With the implementation of automation, AI, and other technological advancements, the risk of cybercrime has also increased. Cyberattackers are using advanced methods and techniques to find loopholes and weaknesses within the network and systems. As a result, maintaining a secure IT infrastructure has become a top priority for organizations of all sizes. A single unpatched vulnerability can be an open gate for attackers to make their way into your system and breach data, resulting in financial loss or reputational damage. This is why organizations must invest in network vulnerability scanners.
Network vulnerability scanners allow IT teams and network administrators to detect, prioritize, and remediate weaknesses before they are exploited. Be it a small business or a large enterprise, having this tool can be a great benefit. IT administrators, cybersecurity professionals, managed service providers, and compliance officers; all can rely on these tools to maintain overall network security.
Here are some of the key pain points that are pushing businesses and security teams to adopt vulnerability scanners:
- You patched your systems last month, but new threats keep emerging, and you are not sure what’s been missing.
- There are hundreds of devices on your network, but you are unable to figure out which ones are vulnerable or outdated.
- A recent penetration test revealed critical flaws, but your current tools didn’t catch them.
- You get alerts when something’s wrong, but no clarity on how serious the issue is or how to fix it.
Investing in the right network vulnerability scanner helps provide solutions to these problems. It shows you exactly where the risk lies and what to fix first. But with so many options available in the market, choosing the one that really fits your business needs can be challenging.
To help you determine, our professionals have performed thorough research and shortlisted the most effective network vulnerability scanner. With the right tool in hand, your business can stay secure and compliant. Further, staying a step ahead of cyber threats.
Our goal is to help you find a scanner that makes vulnerability management simple and less stressful.
Here is our list of the best network vulnerability scanning tools:
- ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus EDITOR’S CHOICE Both free and paid versions for Windows and Windows Server environments, includes vulnerability scanning and automated mitigation. Download a 30-day free trial.
- Site24x7 (FREE TRIAL) This cloud-based package of system monitoring and management services includes a network configuration manager, which implements security controls for vulnerabilities in firmware. Get a 30-day free trial.
- Paessler Network Vulnerability Monitoring with PRTG Part of the PRTG resource monitoring system, this tool checks logs and monitors traffic patterns as well as guarding ports and resource usage. It is free to use for up to 100 sensors.
- SecPod SanerNow Vulnerability Management A SaaS cyber-hygiene platform that centers on a vulnerability manager and system protection tools that act on the findings of the scanner.
- Intruder Vulnerability Scanner A subscription vulnerability scanning service based in the cloud. Plans offer monthly scans, on-demand scans, and human penetration testing.
- CrowdStrike Falcon A cloud-based next-generation AV that protects networks and endpoints. Includes threat-hunting module.
- SolarWinds Network Configuration Manager Our top choice as it’s the most comprehensive tool available. NCM has advanced options to create and monitor configuration policies and issues arising from them.
- ImmuniWeb An AI-driven web-based vulnerability scanner with options from free to human expert pen testing.
- OpenVAS The Open Vulnerability Assessment System is a free vulnerability manager for Linux that can be accessed on Windows through a VM.
- Nexpose Vulnerability Scanner This tool discovers and logs your network-connected devices, highlighting any known vulnerabilities in each.
If you need to know more, explore our vendor highlight section just below, or skip to our detailed vendor reviews.
Best network vulnerability scanning software highlights
Top Feature
End to end vulnerability management, complete visibility, integral remediation, from a single dashboard
Price
100 workstations single user, Subscription Pro $695/year, Enterprise $1,195/year, Free $0; Perpetual Pro $1,737 + $348 AMS, Enterprise $2,987 + $598 AMS; Free edition - 20 workstations and 5 servers; higher slabs and server/network packs, flexible pricing - contact sales
Target Market
SMBs and large enterprises seeking comprehensive vulnerability management across diverse operating systems
Free Trial Length
30-day free trial available, demo available upon requestAdditional Benefits:
Features:
Top Feature
Detects firmware CVEs, ranks severity, suggests remediation steps
Price
Starter $9/month, Pro $35/month, Classic $89/month, Enterprise starts at $225/month - paid annually
Target Market
IT teams and businesses - securing network devices against firmware vulnerabilities
Free Trial Length
30-day free trial
Read more ▼
Top Feature
Visual dashboard with real-time alerts for anomalous traffic, unknown devices, suspicious behavior, enabling fast response
Price
50 devices - $179, 100 devices - $325, 250 devices - $675, 500 devices - $1,183, 1,000 devices - $1,492, PRTG Enterprise - quote-based, all prices per month paid annually
Target Market
Enterprises requiring unified network performance, quick incident response, centralized security monitoring
Free Trial Length
30-day free trial available
Read more ▼
Top Feature
3-in-1 endpoint security and vulnerability management, scans, fixes, checks compliance, from a single console
Price
Negotiated pricing
Target Market
Teams seeking endpoint security with vulnerability management
Free Trial Length
30-day free trial
Read more ▼
Top Feature
Probes networks from an external perspective like a hacker, runs cloud based scanning to surface critical weaknesses in real time
Price
Essential from $99/month, Cloud from $180/month, Pro from $240/month, Enterprise custom pricing
Target Market
Small to mid sized businesses seeking automated regular scans for security weaknesses and vulnerabilities
Free Trial Length
14-day free trial
Read more ▼
Top Feature
Links EDR with vulnerability management, detects exploit attempts
Price
Go $59.99/device - limit 100, Pro $99.99/device, Enterprise $184.99/device, Complete Next-Gen MDR - sales quoted, billed annually
Target Market
Security teams and network engineers, large enterprises with complex needs
Free Trial Length
15-day free trial
Read more ▼
Top Feature
Detects configuration changes in real time and audits compliance
Price
Negotiated pricing
Target Market
Network engineers - automating network device configuration and compliance
Free Trial Length
30-day free trial available
Read more ▼
Top Feature
AI driven discovery and continuous monitoring of external assets, prioritizes vulnerabilities for proactive defense
Price
Negotiated pricing
Target Market
Individuals and businesses seeking comprehensive external attack surface management
Free Trial Length
Demo available upon request, duration not disclosed by the vendor
Read more ▼
Top Feature
Customizable scans, targets, depth, schedules, exclusions
Price
Community Edition free, enterprise features and support via Greenbone - sales quoted
Target Market
Individuals and businesses, seeking an open-source vulnerability scanning solution
Free Trial Length
Community Edition free - no trial, OpenVAS Basic free 14-day trial, Cloud Service free 14-day trial
Read more ▼
Top Feature
Live risk dashboards, prioritized remediation guidance
Price
Negotiated pricing
Target Market
Small businesses and large enterprises, dynamic vulnerability management, real-time analytics
Free Trial Length
30-day free trial
Read more ▼
Key points to consider before purchasing a Network Vulnerability Scanner
Technology advancements and digital infrastructure have increased the demand for cybersecurity. Hence, selecting the right vulnerability scanner that matches your business needs can be a tough decision. To make it easier for you, we have listed some important factors to consider before purchasing a vulnerability scanner.
- Automated Scanning and Real-Time Alerts: One of the major reasons why most organizations demand vulnerability scanners is they help identify risks before they exploit systems. Hence, check if your selected tool can perform automated scans at regular intervals for your system and immediately alert in case of threat detection. Having this feature in you will not only faster response but also minimize the risk of breach.
- Centralized Management: Managing multiple scanners or agent installations can be a tough task, especially if the platform lacks central control. Try to look for a scanner that allows centralized management of agents and scanning activities, making it easier to monitor, schedule, and deploy scans across large networks from a single dashboard.
- Severity-Based Reporting: Not all vulnerabilities are equally dangerous. A good vulnerability scanner must be able to clearly display and categorize vulnerabilities based on severity levels. This helps prioritize actions and focus on high-risk issues first, ensuring effective risk mitigation.
- Historical Vulnerability Tracking: Tracking how vulnerabilities change over time is crucial. Some low-risk issues might escalate in the future if not monitored properly. Hence, look for a tool that allows security teams to track vulnerabilities over time and provide insights into unresolved issues.
- Deep Scanning with Authentication: Standard scans may not uncover hidden misconfigurations. Scanners that use administrative credentials can access deeper layers of systems and applications to check for hidden flaws in security settings. Thus, offering a more accurate and detailed scan.
- Frequency of Signature Updates: The scanner’s database of known vulnerabilities must be regularly updated. Check how frequently the tool updates its vulnerability signatures to ensure you’re protected against the latest threats.
- Ease of Use and Interface: A user-friendly dashboard and simple navigation can significantly reduce the learning curve. Hence, make sure your selected tool is easy to operate. Thus, making it easier for the security team to manage scans and reports without any technical delays.
- Cloud and Mobile Support: Modern infrastructures are often hybrid. Opt for a scanner that supports cloud-based environments and mobile devices. This ensures complete visibility across all digital assets.
- Pricing and Licensing: Each vendor follows different pricing structures. It is best to evaluate upfront and ongoing costs such as software licenses, agent costs, or usage limits. Select a scanner that not only fits your budget but also provides value for the features offered.
- Support and Documentation: Reliable support is crucial, especially when dealing with critical vulnerabilities. Check if the vendor offers full-time support, detailed documentation, and user community resources to help resolve any issues quickly.
To dive deeper into how we incorporate these into our research and review methodology, skip to our detailed methodology section.
Who needs a network vulnerability scanner?
A network vulnerability scanner is an essential tool for organizations and individuals concerned with cybersecurity. Its primary role is to identify potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and security gaps within a network before attackers can exploit them. Here’s who benefits most from using one:
- Businesses of All Sizes From small businesses to large enterprises, any organization that relies on IT infrastructure is at risk of cyberattacks. Small and medium businesses (SMBs) often think they are too insignificant to be targeted, but attackers exploit this assumption. A vulnerability scanner helps detect weak points, ensuring even smaller companies stay protected.
- IT Security Teams Security professionals use vulnerability scanners to gain real-time insights into the security posture of their networks. These tools streamline the process of identifying risks, making it easier to prioritize and remediate issues efficiently.
- Organizations Handling Sensitive Data Industries like healthcare, finance, and e-commerce handle sensitive information such as personal, financial, and health records. Vulnerability scanners help these organizations comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS by maintaining secure environments.
- Managed Service Providers (MSPs) MSPs manage IT services for multiple clients and use vulnerability scanners to monitor and secure diverse networks, ensuring client data and systems remain safe.
- Government and Educational Institutions These entities face increasing cyber threats and must protect sensitive data. Vulnerability scanners ensure system integrity and secure public resources.
Ultimately, anyone responsible for maintaining network security benefits from a vulnerability scanner, as it provides proactive defense against ever-evolving cyber threats.
How does network vulnerability scanning work?
Vulnerability scanning software relies on a database of known vulnerabilities and automated tests for them. A limited scanner will only address a single host or set of hosts running a single operating system platform. A comprehensive scanner scans a wide range of devices and hosts on one or more networks, identifying the device type and operating system, and probing for relevant vulnerabilities with lesser or greater intrusiveness.
A scan may be purely network-based, conducted from the wider internet (external scan) or from inside your local intranet (internal scan). It may be a deep inspection that is possible when the scanner has been provided with credentials to authenticate itself as a legitimate user of the host or device.
Vulnerability management
Vulnerability scanning is only one part of the vulnerability management process. Once the scanner discovers a vulnerability, it must be reported, verified (is it a false positive?), prioritized and classified for risk and impact, remediated, and monitored to prevent regression.
Your organization needs a process – more or less formal – for addressing vulnerabilities. A vulnerability management process includes scheduled scans, prioritization guidance, change management for software versions, and process assurance. Most vulnerability scanners can be part of a full vulnerability management solution, so larger organizations need to look at that context when selecting a scanner.
Many vulnerabilities can be addressed by patching, but not all. A cost/benefit analysis should be part of the process because not all vulnerabilities are security risks in every environment, and there may be business reasons why you can’t install a given patch. Thus it’s useful when remediation guidance from the tool includes alternative means (e.g., disabling a service or blocking a port via firewall).
Related post: Alternatives to Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer
Features to consider
When choosing a vulnerability scanner there are many features to evaluate.
- Is the scanner network-based, doing host/device discovery and target profiling?
- What is the range of assets it can scan – hosts, network devices, web servers, virtual machine environments, mobile devices, databases? Does that fit your organization’s needs?
- Is its vulnerability database comprehensive and a good match for your network’s platforms? Does the database automatically receive a regular feed of updates?
- Is the scanner accurate in your environment? Does it swamp you with uninformative low-level results? What is the incidence of false positives and false negatives? (A false positive entails wasted effort to investigate, and a false negative means an undetected risk.)
- Is the scanner reliable and scalable?
- Are the scanner’s tests unnecessarily intrusive? Does scanning impact hosts/devices thereby slowing performance and potentially crashing poorly-configured devices?
- Can you set up scheduled scans and automated alerts?
- Does it provide canned policies (e,g. for particular compliance regimes)? Can you define your own policies?
- Are scan results easy to understand? Can you sort and filter? Can you visualize trends over time? Does it provide useful guidance about prioritization?
- Does it help with remediation? Are the instructions clear? How about automated remediation through scripting? Does it provide, or integrate with, automated software updating services to install service packs and patches?
- What is the range of canned reports it provides, and what is their quality? Does it provide any compliance reports you need? Can you easily define your own report formats?
Caveats
The vulnerability scanner is only one source of information and is not a replacement for having knowledgeable staff.
Like many network administration tools targeted at enterprises, a high-end vulnerability scanner tends to be expensive. Good no-cost options are available, but many are limited in the size of the network they’ll handle, and all entail the cost of paying staff to learn the tool, install and configure it, and interpret its results. Thus, you should evaluate whether paying for more automation and support may be cheaper in the long run.
Installing a scanner can be complicated, and likely the scanner will initially grind for a few hours to fetch updates to its vulnerability database and preprocess them. Also, depending on the number of hosts and the depth of the scan selected, a given scan can also take hours.
Network vulnerability scanning and penetration testing
Penetration testing is another method of checking on the security of an IT system. Some data security standards, such as PCI-DSS require both. The definition of the two concepts often gets muddled.
A vulnerability scan is usually automated and searches an IT system for known weak points. These might be browser loopholes that need protection software in place to block attacks such as file-less malware. The network vulnerability scan is like running through a checklist of vulnerabilities and reporting which of those problems exist on the system and need to be addressed.
Penetration testing is usually a manual task. This sets a technician to act like a hacker and try to break into or damage the system. The confusion between the definition of vulnerability scanning and “pen-testing” arises from the increasing sophistication of penetration testing tools. The technician testing the system needs certain tools to implement trial attacks. As software houses compete to sell in the lucrative pen-testing market, they include more and more automation to attract “white hat hackers.”
Similarly, the developers of vulnerability scanners are looking for the same entry points that hackers use and so procedures in the vulnerability detection software use the same techniques that pen-testing tools provide.
It is worth investigating pen-testing tools because you will need to implement this security strategy as well as network vulnerability scanning. Pen-testing for website vulnerabilities is a particularly strong growth area at the moment. However, keep in mind that you will still need a vulnerability scanner.
The best network vulnerability scanning software
When selecting the tools that would make up this list, primary considerations included the reliability and industry reputation of the software vendor, their ability to keep their product maintained and up to date. Unique features, ease of setup and use, and scalability options.
1. ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL)
Best for: SMB or large enterprises who are looking for comprehensive vulnerability management across diverse operating systems must invest their time, money, and energy into this tool. It is the go-to solution for organizations wanting to scan their vulnerabilities, security misconfigurations, and web server misconfigurations, and identify high-risk software in real-time.
Price: Subscription for 100 workstations, single user: Professional $695 per year, Enterprise $1,195 per year, Free $0; higher slabs for 250–10,000 workstations plus server and network device packs are listed on the ManageEngine Store. Perpetual for 100 workstations, single user: Professional $1,737 license + $348 Annual Maintenance and Support (AMS), Enterprise $2,987 license + $598 AMS; higher slabs, server, and network device packs are listed. Free edition suitable for up to 20 workstations and 5 servers. 30-day free trial, online demo, and personalized demo available. Flexible pricing beyond prescribed slabs; contact sales to get the pricing for the actual number of devices/technicians that you want to purchase.
ManageEngine produces a wide range of IT infrastructure management tools and Vulnerability Manager Plus is the company’s competitor in the system protection market. The full list of features of this tool is only available to the paid version of the utility, which is designed for large LANs and multi-site networks. The free version is suitable for small and middle-sized enterprises and it will protect up to 25 devices.

