The world of telecommunications and networking is built on the foundation of how data is transmitted across various networks. Two primary methods used to transmit this data are circuit switching and packet switching, each with its own advantages, limitations, and use cases. Understanding these two methods is crucial for network administrators, IT professionals, and businesses that rely on reliable communication systems.
Circuit switching is the traditional method used in telephone networks, where a dedicated communication path is established between two endpoints for the duration of the conversation or data transfer. This method ensures consistent and predictable communication, but it can be inefficient, especially when the communication is idle or when the network is under heavy load. It is most commonly associated with older, analog systems, though it has evolved into digital forms in modern telephony.
On the other hand, packet switching is the method used by most modern data networks, including the internet. In packet switching, data is broken down into small packets, which are transmitted independently across the network and reassembled at the destination. This method is more flexible, efficient, and scalable compared to circuit switching, as it allows for dynamic routing of data and optimal use of available bandwidth. It also enables multiple users to share the same network resources without requiring a dedicated connection.
In this article, we explore the key differences between circuit switching and packet switching, highlighting their respective benefits, drawbacks, and typical applications. By understanding how these two methods work, organizations can make informed decisions about network design and optimize their communication systems for both performance and cost efficiency.
What is Circuit Switching?
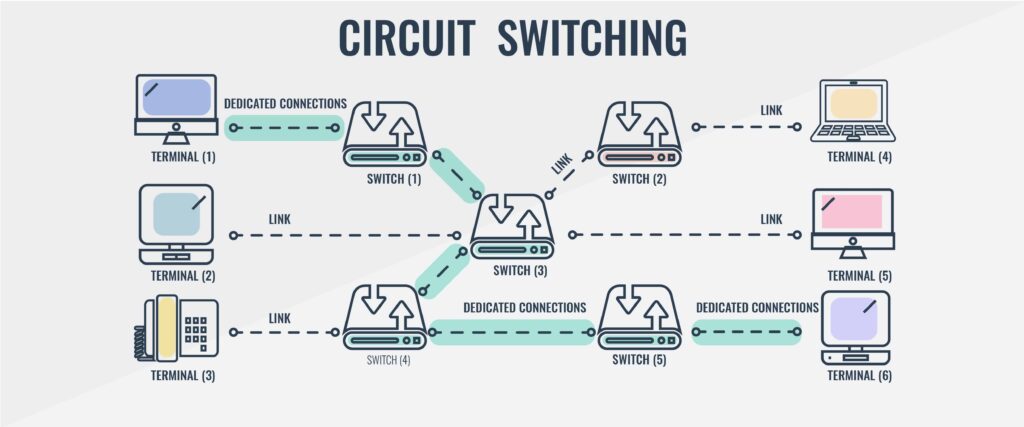
Circuit switching is when a dedicated channel or circuit needs to be established before users can speak to each other on a call. A channel used in circuit switching is kept reserved at all times and is used once the two users communicate.
Circuit switching connections are classified as half-duplex or full-duplex. Half-duplex communications allocate one channel and full-duplex communications allocate two channels.
Circuit switching is most commonly used to sustain telephone systems so that whenever the phone is picked up the conversation can begin. Circuit switching is considered to be distinct from packet switching because it provides a physical path between the source and destination. Packet switching offers no such physical path for data packets that travel independently through a range of dynamic routes.
What is Packet Switching?
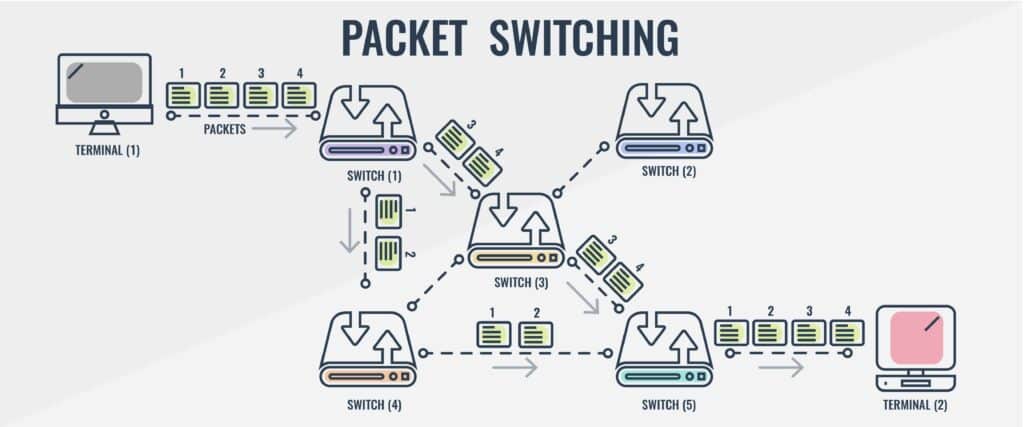
Packet switching is different from circuit switching because there is no requirement to establish a channel. The channel is available to users throughout the data network. Long messages are broken down into packets and sent individually to the network.
These data packets are handled by datagram or virtual circuit. Datagram sends each packet of data individually and can travel any route. The problem with this method is that packets can arrive out of sequence or even be lost in transit altogether.
On the other hand, a virtual circuit establishes a predefined route before the data packets are transmitted. As a consequence routing decisions don’t need to be made for the packet path as they are with a datagram. Every packet contains a virtual circuit identifier (VCI) so that the packets can reach their destination address. Call requests and accept messages are used to identify the route before packets are in transit. Packet switching is used to sustain data and voice applications that don’t require real-time service.
Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching Comparison
| Feature | Circuit Switching | Packet Switching |
|---|---|---|
| Dedicated Path | Yes | No |
| Path Formation | Path dedicated for one conversation | Route is established on a per packet basis of the conversation using datagram (or per conversation with virtual circuit) |
| Delay | Call setup delay | Packet transmission delay (call setup delay for virtual circuit) |
| Bandwidth Type | Fixed Bandwidth | Dynamic bandwidth |
| Overload Effects | Stops call establishment | Increases packet delay (can block call establishment and increase packet delay with virtual circuit) |
The Advantages of Circuit Switching
The circuit switching model has become popular for many different reasons. One of the main reasons is that it decreases the amount of delay the user experiences before and during a call. Circuit switching is adept at making sure that delay is minimized during phone calls so that the callers can enjoy the best end-user experience possible. Packet switching is unable to sustain the same standard of service to users throughout the call.
Under circuit switching the call will be provided with consistent bandwidth, channels, and an ongoing data rate. As a consequence, the user is able to stay on the phone for longer periods of connection time without running into any performance issues. Circuit switching also has the advantage of making sure that data packets are delivered in their correct sequence. The lower level of delay makes sure that data packets are delivered in order so that all the content in the call can be understood.
The Disadvantages of Circuit Switching
Though circuit switching is ideal for voice communications it isn’t right for any other type of connections. The reason for this is that the channel is reserved for future conversations. As a consequence, circuit switching isn’t a good choice if you’re looking to use your resources efficiently. Dedicating one channel to a single service leaves it unavailable to other services. This disadvantage also doubles up to make circuit switching more expensive. It is expensive to provision an entire channel to one service and one individual routing path.
However, even for calls circuit switching still poses challenges. If active users exceed the number of channels you have available then calls will fail to take place or will be dropped in the middle. Administrators are under pressure to make sure that channels keep up. In addition, even setting up calls results in delay so the connection needs to be fully established before the conversation can take place.
The Advantages of Packet Switching
While packet switching may not be as suited to voice calls as circuit switching, it has a number of advantages that are hard to ignore. The main advantage that packet switching has over circuit switching is its efficiency. Packets can find their own data paths to their destination address without the need for a dedicated channel. In contrast, in-circuit switching network devices can’t use the channel until the voice communication has been terminated.
Packet switching is also reliable because it helps to eliminate packet loss. With packet switching, data packets can be resent if they don’t reach their destination. This isn’t the case for circuit switching which doesn’t have the means to send lost packets. As a result, packet switching is the more reliable method of the two because it ensures that packets reach their destination.
Packet switching also reduces the costs associated with running the network. Packet switching networks can transfer general network traffic and voice traffic across the network without the need for a dedicated channel. This saves you money because you don’t need to pay to have one channel available for voice communications.
The Disadvantages of Packet Switching
The biggest limitation of packet switching is that it is unsuitable for applications that require minimal latency. In a network that uses lots of voice calls circuit switching is a necessity because it is the only setup that delivers a high-quality end call. Packet switching can only provide a voice call experience that results in choppy audio that makes it difficult for the users to understand each other.
Similarly, though packet switching is able to resend lost data packets, this isn’t the case if the network becomes overwhelmed by traffic. If there is too much traffic then packets will be dropped in transit. The end result is the loss of important data. This risk is further increased by the lack of security protocols used to protect packets during data transmission. There is no IPsec to give packets that extra barrier of security against damage. Though packet switching reduces costs in a number of ways it is significantly expensive to implement. Packet switching relies on a range of complex protocols that must be managed from deployment onward.
Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching
Circuit switching and packet switching are undeniably two of the most widely-used techniques for transferring data across enterprise networks. Both of these two techniques have their own space within modern networking. Using circuit switching allows you to keep a channel established for high priority voice calls to give the users the best chance to communicate with each other. In contrast, packet switching uses a more malleable approach so that traffic can travel a variety of paths.
Which one is better depends on what you’re trying to achieve. If you want to ensure that voice calls are adequately supported so that delay is minimized then you’ll want to deploy circuit switching. However, if you need to sustain lots of services at once then you’ll want to use packet switching.
Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching FAQs
What is time-division switching?
Time-division switching is a method to allow several connections to travel along the same trunk line. It involves time-division multiplexing (TDM) which splits up a stream into segments and sends them out on the line at a specific interval. The receiving de-multiplexer uses a synchronized clock to detect the elements of each stream.
Which switching method reduces traffic congestion?
Congestion is a symptom of an overloaded network. Packet switching is more efficient than circuit switching because it ensures that more of the bandwidth of all cables are fully utilized. As it makes better use of resources, packet switching is more likely to reduce congestion than circuit switching.
What is a frame relay circuit?
A frame relay is a connection-oriented virtual circuit service. It is like a temporary rental of a line between two networks. Several conversations between different endpoints can be carried through the same connection over a connecting public line.
What is ISDN?
ISDN stands for Integrated Service Digital Network. It is a method of sending voice and data simultaneously over the circuit-switched public telephone system. Several devices can be connected to the same line and each sends voice or data at the same time over a number of “bearer channels” (“B” channels). The line also has a data channel (“D” channel), which carries connection administration information.