USB drive helps users share information and move large files with ease, but it can serve as a gateway for malware and data theft when left unrestricted. In this article, we’ll explore the best USB port locking tools you can use to secure your ports without sacrificing productivity. Let’s dive in.
Here’s our list of the best USB port locking tools:
- ThreatLocker Storage Control EDITOR’S CHOICE This USB control system installs an agent on each enrolled endpoint and then blocks its USB ports. Users can be permitted to use specific USB devices for a short period. This is a cloud-based service – access a demo to assess it.
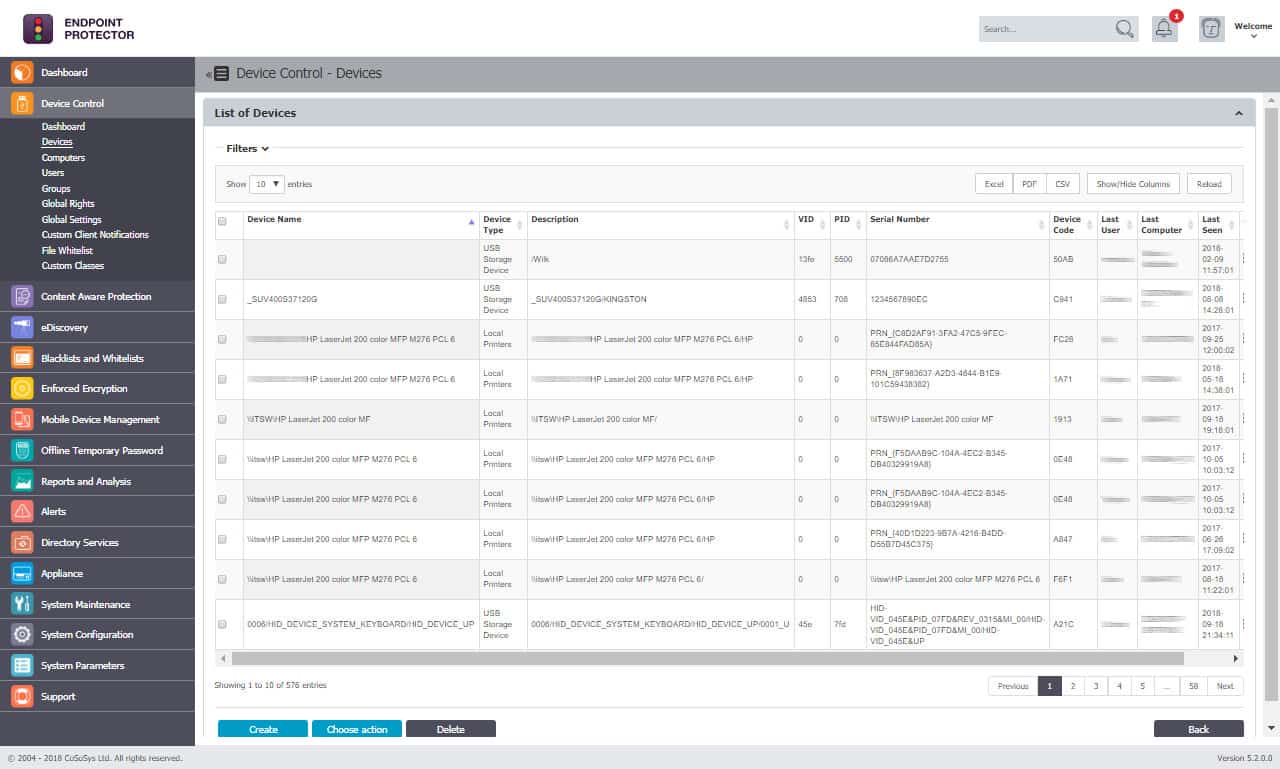
- Endpoint Protector by CoSoSys (GET DEMO) Robust DLP platform that offers USB port locking and granular device control, content-aware scanning for data protection, and automatic USB encryption enforcement for both company-owned and BYOD environments. Access the free demo.