The free version gives you both on-demand and scheduled network vulnerability scanning that will detect issues with your in-house network. The advanced technology deployed in the scanner can detect anomalous behavior. This strategy is more effective at identifying zero-day vulnerabilities than conventional rule-based threat database-driven detection systems. You also get threat mitigation actions built into the free edition of Vulnerability Manager Plus.

System and security threats may lie in weak configuration security or out of date software. Vulnerability Manager Plus includes Configuration Management and Patch Management functions that close off these weaknesses. The vulnerability scan will highlight misconfigured devices and enable you to roll out standard configuration policies. The scan also checks on software versions and lets you automate patch installations. You get the option of which patches to roll out, letting you skip versions in cases where essential customizations could be lost through automated software updates. These configuration and software monitoring capabilities extend to web servers and firewalls.
The scanner will identify risky software installed on your equipment and automatically remove unauthorized or unadvised installs.

System administrators get special tools in a dashboard that enable them to extend the basic capabilities of the vulnerability manager. These extend to the integration of Active Directory authentication. The utilities available on the dashboard can be tailored according to the administrator role, which enables team managers to limit the functions available to individual technicians.
When we tested Vulnerability Manager Plus we found the following key features.
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus Key Features:
- Integrated Configuration and Patch Management: Enhances security by addressing configuration errors and outdated software.
- Free Version Availability: Offers a free version suitable for small and mid-sized businesses, covering up to 25 devices.
Unique buying proposition
It is an end-to-end vulnerability management tool that provides complete visibility and integral remediation of threats and vulnerabilities from a single dashboard. Buyers can scan, assess, and manage loopholes from further development.
Feature-in-focus: Automates patching across Windows macOS Linux and third-party apps
Patch management helps buyers to handle the entire patching process in one place. You can set up the patching system the way you want, control how and when patches are applied across all devices, and let the tool do most of the work automatically. It works not only for Windows, but also for Mac, Linux, and even more than 500 third-party apps.
Why do we recommend it?
The most important feature of ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus is that the package includes both a vulnerability scanner and a patch manager. Setting these two services up to work together means that discovered weaknesses that relate to out-of-date software can be fixed automatically. Generally, vulnerabilities that don’t relate to software versions are caused by misconfigurations in devices and endpoints, such as open ports or not having logging activated on a router or a firewall. The Vulnerability Manager Plus package also includes a Configuration Manager, so you can get those problems fixed as well. This tool will look after endpoints running Windows, macOS, and Linux. The tool discovers, logs, and assesses network devices as well.
Powerful actions available through the dashboard include Wake-on-LAN and shutdown capabilities, which can be set as automated mitigation processes or commanded manually. Management reports and system audit recording are included in the Vulnerability Manager Plus package.
Who is it recommended for?
ManageEngine is very good at expanding its potential market by creating a free version of all of its systems. In many cases, the capacity restrictions on the free package are so tight that only the very smallest businesses would be able to use it. However, the free edition of Vulnerability Manager Plus is really worth downloading. It will protect up to 25 endpoints, which includes a decent size of small business. The single LAN edition is also reasonably priced and large organizations will appreciate the Enterprise edition, which covers multiple sites. While ManageEngine produces versions of its software to run on Linux or cloud platforms, the Vulnerability Manager Plus system is only available for Windows Server.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to Vulnerability Manager Plus.
Pros:
- Automated Patch Deployments: Automates the rollout of software updates, improving efficiency and security.
- Enterprise-Level Reporting: Provides robust reporting capabilities, suitable for large network environments.
Cons:
- Learning Curve for Detailed Platform: Requires time investment to fully learn and utilize all its features.
The free edition of the package includes almost all of the capabilities of the two paid versions, which are called Professional and Enterprise editions. You can get a 30-day free trial of either of the two paid versions if your device inventory is too large to qualify for the use of the free version.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus is our editor’s top pick for the best vulnerability scanner because it provides a 360-degree visibility into your security posture. Using this tool, you can get insights into vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, high-risk software, and any other aspect that can provide a gateway for malicious actors to enter your system. It can also assess and prioritize vulnerabilities to help you assign resources optimally. With such features, it is undoubtedly the best tool on our list.
Download: Start a 30-day FREE Trial
Official Site: https://www.manageengine.com/vulnerability-management/
OS: Windows Server
2. Site24x7 (FREE TRIAL)
Best for: IT teams or businesses focused on securing network devices against firmware vulnerabilities might find it a suitable solution.
Price: Starter $9 per month paid annually with 1 NCM device and 5 Network Monitoring Interfaces. Pro $35 per month paid annually with 1 NCM device and 5 Network Monitoring Interfaces. Classic $89 per month paid annually with 1 NCM device and 10 Network Monitoring Interfaces. Firmware vulnerability checks are delivered through Network Configuration Manager (NCM). For higher tiers and any add-ons, contact sales for current pricing and capacity details. 30 day free trial available.
Site24x7’s Firmware Vulnerability Management tool provides businesses with a proactive approach to managing security vulnerabilities found in firmware across devices and networked systems. This tool is essential for businesses that rely on connected devices, network hardware, or embedded systems, as it enables them to stay ahead of evolving security threats.
Site24x7’s Key Features:
- Continuous Firmware Scanning: Regularly scans and monitors firmware versions across devices to detect known vulnerabilities and potential security risks in real time.
- Vulnerability Database Integration: Leverages an extensive database of known firmware vulnerabilities, sourced from security advisories and public repositories.
- Vulnerability Alerts and Notifications: Sends instant alerts for detected vulnerabilities, allowing teams to take timely action to mitigate risks and prevent security breaches.
Unique buying proposition
From a buyer’s standpoint, Site24x7 is a perfect solution for businesses wanting to identify potential risks of firmware vulnerabilities. The tool combines network configuration management with firmware vulnerability scanning for comprehensive device security.
Feature-in-focus:Detects firmware CVEs, ranks severity, suggests remediation steps.
A firmware vulnerability scanner, the built-in software found in devices like routers, firewalls, switches, and printers, helps check if there are any known security issues. It then tells you how serious each issue is, so you know which ones need urgent attention. Along with that, it also gives you information on how to fix the problem.
Why do we recommend it?
By continuously scanning firmware versions for known security flaws, Site24x7 helps organizations identify and mitigate risks that could potentially lead to system breaches, data leaks, or compromised infrastructure. The platform leverages a comprehensive vulnerability database to assess firmware versions, comparing them against known vulnerabilities from security advisories and databases.
Once vulnerabilities are detected, Site24x7 generates detailed reports, allowing businesses to prioritize patching and remediation efforts. The tool also helps identify outdated firmware versions, ensuring that devices are kept up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates. This feature significantly reduces the attack surface and enhances overall system security.

Site24x7’s Firmware Vulnerability Management unit integrates with its broader IT infrastructure monitoring suite, offering organizations a unified platform for managing and securing their entire network. For example, the service is part of the Network Configuration Manager, which backs up the configurations of switches and routers and prevents those services from being tampered with.

