make it a NIDS as well. This is a SIEM system, which combines NIDS and HIDS. The package includes a data collection service, which stores log messages.
Once the program has scanned the network, you can use the captured data in risk assessment reports to inform your cybersecurity policy. You can schedule these reports so that you have periodic updates to show other members of your team.
Who is it recommended for?
This system provides both log management and security services. The security part of the package scans log messages for signs of malicious activity, which could be implemented by malware or by intruders. The anomaly detection function also looks out for insider threats and account takeover events. This is suitable for large businesses.
SolarWinds Security Event Manager focuses on highlighting security events to you in a way that you can understand in real-time. The tool will help pinpoint the security events that triggered the alerts so you can find a root cause. The software is priced at $3,540 (£2,732) and there is also a 30-day free trial version.
The issue of configurations
Just because you have a new IPS doesn’t mean that you’re protected against the latest threats. One unique issue shared by IDS and IPS systems is that of configurations. The configurations determine how effective these tools are. They both need to be properly configured and integrated carefully into your own monitoring environment so that you don’t run into problems like false positives.
If these tools aren’t properly set up or monitored then your security policy will have significant gaps. For example, an IPS must be configured to decrypt encrypted traffic so that you can catch attackers who are using encrypted communications. Similarly, if your alert parameters aren’t specific enough you’ll be inundated with false-positive alerts that will obscure more important security concerns.
To be effective, both IDS and IPS systems must be consistently managed by trained employees. So when deploying a new solution it is important to train employees to make sure that they can deploy custom settings. No two companies have the exact same risk factors so creating custom configurations is important for mitigating the risk factors you’re exposed to every day.
How to choose an IDS Or IPS
First and foremost, when choosing an IDS or IPS solution you want to consider what your goals are. Consider what capabilities you need, what assets you want to protect, and how a new solution would integrate into your broader cybersecurity strategy.
Don’t make the mistake of paying a premium for an advanced IPS solution if you’re not going to use most of its features. Spending time defining your goals first will help you to produce a solution that’s cost-effective and targeted towards your needs.
An important part of that decision will be choosing between an IDS or IPS. We’ve outlined the strengths of each above, but ultimately the choice between the two should come down to whether you want a passive or active defense solution.
That being said, cost will be a pressing issue for most enterprises. To manage your spending, set a budget for deploying a new solution and take into account the cost of training employees how to use it.
IDS and IPS: Make your choice and stay safe online
A proactive cybersecurity strategy is critical to minimizing entry points to your network. IPS and IDS solutions equip you to identify cyber-attacks so that you can react effectively when the time comes. An Intrusion Prevention System makes sense for most organizations that want to simplify and speed up the remediation process.
However, don’t be fooled into thinking that IPS solutions will take care of your cybersecurity for you. You will still need to train employees on how to use an IPS solution to make sure they know how to configure the software and follow up after security events.
IDS vs IPS FAQs
What is an IDPS?
IDPS stands for Intrusion Detection and Prevention System. This is the same as an IPS, or Intrusion Prevention System. When people use the term “Intrusion Prevention System,” the “Detection” action is implied.
Will a NGFW replace an IPS?
There are many similarities between the capabilities of IPS and the next-generation firewall. However, do not forget that the reason that IDS was first thought of was because security analysts determined that, no matter how strong a firewall is, some malicious traffic will always get through. IPSs are IDSs with added mitigation strategies. So, a firewall operates at the boundary of the network to block all malicious traffic and the IPS operates within the network as a second line of defense.
Which OSI Layer does an IDS use?
Many claim that IDS operates at Layer 3 and Layer 4 of OSI while IPS works at every level from Layer 2 to Layer 7. However, consider a HIDS, which compiles traffic data from several locations, so it is not only operating across packets but sourcing data from different streams. That can only be described as Layer 7 behavior.