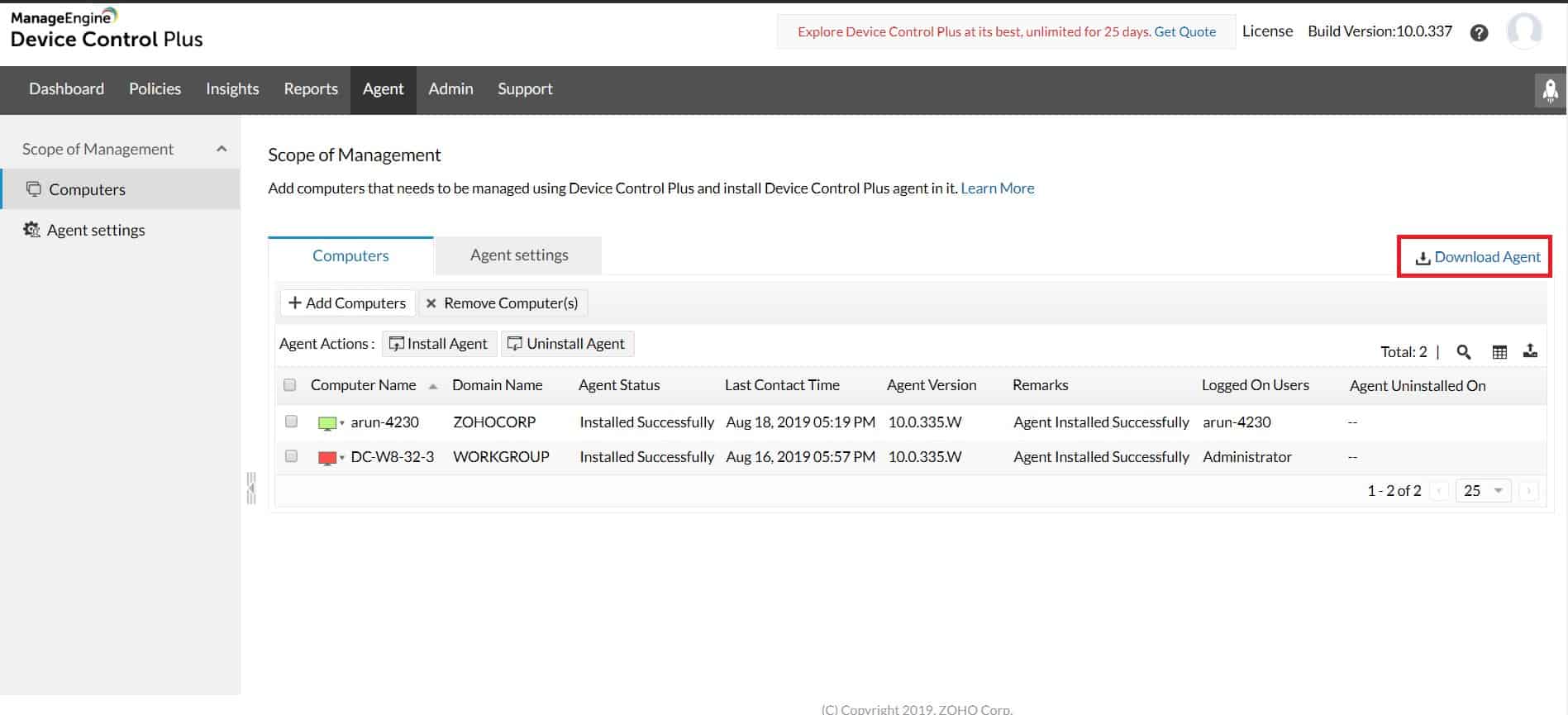
- ManageEngine Device Control Plus (FREE TRIAL) End-to-end device control and flexible port locking options for any businesses environment. Start a 30-day free trial.
- Gilisoft USB Lock Device control for small networks and home environments
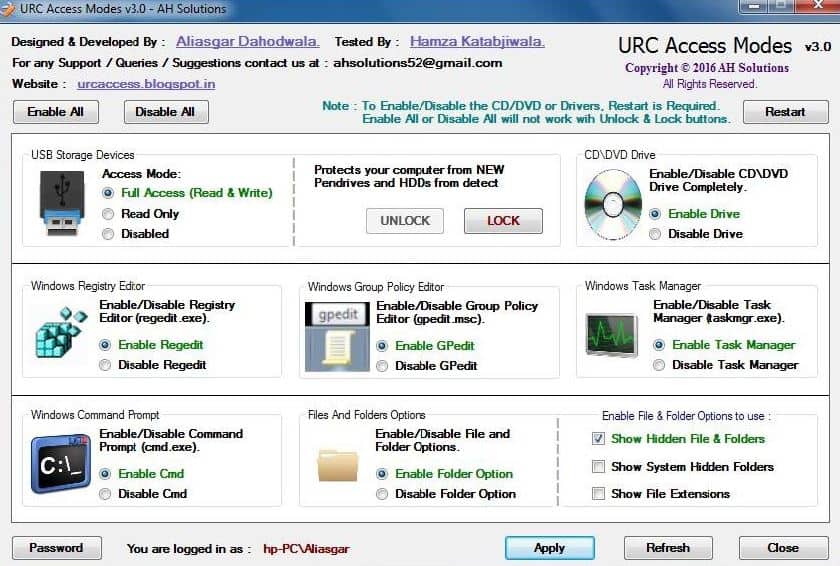
- URC Access Modes Simple interface that controls ports as well as system access for single PCs
- Edit your registry Requires technical knowledge in place of software
What should I look for in a USB port locking tool?