The full Site24x7 package discovers and documents all of the equipment connected to your network. That includes servers as well as switches and routers. The Server Monitoring unit extends into application monitoring. The network monitoring system provides device health monitoring and also traffic analysis. The traffic monitoring services extend to internet links between sites and to cloud services.
Application monitoring covers on-premises software and also middleware and services, such as databases and Web servers. The package has a code profiler for the developers of Web applications and a distributed tracing service for Operations teams that needs to watch over those Web applications. Other tools include synthetic and real user monitoring for websites and a log manager.
Who is it recommended for?
Site24x7’s Firmware Vulnerability Management is recommended for businesses of all sizes that rely on networked devices, embedded systems, or connected hardware. This includes industries such as IT infrastructure, telecommunications, manufacturing, healthcare, and retail, where devices and firmware are integral to operations. Organizations that need to manage a large number of devices across multiple locations or cloud environments will particularly benefit from this security automation.
Pros:
- Prioritization and Remediation Guidance: Provides actionable insights by ranking vulnerabilities based on severity and offering guidance on patching and remediation.
- Firmware Version Tracking: Tracks firmware versions and compares them against current, secure releases, ensuring all devices are up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Risk Mitigation for IoT and Embedded Systems: Specifically designed to manage the security risks associated with connected devices and embedded systems, ensuring end-to-end protection.
Cons:
- Lack of Automated Firmware Patching: Does not directly automate the firmware patching process, requiring manual intervention for applying patches.
Site24x7 is a cloud-based system and sold on subscription plans. You can assess the platform by accessing a 30-day free trial.
3. Paessler Network Vulnerability Monitoring with PRTG
Best for: Enterprises requiring unified network performance, quick incident response, and centralized security monitoring must apply for this tool.
Price: Five subscription options plus one quote-based Enterprise tier are available from Paessler for various organizations. Small firms can monitor up to 50 devices with the initial package at $179. Up to 100 devices can be monitored with a $325 plan, which is a good fit for small and mid-sized enterprises. Medium-sized environments can choose a $675 package for 250 devices. A $1,183 package suits 500 devices, enabling larger enterprises to oversee complex networks. A $1,492 package covers 1,000 devices with PRTG 10000. For larger needs, PRTG Enterprise is quote-based and scales beyond 10,000 sensors. All prices are per month paid annually, the number of devices is approximate. A 30-day free trial is available, and after 30 days PRTG automatically reverts to the freeware edition that lets you use up to 100 sensors.
The Paessler system monitoring product is called PRTG. It is a unified infrastructure monitoring tool that covers networks, servers, and applications. PRTG is a bundle of tools and each of those utilities is called a ‘sensor.’ The package has a number of sensors that guard your business against network attacks.
When we tested Network Vulnerability Monitoring with PRTG we found the following key features.
Paessler Network Vulnerability Monitoring with PRTG’s Key Features:
- Automated Device Inventory: Automatically assembles a comprehensive inventory of network devices.
- Real-Time Hardware Monitoring: Constantly checks for hardware changes to maintain network integrity.
Unique buying proposition
Visual dashboard with alerts for anomalous traffic and potential intrusions in real time. Hence, if there is a sudden spike in traffic, unknown devices connecting, or behavior that looks like a cyberattack, the tool will immediately send you an alert. This will help quickly detect and respond to threats before they cause major damage.
Feature-in-focus: Uses SNMP and packet sniffing to detect rogue devices and anomalies
SNMP and packet sniffing features help detect rogue devices, bandwidth spikes, and unusual port activity. It’s like having a security camera for your network that watches for anything odd or suspicious.
Why do we recommend it?
The Paessler Network Vulnerability Monitoring service is part of the PRTG package. PRTG is an on-premises bundle of many monitoring tools, called “sensors.” The PRTG system isn’t a classic vulnerability scanner and the exact functions of your implementation depend on which sensors you decide to activate. However, by selecting certain sensors, you can create a service that spots anomalous activity on the network, which provides intrusion detection.
Any security assessment has to begin with a check on all of your existing infrastructure. PRTG discovers and monitors all of your network devices for status changes and alert conditions. Network traffic monitoring provided by PRTG can also highlight unusual activities that might indicate an intrusion.
A packet sniffing sensor can be used for deep packet inspection, giving you data on the protocol activity in your traffic. This can be identified by port number or traffic source or destination, among other identifiers.
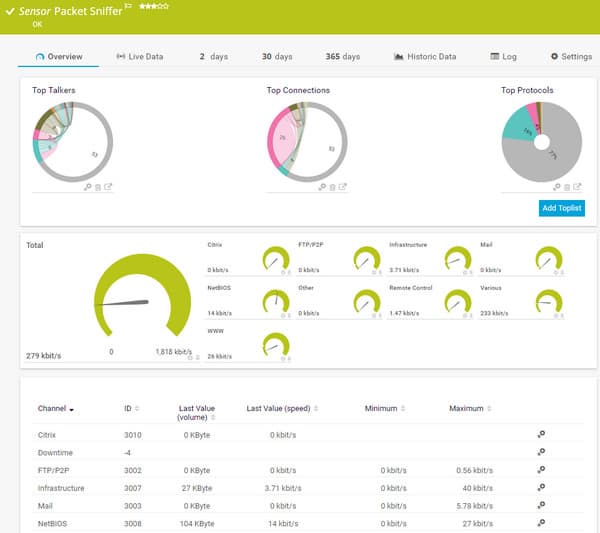
PRTG packet sniffer sensor output screen.The Syslog Receiver module in Paessler PRTG will provide more security scanning features to your system defense strategy. Network attacks leave a paper trail and gathering Syslog and Windows Event Log messages is step one in your vulnerability scan strategy.
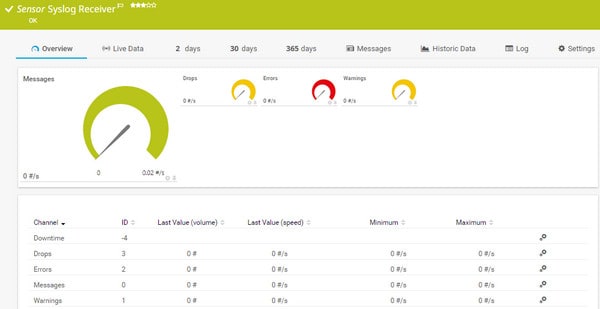
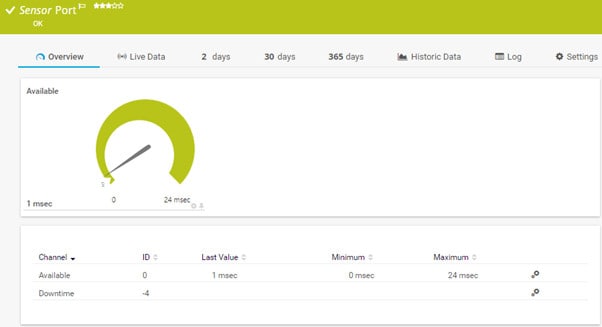
PRTG is a pure monitoring system, so it doesn’t include any active management and resolution functions, such as patch management or configuration management. However, it does include some extra security assessment features, such as its port scanning and monitoring utility.
Any factor monitored by PRTG can be used as a feed into the tool’s alerting system. Factors such as log message volume, log message severity, SNMP Trap data and port activity can all be included in custom alerts.

Paessler sets charging bands for PRTG that are based on the number of sensors that are activated. Every customer receives delivery of the full PRTG system, but with all of its sensors inactive. You customize your implementation by activating the desired sensors.
Who is it recommended for?
PRTG runs on Windows Server and it is now also available as a SaaS platform, so you don’t have to worry about whether you have the right operating system to run the software. This system is priced according to the number of sensors that you pay for and if you only want to activate 100, you never have to pay for the system. That is a very appealing offer for small businesses. As this isn’t an out-of-the-box vulnerability scanner, larger organizations with money to spend will be more likely to opt for one of the vulnerability managers on this list, such as ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus or SecPod SanerNow.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to Network Vulnerability Monitoring.
Pros:
- Scalable and Flexible: Offers scalable pricing based on the number of sensors used, with a free version for small networks.
- Diverse Monitoring Capabilities: Capable of monitoring a range of network, server, and application activities.
Cons:
- Complexity of Features: Presents a detailed platform that may require time to fully understand and leverage its capabilities.
You can use PRTG for free permanently if you only activate up to 100 sensors. You can get a 30-day free trial of PRTG with unlimited sensors to check out its network protection features for yourself. You benefit from full user support, system updates, and security patches even while you are in the free trial period.
Related post: Best Alternatives to Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer
4. SecPod SanerNow Vulnerability Management
Best for: If you are looking for a tool that helps with endpoint security along with vulnerability management, it is a perfect fit.
Price: Buyers have the option to start a free trial session, but pricing details for the product are not available on the official portal.
SecPod SanerNow Vulnerability Management is a cloud-based cyber-hygiene platform that includes security management tools for private networks. It lets you scan, detect, assess, prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities across network devices from the same console seamlessly.
The vulnerability scanner in his package of tools is the key service that triggers other functions and supplies system management tools with asset data. The scanner operates periodically, probing vulnerabilities on endpoints running Windows, macOS, and Linux. This service is suitable for businesses complying with HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR.

The vulnerability manager probes devices to check on all ports and also checks all of the settings of the operating system. It examines the version of the operating system, which tells the scanner its patch status. Tests continue to search through for all software and identify the version numbers of those packages. All of this information is passed through to an asset manager, which maintains a software inventory.

The vulnerability manager can be set to perform scans at a frequency of up to every five minutes. The weaknesses that the vulnerability scanner looks for are dictated by a SCAP database. SCAP stands for Security Content Automation Protocol. There are more than 100,000 factors in the SCAP system for the SanerNow vulnerability manager.
The remediation processes of the vulnerability scanner are implemented by the patch manager of SanerNow. The patch manager interfaces with the software inventor and the vulnerability scan results and then accesses the sites of each software and operating system supplier to get patches and updates. The patch manager copies over the installers of these systems and then applies them at the next available maintenance window.

As it is a cloud-based system, the main processing service of SanerNow is hosted for you. This SaaS package includes a comprehensive dashboard, which gives administrators access to the system settings for the monitoring service and also screens of data and action results. All information in the dashboard gets automatically updated every time the vulnerability scanner runs.
When we tested SanerNow Vulnerability Management we found the following key features.
SecPod SanerNow Vulnerability Management’s Key Features:
- Integrated Patch and Asset Management: Links scanning results with patch management and asset inventory for efficient remediation.
- Compliance-Focused: Suitable for businesses adhering to standards like HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR.
Unique buying proposition
It is a 3-in-1 tool that scans your systems to find weaknesses or security flaws, fixes issues by automatically downloading and applying software updates, and checks if your systems meet industry or company security standards to avoid penalties.
Feature-in-focus: Performs continuous endpoint scans with automated vulnerability remediation
Automated detection and remediation of vulnerabilities across endpoints. You don’t need to manually scan each device or track every issue. The system regularly checks for known vulnerabilities, and when it finds them, it can take action right away.
Why do we recommend it?
SecPod SanerNow Vulnerability Management is one of the modules available in the SanerNow CyberHygiene Platform. Other tools include Compliance Management and Patch Management. The full platform provides security checks for cloud and on-premises packages with both external and internal scanning for networks. This system checks configurations and software – it has a library of more than 160,000 software vulnerabilities to look for. The Vulnerability Management service can link directly to the platform’s Patch Management service to automatically update software where patch statuses are discovered to have fallen behind.
All of the functions of SanerNow log and document all of the system and all of their actions thoroughly. The reporting feature of the package includes summaries of this data and stored logs are very useful for standards compliance auditing.
Who is it recommended for?
The SanerNow CyberHygiene Platform is a very comprehensive system and it will probably be too much for small businesses. Unfortunately, SecPod doesn’t publish its price list and that makes it difficult to assess whether this system would appeal to mid-sized businesses. It would certainly be suitable for large organizations and particularly those that need to comply with HIPAA, PCI DSS, NIST 800-53, NIST 800-171, and ISO.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to SanerNow CyberHygiene Platform.
Pros:
- Frequent Scanning Options: Allows setting scan frequencies up to every five minutes for up-to-date vulnerability insights.
- Extensive Vulnerability Database: Utilizes a comprehensive SCAP database with over 100,000 factors.
Cons:
- Complex for External Management: Some users may prefer in-house security management over external platforms.
The platform for SecPod SanerNow is a subscription service. SecPod doesn’t publish a price tariff. Instead, the Sales Department negotiates a price with each new customer individually. The best way to get to know the SanerNow service with its vulnerability scanner is to access a 30-day free trial.
5. Intruder Vulnerability Scanner
Tested on: SaaS/Cloud
Best for: Small to mid-sized businesses looking for automated, regular scans for security weaknesses and vulnerabilities must try this tool.
Price: Buyers can choose from four editions: Essential, Cloud, Pro, and Enterprise. The Essential plan starting at $99/month offers 1 scheduled scan, unlimited ad hoc scans, unlimited users, and includes 5 infrastructure licenses. Cloud-native companies can choose the Cloud package, starting at $180/month, with unlimited scheduled scans, Cloud Security for up to 3 AWS and Azure accounts, Emerging Threat Scans, Advanced analytics, Role-based access, and 15+ integrations. Companies with hybrid environments might choose the Pro edition, starting at $240/month, with unlimited scanning for internal targets and mass deployment options for internal targets. Lastly, companies with sprawling attack surfaces can opt for the Enterprise edition with custom pricing that includes 1000+ attack surface checks and cloud security for unlimited AWS and Azure accounts. 14-day free trial available.
Intruder is a cloud-based SaaS product that offers three levels of vulnerability scanning services. The basic service of Intruder launches a monthly scan of the protected system, looking for vulnerabilities. Intruder constantly updates its central database of known attack vectors whenever a new one is discovered. This information leads to an understanding of the system vulnerabilities that make those attacks possible.
The vulnerability might be one that has already been used for other attack strategies. In which case, the system security weakness will already be flagged by Intruder and all of its customers would already have been notified of this problem if the monthly scan revealed its presence.
If a new hacker strategy is found to be using a new vulnerability, then that weakness gets registered in the scanner’s rule base and all customers’ systems get re-scanned.

A typical vulnerability report delivers an itemized list of all system features and whether or not that element needs to be hardened. Problems generally fall into the categories for unpatched systems, software that should be updated, open ports, exposed databases. Content management system security loopholes, usage of default passwords, and configuration weaknesses.
When we tested Intruder we found the following key features.
Intruder Vulnerability Scanner’s Key Features:
- Continuous Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scans for system weaknesses and missing patches to maintain security.
- Versatile Architecture Integration: Compatible with most commonly used network architectures for comprehensive coverage.
Unique buying proposition
Provides proactive protection to your network against critical threats by emulating attacker behaviors and identifying vulnerabilities in real-time. It helps find loopholes in web applications, ports, and other external-facing systems.
Feature-in-focus: Performs continuous scans for missing patches, misconfigurations, vulnerabilities
Allows security teams to perform continuous vulnerability scans and identify missing patches, misconfigurations, or remotely vulnerable software.
Why do we recommend it?
Intruder Vulnerability Scanner is a SaaS package. This service can probe a network from an external perspective, acting exactly like a hacker. The base package of this service scans by default once a month but it also provides an intermediate emergency scan looking specifically for a newly discovered exploit. A higher plan can also scan cloud services. The top plan gets you access to a human team of penetration testers. The platform also offers internal vulnerability scans.
Intruder’s vulnerability scans cover all on-premises resources on a client’s site. Higher plans also scan all of the cloud services used by the client. The intruder system console, being cloud-based, is available from anywhere through a browser.
The Intruder system is offered in three plan levels. Each can be paid for either monthly or annually. However, all of the selected subscription period has to be paid for upfront. The three plans are Essential, Pro, and Vanguard. Apart from the emergency scans that are performed when a new vulnerability is discovered, all plans also get a routine, scheduled monthly scan. The Pro plan has an additional on-demand scanning facility and the Vanguard plan includes the services of human penetration testers.

Who is it recommended for?
This tool can be used to provide a range of vulnerability scans and it is a necessary security service for any business operating a network. The tool offers all levels of vulnerability detection: internal network scanning, external testing, and penetration testing. Small businesses might find this system a little expensive, so this system is suitable for mid-sized and large organizations.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to Intruder.
Pros:
- Intuitive User Interface: Offers a sleek, highly visual interface for easy navigation and operation.
- Cloud-Based Operations: Facilitates remote accessibility and eliminates the need for on-premise servers.
- Comprehensive Vulnerability Detection: Capable of assessing a wide range of vulnerabilities in web applications, databases, and operating systems.
- Tiered Pricing Structure: Offers three pricing tiers, making it accessible for businesses of various sizes.
Cons:
- Complex Feature Set: While user-friendly, the platform can require significant time to explore all its features comprehensively.
The Intruder service is available for a 14-day free trial.
6. CrowdStrike Falcon
Best for: Security teams and network engineers who require advanced threat detection and response capabilities must invest in this tool. Large enterprises might find it a relevant option for their complex business needs.
Price: Four editions are available. Falcon Go is $59.99 per device billed annually and limited to 100 devices per purchase; Falcon Pro is $99.99 per device billed annually; Falcon Enterprise is $184.99 per device billed annually; CrowdStrike Falcon Complete Next-Gen MDR is priced via sales on request.
CrowdStrike Falcon is a cloud-based endpoint protection system, which covers an entire network by defending the boundary of the system as well as examining all activity on the network for suspicious activity. The Falcon platform is composed of a series of modules that includes threat hunting, and malware identification.
The vulnerability management system of CrowdStrike Falcon is called Falcon Spotlight. This is a standalone product that can be integrated with other modules that are bought as part of a Falcon bundle. The CrowdStrike Falcon bundles are available in four editions: Pro, Enterprise, Premium, and Complete.
CrowdStrike Falcon Spotlight uses a blend of AI processes and a threat intelligence database to spot vulnerabilities in endpoints and networks. The threat intelligence database is continuously updated and includes information about attack incidences that are sourced from around the world.

As a remote system, Spotlight requires an agent on the site so that it can gain full access from within the network and scan all devices. Another benefit of the agent is that it enables the Spotlight system to continue to manage vulnerability issues even if the connection to the internet gets lost. This is the same agent used for the Falcon Platform, so if you already have the Falcon Platform services, you won’t have any further installation tasks to undertake to use Falcon Spotlight.
When we tested Falcon Spotlight we found the following key features.
CrowdStrike Falcon Key Features:
- Cloud-Based Endpoint Protection: Offers comprehensive protection for network endpoints through a cloud-based platform.
- Falcon Spotlight Vulnerability Management: Provides detailed insights into vulnerabilities using AI and a constantly updated threat database.
Unique buying proposition
Cloud-native platform that continuously pulls in real-time threat intelligence, i.e., data about the latest global cyber threats and uses that information to identify which vulnerabilities in your system are most likely to be targeted. Instead of treating all security flaws the same, it uses a risk-based approach, helping you focus on the most dangerous ones first.
Feature-in-focus: Links EDR and vulnerability management to detect exploit attempts.
Integration of endpoint detection with vulnerability management for comprehensive security. By linking these two, the tool gives you a full picture. It not only shows where the weaknesses are but also alerts you if someone is trying to exploit them.
Why do we recommend it?
CrowdStrike Falcon Spotlight is a vulnerability scanner that includes both exploit scanning and anomalous behavior tracking. This gives the service a double function as an intrusion detection system as well as a vulnerability scanner. The tool, therefore, spots ways that hackers can get into your network and then also finds them if they have already got in. Spotlight uses AI to identify combinations of settings that together can create a vulnerability whereas, individually, those settings might not be registered as a weakness on public CVE lists.
A benefit of the cloud location of Falcon Spotlight is that it is site-neutral. It can scan the endpoints of a business no matter where they are, so it can easily be deployed for multi-site operations and controlled by a central administrator.
Falcon Spotlight doesn’t perform system scans. It logs the devices connected to the network and then reports on the known vulnerabilities of those endpoints as new information on those weaknesses is discovered.
Vulnerability information is made available in the Falcon dashboard, which is accessed through any standard browser. The Spotlight vulnerability information is also available as a feed, which, through the use of a Falcon API, can be channeled through to other applications for incident response and threat mitigation.

Who is it recommended for?
CrowdStrike is a highly respected cybersecurity consultancy and it is capable of providing very complicated systems, such as Spotlight. The complexity of this service ensures that the tool has greater detection capabilities than many of its rival systems. However, it also makes the system’s scan results difficult to understand. That means the tool is ideal for large businesses that have cybersecurity experts on staff to run the Spotlight system and act upon its results. This isn’t a solution for small or mid-sized businesses.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to Falcon Spotlight.
Pros:
- Advanced Threat Intelligence: Utilizes a sophisticated threat intelligence database for proactive vulnerability detection.
- Seamless Integration with Other Falcon Modules: Enables easy integration with additional CrowdStrike Falcon services for enhanced security.
- Agent-Based Scanning: Facilitates continuous management and scanning, even during internet outages.
Cons:
- Complexity for Non-Experts: May be challenging for businesses without dedicated cybersecurity expertise to fully utilize.
- Premium Pricing: Could be cost-prohibitive for smaller businesses or those with limited security budgets.
CrowdStrike offers a free trial of the Falcon system so you can try out its modules for free.
7. SolarWinds Network Configuration Manager
Tested on: Windows Server
Best for: Network engineers who are in need of a powerful tool that automates network device configuration and compliance might find it useful.
Price: SolarWinds does not publicly list the pricing for Network Configuration Manager. Interested buyers can obtain detailed pricing information by contacting SolarWinds directly. The company also offers a 30-day free trial, allowing potential users to evaluate the product before making a purchase decision.
SolarWinds Network Configuration Manager (NCM) is an outlier in our list; it is only free for an evaluation period and covers a particular (but important) subset of vulnerabilities. NCM handles both vulnerability scanning and management for the domain of vulnerabilities arising from the router and switch misconfiguration. It focuses on remediation, monitoring for unexpected changes, and compliance security auditing. NCM is only free during a fully-functional trial of 30 days.
NCM scans for vulnerabilities in the configurations of Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) and Internetwork Operating System (IOS®)-based devices.
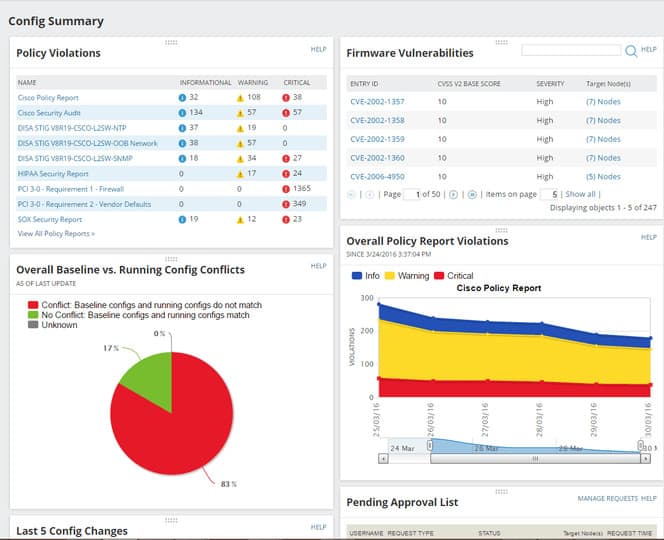
For vulnerabilities due to configuration errors, it provides the ability to run remediation scripts automatically upon detection of a violation, and automatically deploy standardized configuration updates to hundreds of devices.
When we tested Network Configuration Manager we found the following key features.
SolarWinds Network Configuration Manager’s Key Features:
- Configuration Protection: Safeguards device configurations and rolls back unauthorized setup changes.
- Activity Monitoring: Detects and reports malicious activities and standardizes network setup.
Unique Buying Proposition
In my professional opinion, what sets SolarWinds apart from the other tools is its ability to automatically run network configuration backups and vulnerability assessments. If something goes wrong like a misconfiguration or a device failure, the buyer can quickly restore the original settings. At the same time, it also scans these devices for known security weaknesses without needing manual effort.
Feature-in-focus: Detects configuration changes in real time and audits compliance.
What really stands out to users is SolarWinds’s ability to offer real-time change detection and compliance auditing for network devices. It alerts you immediately if there’s an unauthorized or unexpected change. It also checks whether your device settings follow company policies or industry regulations.
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Network Configuration Manager provides CVE scanning of network devices and supports your adjustments of settings to close those exploits. You create a library of configuration images with this service and that will enable you onboard similar devices quickly. The tool also updates firmware when new releases are available. The NCM keeps a constant watch on updated configurations and prevents unauthorized changes by reapplying the stored version.
To address unauthorized changes including regressions, it provides configuration change monitoring and alerting. It can continuously audit routers and switches for compliance. It performs the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST®), Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA), and Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA®) Security Technical Implementation Guide (STIG) compliance reporting out-of-the-box.
SolarWinds NCM has advanced options to create and monitor configuration policies and issues arising from them (issues most commonly arise when configurations are being changed). On top of that, it offers vulnerability scanning, as well as the ability to run remediation scripts automatically for configuration issues and roll out standardized configurations to hundreds of clients. Our choice as it’s the most comprehensive network scanning tool listed.
Who is it recommended for?
This system is an on-premises package that runs on Windows Server. It operates on devices on a single network and so this system is only relevant to businesses that run a large network rather than relying on SaaS systems. The package only watches over vulnerabilities in network devices. While those exploits are important, you will also need to get a vulnerability scanner that checks on operating systems and software on your endpoints.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to SolarWinds NCM.
Pros:
- Automated Remediation: Capable of running scripts automatically upon detection of configuration violations.
- Compliance Reporting: Offers out-of-the-box compliance reporting for standards like NIST, FISMA, and DISA STIG.
Cons:
- Complex for Non-Professionals: Not designed for home users, targeting professional business environments.
- Limited Free Trial: Offers full functionality only during the 30-day evaluation period.
For the trial, a lightweight install can install and use SQL Server Express, but the database is limited to 10 gigabytes.
You can get the Network Configuration Manager as part of a large package of network monitoring and management tools. This is the Network Automation Manager, which includes the Network Configuration Manager, the Network Performance Monitor, the Netflow Traffic Analyzer, the User Device Tracker, the VoIP & Network Quality Manager, the IP Address Manager, and the SolarWinds High Availability service. All of the modules integrate into a single console. The software installs on Windows Server and you can get it on a 30-day free trial.
8. ImmuniWeb
Best for: Individuals and businesses needing comprehensive external attack surface management might find it a suitable option.
Price: ImmuniWeb provides four different packages for its services, but the pricing for these packages is not publicly disclosed. Prospective customers need to request pricing details directly from ImmuniWeb’s sales team. A free demo session is available as well, enabling users to experience the tool’s features before committing to a purchase.
High-Tech Bridge offers a range of network vulnerability scanning services under the brand ImmuniWeb. This is a very sophisticated AI-based system that can be used as a one-time service or contracted in on an SLA for continuous monitoring, consultancy, and advice.

ImmuniWeb specializes in vulnerability scanning and pen testing. The company doesn’t do anything else but it provides a wide range of options for that one task of checking for faults and loopholes in the systems of companies that would give hackers a way in. The automated system focuses on vulnerabilities in web servers.
When we tested ImmuniWeb we found the following key features.
ImmuniWeb’s Key Features:
- AI-Powered Scanning: Utilizes advanced AI techniques for comprehensive vulnerability scanning and penetration testing.
- Flexible Service Options: Offers a range of services from free community tools to advanced human-led penetration testing.
Unique Buying Proposition
ImmuniWeb provides AI-driven discovery of external assets and vulnerabilities for proactive defense. This proactive approach helps you spot risks before attackers do, even for assets you might have forgotten about or didn’t know were publicly accessible.
Feature in Focus: Continuously monitors external assets for vulnerabilities and compliance
Continuous monitoring of external-facing assets for vulnerabilities and compliance issues. It doesn’t just scan once and stop; it keeps monitoring so you’re alerted as soon as something risky or non-compliant is detected. This helps prevent breaches and ensures your systems meet regulatory or internal security standards.
Why do we recommend it?
ImmuniWeb is a platform of system penetration testing tools and it offers a number of scanning utilities for Web assets and networks. This isn’t a standard vulnerability scanner but a series of scanners and ad-hoc testing tools. These systems were developed for use by a human penetration testing team, who are also available for hire. So, you get a choice of levels of service with ImmuniWeb.
The ImmuniWeb product list ranges from a free Community Edition, through an AI-based automated vulnerability scanner, to the services of a team of human pen testers. The standard of service you get depends on how much you are prepared to pay.
The Community Edition of ImmuniWeb is the lowest level of service available from this company, but it is still pretty good and contributes towards GDPR and PCI DSS compliance.

The main vulnerability scanning product of ImmuniWeb is called ImmuniWeb Discovery. This is the AI-based software that provides automated scans of your system from an outsider’s perspective. It will look at your network for all of the ways they know a hacker will try to get in. Unlike a system that just looks for the existence of a list of known exploits, ImmuniWeb Discovery applies machine learning techniques to verify any detected weakness and this reduces the incidences of false positive reporting.
The key difference between vulnerability scanning and pen testing is that vulnerability scanning is performed by software automatically and pen testing is a human endeavor. The other security services of ImmuniWeb are all in the pen testing category. These are called ImmuniWeb On-Demand, ImmuniWeb MobileSuite, and ImmuniWeb Continuous.
Who is it recommended for?
ImmuniWeb offers solutions for all types of businesses. Small businesses that want to get free cybersecurity systems have a platform of pen testing tools and scanners available that can be used without paying. However, you need to have cybersecurity training to get the best out of them, so maybe this package is not suitable for use by owner-managers or small support teams who have no cybersecurity training. At the other end of the price list is a human penetration testing team. This is an expensive solution no matter which provider you choose and mid-sized businesses would probably need to access such a consultancy on an infrequent basis – such as once a year. The paid ImmuniWeb platform is suitable for use by mid-sized and large organizations.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to ImmuniWeb.
Pros:
- Diverse Testing Capabilities: Capable of conducting various levels of testing, from automated scans to detailed human-led penetration tests.
- Free Community Edition: Provides basic scanning services free of charge, suitable for small businesses.
Cons:
- Multi-Language Support Limited: May not be as accessible for non-English speaking users.
- Higher Cost for Advanced Services: More technical and advanced options come with increased costs.
You can get a demo of ImmuniWeb Discovery or try out the Community Edition over at the ImmuniWeb website.
9. OpenVAS
Best for: Individuals and businesses requiring an open-source vulnerability scanning solution might find it a suitable option.
Price: OpenVAS is an open-source vulnerability scanning tool, and no pricing information is listed on its official website. The core OpenVAS Community Edition is available for use at no cost. For advanced enterprise features or professional support (offered through Greenbone, the company behind OpenVAS), users would typically need to contact the provider for any applicable licensing or subscription details.
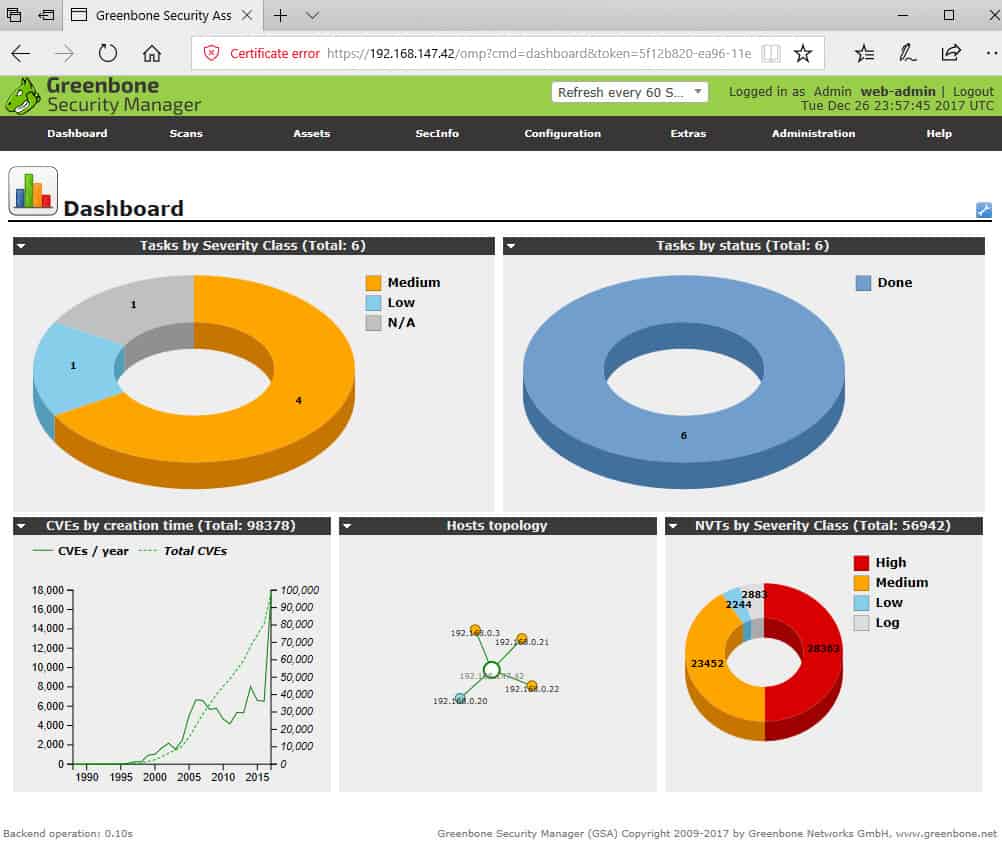
The Open Vulnerability Assessment System, OpenVAS is a comprehensive open-source vulnerability scanning tool and vulnerability management system. It’s free of cost, and its components are free software, most licensed under the GNU GPL. It was forked off the renowned (and costly) vulnerability scanner Nessus when Nessus became a proprietary product. OpenVAS is also part of Greenbone Network’s for-cost vulnerability management solution.
OpenVAS’s Key Features:
- Community-Sourced Vulnerability Database: Utilizes a comprehensive, community-maintained database for vulnerability testing.
- Open Source Solution: Offers a fully open-source platform for vulnerability assessment and management.
Unique Buying Proposition
Offers comprehensive vulnerability scanning with a regularly updated feed of Network Vulnerability Tests (NVTs). These NVTs are regularly updated with the latest threat data, so the scanner can recognize new vulnerabilities as soon as they emerge.
Feature in Focus: Offers customizable scans with targets, depth, schedules, exclusions
The tool comes with extensive scanning capabilities with customizable scan configurations. For example, you can choose to scan only specific systems, set the depth of the scan (quick or full), schedule scans for certain times, or exclude certain devices.
Why do we recommend it?
OpenVAS has a long and respected history. This tool is very competent in both its free and paid editions. You would need to assign a support team member to learn how to use the tool in order to get the best out of this system. However, if you have time to spare, you can get very competent security scanning for networks out of this option. One problem that big organizations would have with the free version is that it doesn’t provide professional support.
OpenVAS uses an automatically-updated community feed of Network Vulnerability Tests (NVTs), over 50,000 and growing. Greenbone’s for-cost product provides an alternative commercial feed of vulnerability tests that updates more regularly and has service guarantees, along with support.
OpenVAS is available as packages in multiple Linux distributions, in source code form, and as a virtual appliance that can be loaded into a VM on Windows. It is also part of Kali Linux.
OpenVAS has a web-based GUI, the Greenbone Security Assistant, a Qt-based GUI, the Greenbone Security Desktop, and a CLI.
Once you are logged in on the web-based GUI you can run your first scan via the Scans menu item: Scans > Tasks. Then on the Tasks page, use the Task Wizard button near the upper left.
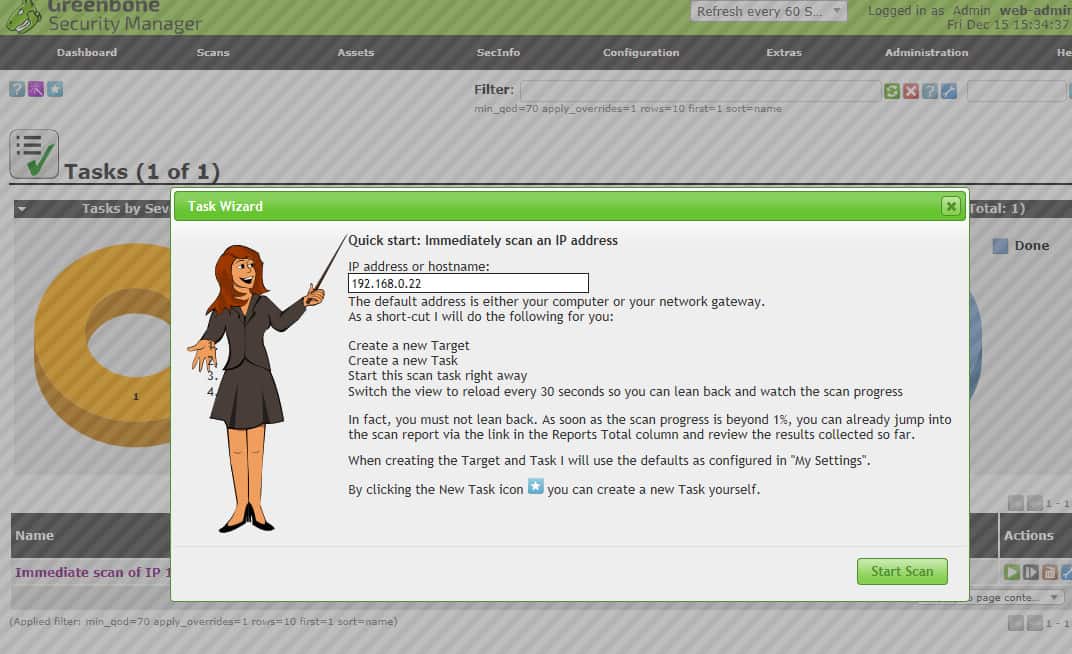
OpenVAS task wizard.When you’ve run a scan task, the Scans > Results page lists the vulnerabilities found.
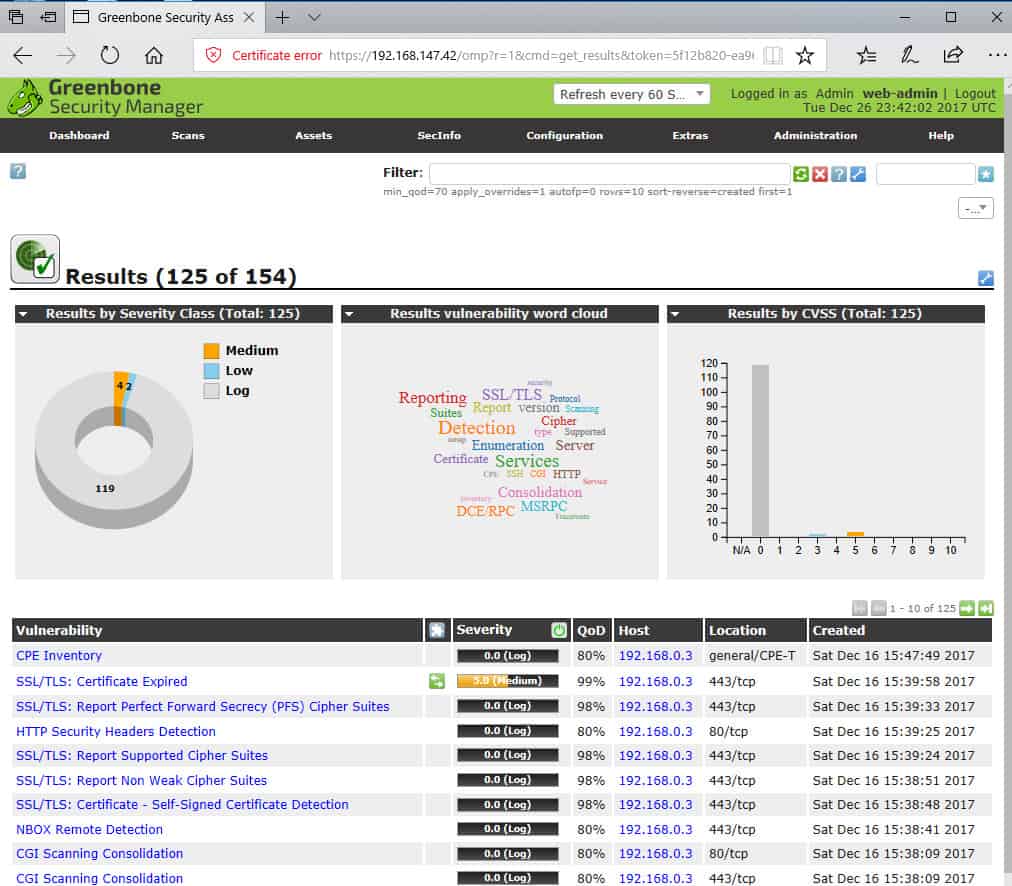
OpenVAS Results page summarizes vulnerabilities found.You can drill down to a particular vulnerability for an explanation and remediation help.
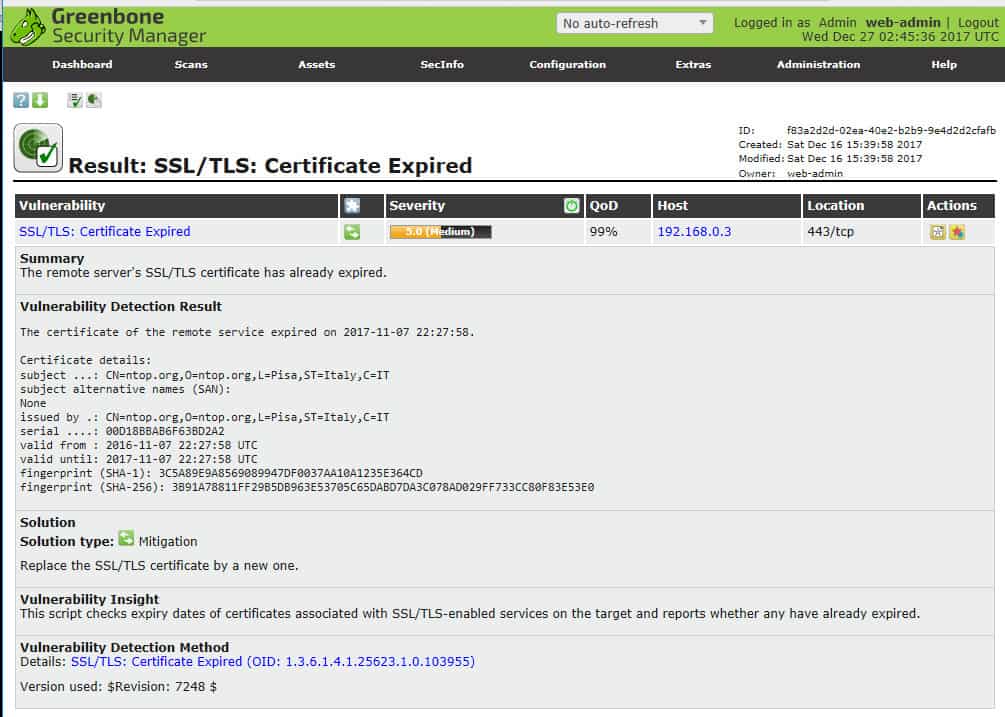
Details on a particular vulnerability.Reports can be exported in various formats, and delta reports can be generated to look at trends.
Who is it recommended for?
A small business owner could use this tool to get strong vulnerability scanning for a network. However, to get the best out of the system, you need to dedicate time to understanding the results and what to do about them. The paid version from Greenbone is a lot easier to use and provides guided steps to detecting problems and solving them. You have to weigh up for yourself whether your time is worth saving by paying for the Greenbone version instead of using the free version. Larger businesses with experienced cybersecurity specialists on staff could get away with using the free Community edition.
Pros:
- Wide Community Support: Benefits from a large and active user community for ongoing development and support.
- No Licensing Fees: Provides a cost-effective solution for businesses looking for a free vulnerability scanner.
Cons:
- No Direct Paid Support: Lacks a dedicated support option, relying on community support.
- Complex User Interface: May present a steep learning curve for those unfamiliar with vulnerability scanning tools.
Alternatives to OpenVAS
Installing and using OpenVAS has a significant learning curve. Although free, OpenVAS is not simply a vulnerability scanner but a full-up free open source vulnerability management platform. The steep learning curve is one of the main reasons many network administrators look for alternatives to OpenVAS, particularly those that prefer a less hands-on approach while still requiring the robustness of a competent tool. This is why OpenVAS comes in at third on our list after the SolarWinds and Paessler offerings.
10. Nexpose Vulnerability Scanner
Best for: Whether you run a small business or a large enterprise, if you demand dynamic vulnerability management with real-time analytics, we recommend you proceed with this tool.
Price: The official website for the Nexpose Vulnerability Scanner (by Rapid7) does not provide any set pricing details. Instead, interested buyers are encouraged to contact Rapid7’s sales team to obtain a quote tailored to their needs. This approach allows the pricing to be customized based on the scope and scale of the organization’s environment.
Nexpose is a comprehensive vulnerability scanner by Rapid7, the owners of the Metasploit exploit framework. Nexpose runs in Windows, Linux, and VM appliances. It scans networks, OSes, web apps, databases, and virtual environments.
The Nexpose system is an alternative product to Rapid7’s InsightVM vulnerability manager. You will notice on the Rapid7 website that the company pushes its InsightVM product much harder, so you can consider either of these tools when looking for a network vulnerability scanner.
When we tested Nexpose we found the following key features.
Nexpose Vulnerability Scanner’s Key Features:
- Compliance Tracking: Highlights compliance shortfalls and assists in maintaining regulatory standards.
- Automatic Device Discovery: Efficiently discovers devices on the network for comprehensive vulnerability analysis.
Unique Buying Proposition
Nexpose is a powerful real-time vulnerability management tool that supports risk prioritization and remediation tracking. It doesn’t just show you a long list of problems, it also tells you which ones are the most dangerous and need to be fixed first.
Feature in Focus: Shows live risk dashboards with prioritized remediation guidance
Live dashboards show the current state of your system’s security. These dashboards aren’t just for display, they give actionable insights, meaning they help you understand what the risks are and what steps you should take next.
Why do we recommend it?
Nexpose is a highly respected vulnerability scanner that was originally developed as an open-source system and, until recently, was available for free in a Community Edition. Rapid7 took over the project and turned it into a commercial product. However, its history means that the tool has a large user community and it is easy to pick up tips and tricks from community forums. The long history and large user base of the tool also mean that you are more likely to find people with Nexpose experience to hire if you are staffing up a cybersecurity team.
Nexpose web-based console. The online help, behind the “?” icon, is your most helpful asset when getting started.
In the web GUI, you define one or more “sites” – networks of interest – for instance, by providing a CIDR address range. You can then choose from one of several predefined scan templates.
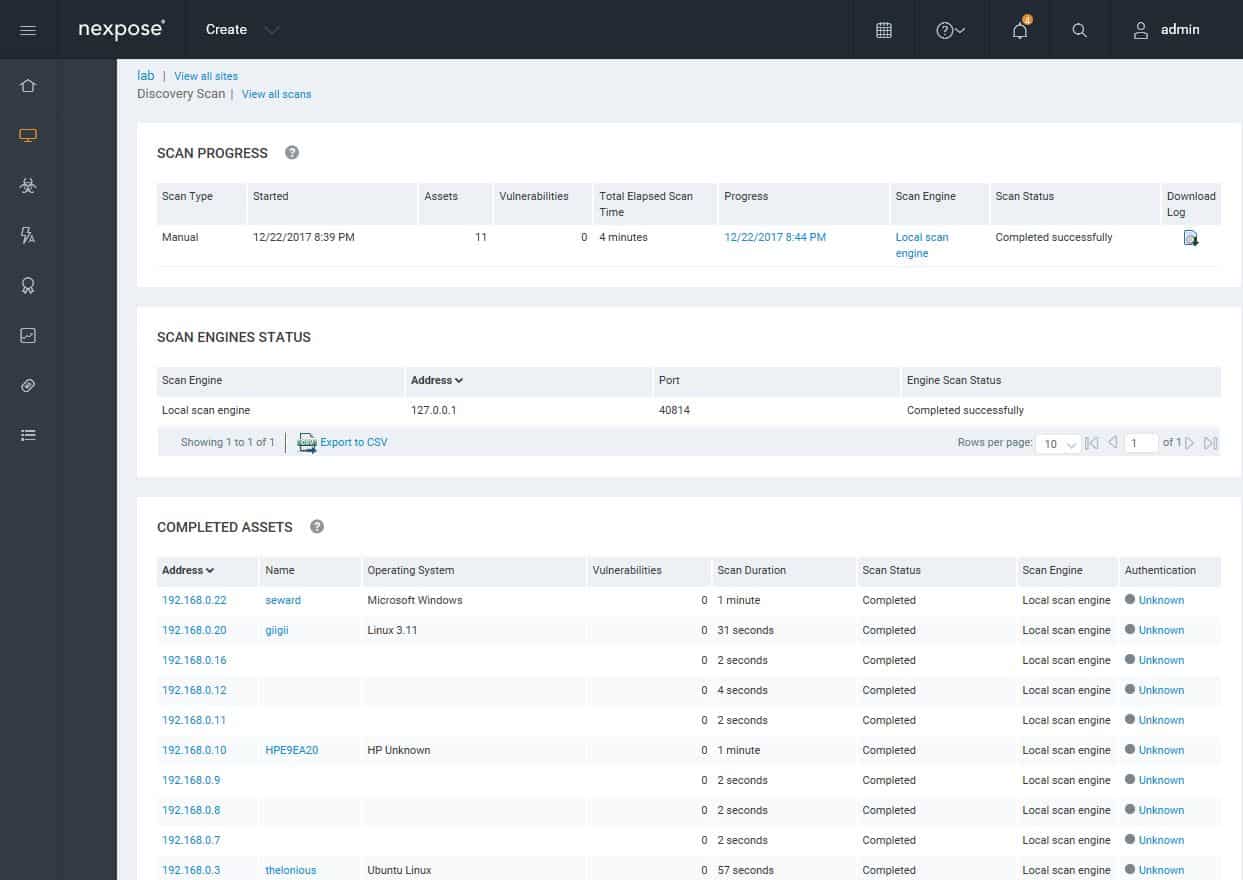
Nexpose web GUI has multiple predefined scan templates.A Discovery Scan identifies all the devices and hosts in your specified address range.
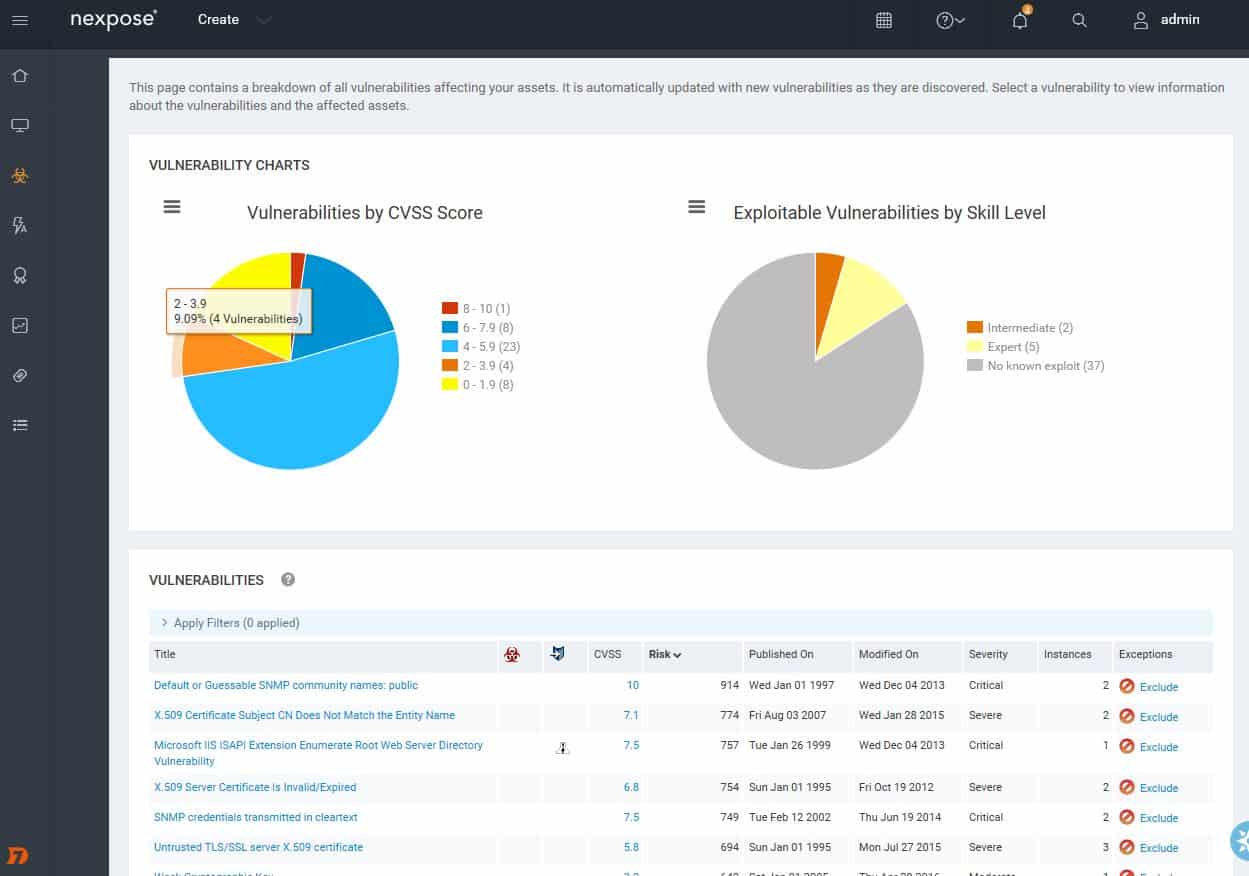
Nexpose Discovery Scan finds assets on the network.After that, running a Full audit enhanced logging without Web Spider gives you a good initial look at vulnerabilities on your site.
Analysis of vulnerabilities found.You can drill down to find details of vulnerabilities.
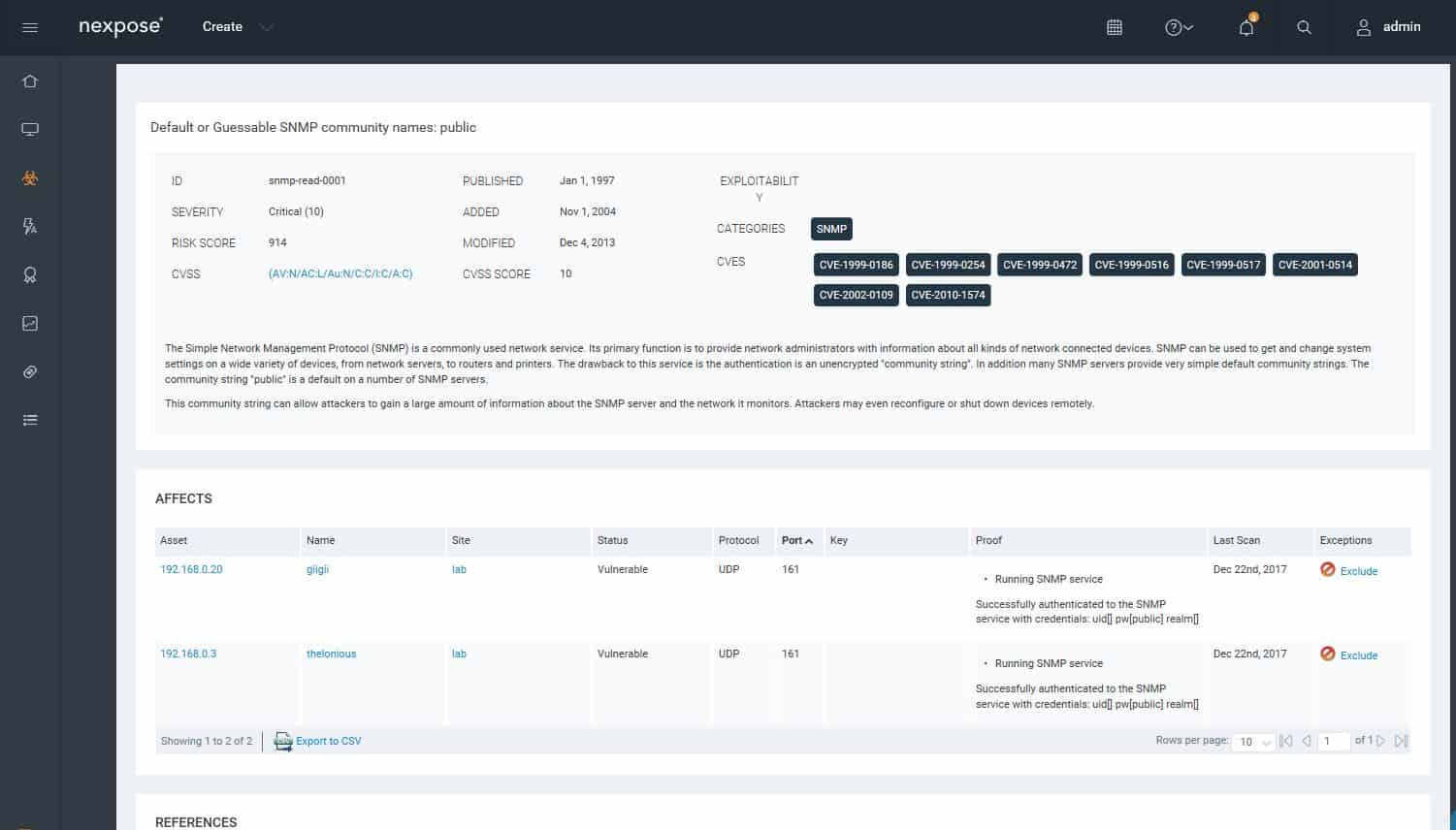
Drilling down to details on a vulnerability.You can look at the vulnerability status of a particular host or device. Each vulnerability includes remediation guidance.
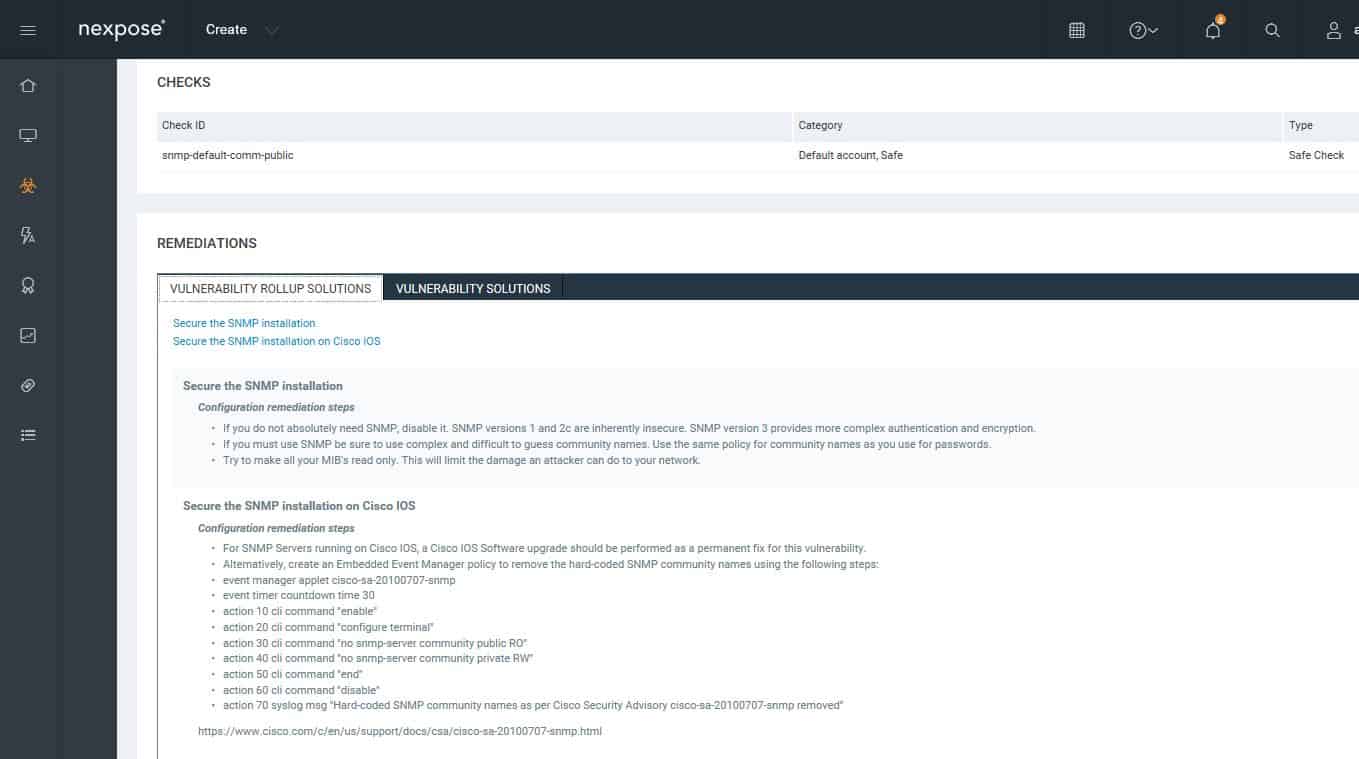
Guidance for remediating.The web console provides multiple predefined reports.
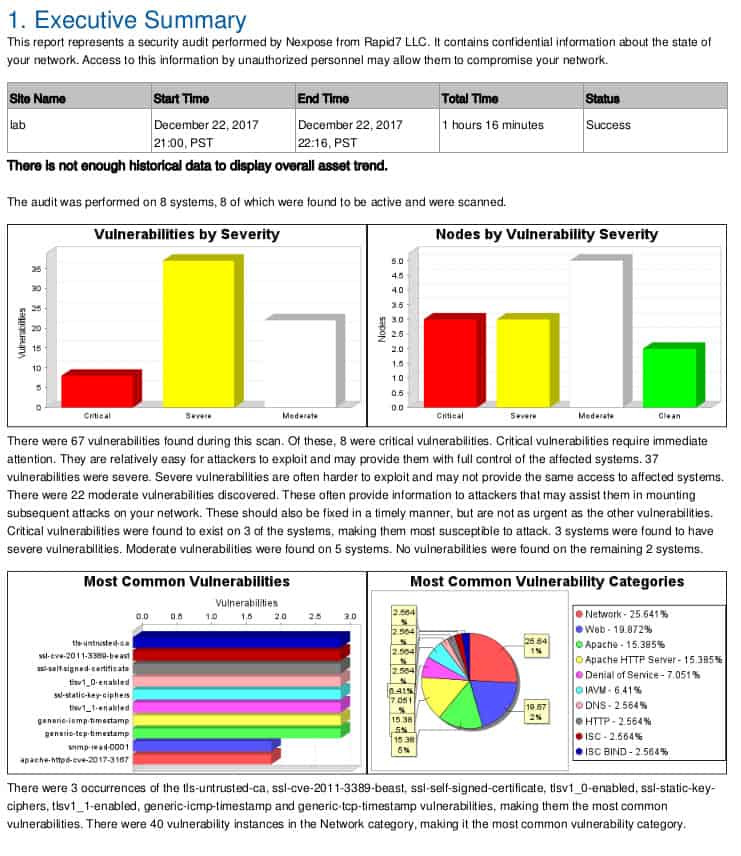
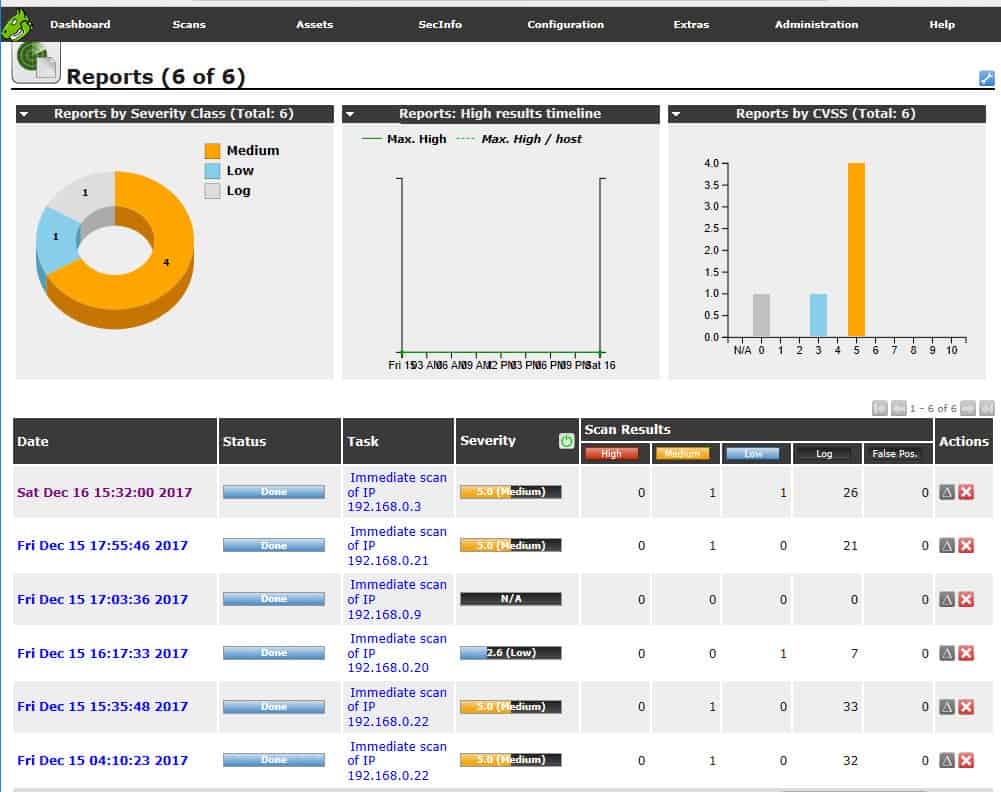
Nexpose’s report analyzes vulnerabilities found.
Who is it recommended for?
The loss of the free Community Edition means that the Nexpose option is going to be less appealing to cash-strapped small businesses and startups than it used to be. Like any cybersecurity tool, this system needs experience to use. However, as demonstrated in our illustrations in this review, the tool is pretty straightforward to run. You just need to be schooled in how to fix the problems that Nexpose reveals. The security technicians of large organizations will certainly enjoy using this tool.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to Nexpose.
- Extensive User Community: Benefits from a large user base and a wealth of shared knowledge and resources.
- Ease of Use: Combines technical capabilities with a user-friendly interface for efficient vulnerability scanning.
- Cons:
- Potential for Lockups During Updates: Updates can occasionally cause system lockups.
- Filtering Limitations: Could benefit from enhanced filtering options for more precise scanning.
Pros:
- Extensive User Community: Benefits from a large user base and a wealth of shared knowledge and resources.
- Ease of Use: Combines technical capabilities with a user-friendly interface for efficient vulnerability scanning.
Cons:
- Potential for Lockups During Updates: Updates can occasionally cause system lockups.
- Filtering Limitations: Could benefit from enhanced filtering options for more precise scanning.
You can also set up scheduled scans, enable compliance policies, and track the history of the site’s exposure to vulnerabilities.
Three more network vulnerability scanners
If the nine best network scanners in our list don’t quite fit your needs, you might consider one of these alternatives, which are “bubbling under” the leaders.
Tripwire Enterprise
The Tripwire Enterprise package of security vulnerability network checks is not free but you can try a demo. However, you can get it on a free trial. This service not only scans your network for anomalies on demand but runs in real-time, alerting you to any configuration or data changes on your network and enforcing change control.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to Tripwire Enterprise.
Pros:
- Supports real-time monitoring
- Can scan for vulnerabilities as well as detect and alert to config changes
- Better suited for larger networks
Cons:
- No free version, only free demo
- Interface could use improvement
Qualys Cloud Platform Community Edition
Qualys offers its Global AssetView (GAV) tool for free on its Global Cloud Platform. Although there are many tools on the platform, GAV is the only one that is available for free forever. This tool replaces the deprecated Qualys FreeScan and it is a similar asset discovery system that generates an asset inventory. The system will perform live availability checks on the discovered devices whether they are on your site or on the cloud. You get details on each device and also scans to discover all installed software.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to Global AssetView.
Pros:
- Free forever
- Can be expanded by subscribing to related paid tools
- Provides continuous unattended monitoring
Cons:
- Security scanning costs extra
Invicti
Invicti is available as an on-premises application or as a cloud service. This is a costly option, which is the main reason that it does not appear in the main list of this guide. The vulnerability scanner is aimed at web servers and authenticates the activities of all applications that operate to support a web-based enterprise.
During our testing, we identified the following pros and cons related to Invicti.
Pros:
- Can be installed both on-premise or in the cloud for additional flexibility
- Tailored for web server monitoring – good option for companies who numerous online applications
Cons:
- Is more expensive than most other solutions
- Aimed at serving massive enterprises, not ideal for small to medium-sized networks
Conclusion
Vulnerability scanning – and in fact, vulnerability management – is one aspect of protecting your network. Scanners can only detect vulnerabilities that already have tests implemented. You also need to develop a sense of your network’s normal behaviors, via bandwidth monitoring and analysis tools, particularly tools that let you specify automated alerts. When you sense an anomaly and must investigate, network analyzers and packet sniffers are key tools. And there are many other kinds of security tools for the network administrator.
Vulnerability scanning software is essential to help defend your network. There are multiple free options to try out; the right one for your organization is based on your needs, funding, and expertise – or willingness to learn.
Relevant: Best Angry IP Scanner Alternatives
Our methodology for choosing Network Vulnerability Scanners
With the rising cyber threats, every business is under constant pressure to secure its digital infrastructure. With several vulnerability scanners available in the market, choosing the right one for your business can be a challenge. Hence, we have penned down some of the key factors that buyers should consider when evaluating a product.
1. Threat Mitigation Capabilities
A vulnerability scanner must not be only limited to detecting risks but also assist in mitigating them. Vulnerability scanner tools that have built-in threat mitigation features allow security teams to take action on vulnerabilities without depending on multiple external solutions. A tool that offers automated responses or integrations for quick action against incoming threats must be considered.
2. Linked Patch Management
Vulnerabilities often occur due to outdated software or loopholes in the system. Hence, if you are planning to invest in a vulnerability scanner, make sure the tool comes with a linked patch management system that is capable enough to automatically fix exposed areas by applying the necessary updates. Such integrations not only reduce manual workload but also guarantee timely remediation of security gaps.
3. Device Configuration Protection
Attackers typically look for entry points to breach your system, and misconfigured devices are common entry sources. Hence, make sure to invest in a tool that comes with configuration management capabilities. Such tools will enable businesses to secure their endpoints by enforcing security policies and preventing unauthorized changes. Thus, adding an extra layer of protection to your systems.
4. OWASP Top 10 Threat Detection
The scanner must be capable of identifying the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities, such as injection flaws, broken authentication, or cross-site scripting. Detecting these widespread issues ensures that your application or network meets the fundamental security standards.
5. Comprehensive Activity Logging
Businesses handling sensitive data must comply with standards like GDPR or HIPAA. Hence, it’s important that the scanner provides full activity logs. These will further help in auditing, incident analysis, and showing compliance during security reviews or audits.
6. Trial or Demo Availability
Trying a tool before investing in it allows teams to assess its ease of use, compatibility, and effectiveness. Vulnerability scanners that offer a free trial or demo help reduce purchase risks and provide firsthand experience.
7. Complete Vulnerability Coverage
Partial detection is as dangerous as no detection. A reliable vulnerability scanner must be capable of providing a deep and thorough scan across systems, applications, and networks. It should leave no room for missed weaknesses, ensuring your security posture is not compromised.
8. Support and documentation
Team members with less experience may find it difficult to handle some tools, so they need assistance even after they have been purchased. Tools with comprehensive documentation and round-the-clock assistance can be excellent options. Therefore, while choosing software for your business needs, be sure it offers appropriate support services.
Broader B2B software selection methodology
Instead of just prioritizing a product’s key features, our team of professionals considers other aspects as well when selecting a B2B software for the reader or buyer. We understand the company behind the product will play an important role in the future, and so their analysis is also crucial. That’s why, every time we review a software or product for a buyer, we cover vendors and development teams along with feature analysis and pricing structure.
Some key pointers that our Comparitech experts take into account when reviewing or evaluating a product/software are:
- Check whether the cost is justified by the value each software is providing to solve real business challenges.
- Evaluate the performance and product’s potential to scale with your business if it expands in the future or grows.
- Measure overall satisfaction by reviewing user feedback and testimonials related to the company, product, or service.
- Track the responsiveness of customer support and how actively the vendor improves the product based on user input.
- Review the transparency around features, functionality, and limitations.
Please note that not every product review addresses all of these areas. Our professionals highlight key pointers only when they are relevant, either as standout strengths or key considerations for potential buyers.
To get a clear understanding of our entire evaluation process, check the detailed B2B software methodology page.
Why Trust Us?
For the past many years, Comparitech has been delivering quality, informative product and software reviews. Our team of cybersecurity and software testing professionals use their practical experience and expertise to evaluate every software and bring the best one for you to choose. We further conduct thorough research and rigorous testing to ensure our readers receive reliable, unbiased insights.
At Comparitech, we recognize that evaluating a product’s features alone isn’t enough. We assess each tool and platform using strict, transparent criteria, enabling buyers to make informed decisions. Post-purchase customer support is one of the key criteria we take into account to analyze overall user experience. That’s why we also rate brands based on the quality of their support services, further reinforcing our reputation as a trusted and comprehensive resource for expert guidance.
Network Vulnerability FAQs
What are network vulnerability assessment tools?
A network vulnerability assessment tool checks an entire business system for known weaknesses. These vulnerabilities are software quirks, hardware configuration weaknesses, or combinations of valid processes that can assist a hacker or malicious actor within the organization. At the heart of the vulnerability assessment system is a checklist of vulnerabilities that have been uncovered by the producer of the assessment tool. The vulnerability database needs to be updated frequently.
What is a common open-source vulnerability scanning engine?
OpenVas is probably the most widely-used open-source vulnerability scanning system. One problem of open source scanning engines is that knowledge of how the vulnerability scanner operates gives hackers an opportunity to plan attacks that won’t be spotted. Most of the leading vulnerability scanners are proprietary and have private source code and procedures.
Which security tool would you use to scan a host for HTTP vulnerabilities?
HTTP vulnerabilities are part of “website vulnerabilities.” This problem concerns both the websites that your businesses run and websites that users on your network access. Of the security tools in this guide, OpenVAS, Nexpose, Netsparker have the best HTTP vulnerability checks.
How often should you run a vulnerability scan?
Vulnerability scanners are automated processes, so there is no reason not to run vulnerability scans continuously. Check your data security standards for compliance requirements. These usually require comprehensive vulnerability scans to be executed one a month or quarterly. It is also advisable to run a vulnerability scan whenever the vulnerability database gets updated with newly discovered weaknesses.
How long does a vulnerability scan take?
A vulnerability scan performed by installed monitoring software should complete in around 30 minutes. A certified external vulnerability scan for security standards compliance should last between 30 and 90 minutes.













The credibility of this article is diminished by the fact that it recommends a tool (Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer) which was last released in 2015 and has been EOL for quite some time.
Thanks for the heads-up Marshall. There will no doubt be a few sad to see this free tool gone. We have swapped this out for ImmuniWeb for its more modern offerings, and it also has a Community Edition so people can try it out before committing.
Nice and thanks for that