In theory, USB port locking is a relatively simple process. But depending on what your goals are, you may want to consider your options. Some simple free tools allow you to lock down USB ports, but what happens if they need to get work done? For example, can you create permission groups one-time passwords or set up default encryption? Let’s go over a few key features you should consider when choosing a USB port locking tool.
Customization
Customization is king when it comes to USB port locking tools for a few reasons. First, USB ports play a vital role in the workplace. Simply locking down all USB ports indiscriminately would cause a flood of help desk tickets anytime someone wanted to play a PowerPoint presentation.
Even if you’re on a smaller network, consider a USB port locking tool that has many options for whitelisting and supports logical groups. For instance, some enterprise USB port locking tools allow administrators to connect to use permission groups from Active Directory to shape their USB locking policies. This not only helps you get up and running faster but reduces the number of frustrated users you’ll hear from.
You want to lock down your USB ports, but what about CD/DVD drives? If you’re looking for more control over your devices, consider a tool that can identity and sort devices in multiple ways. For example, serial numbers, hardware ID, and vendor are often used to filter and whitelist different company devices.
If you’re a part of a more extensive network, consider a tool with a wide variety of integrations. Simple integrations and a robust API allow you to integrate USB port locking into your helpdesk team. When endpoints experience problems, you can automatically move that event over to your ITSM solution to create a ticket.
Auditing
Understanding your environment is key to ensuring device control is working and data policies are being abided by. In addition, having a level of visibility into your endpoints helps you gauge how successful the device control policy is and if you’re meeting compliance standards.
Some more advanced USB port locking tools can record when data is removed or added through an endpoint. In addition, auditing can help identify and stop malicious behavior in real-time when paired with automation and serves as a strong starting point for a forensic investigation.
Enterprise tools often come with robust auditing features that are passively collected. These logs can be stored for the historical record, input into a SIEM, or sent to the administrator for review through integrations. In addition, if your organization adheres to specific compliance standards such as HIPAA, FISA, or PCI, consider a tool that supports those compliance standards.
In the realm of auditing, reporting may be necessary to your organization. HIPAA and PCI DSS often require that you undergo an audit or self-assessment to confirm you’re complaint. Tools built with compliance in mind can make proving compliance simple and save you a lot of headaches down the road. For example, many device control tools have compliance auditing built-in, while smaller USB locker tools do not.
Encryption
Many organizations pair their USB port-locking tools with encryption. This not only keeps them compliant with regulatory standards but prevents data from being used if that device is lost or stolen. Organizations looking to leverage encryption should consider finding a tool that supports default encryption.
This automatically encrypts the data before being sent to the flash drive. Specific policies can make it mandatory that any data leaving the network must be encrypted before going on a flash drive.
How exactly does USB port locking work?
USB port locking works by controlling the policies on each endpoint through an agent installer. These agents can usually be pushed out via login script or group policy and allow you to automatically set your company device policies on that machine in just a few minutes.
Like endpoint antivirus, the agent changes to lock down the local environment and monitor the machine’s compliance. In addition, the agent monitors the USB ports and ensures any new USB hubs or ports added also adhere to the company policy. Some enterprise-focused tools even monitor for specific malicious behavior such as insider attackers or Bad USB malware.
The administrator controls these agents through a centralized dashboard. Here, the sysadmin can easily see his endpoints, their status, and any outstanding issues that might be present. While a centralized dashboard may not be necessary for home users, sysadmin should carefully test out the management console, especially if they plan on having multiple technicians or teams access its metrics.
Is USB port locking the same as device control?
You may hear the term “device control” alongside “USB locking”. The critical difference between the two is that device control encompasses all devices and usually is geared more towards businesses that want to prevent data loss. Device control in almost every case includes USB locking capabilities. However, not all simple USB locking tools have advanced features found in device control platforms.
Home users looking to restrict access to a few computers can use small USB locking tools to get the job done and don’t usually need a complete device control solution. However, big and small businesses typically want to invest in device control software when implementing port-locking policies.
With the basics out of the way, let’s explore some of the best USB port-locking tools on the market.
Our methodology for selecting the best USB Port Locking Tools:
We’ve broken down our analysis for you based on these key criteria:
- Priority was given to tools offering robust security features.
- Ease of use and installation process were critical considerations.
- Compatibility with a range of operating systems was essential.
- We evaluated the level of control over USB port access.
- Customer support and resources availability weighed heavily in our decision.
The Best USB Port Locking Tools
1. ThreatLocker Storage Control (GET FREE DEMO)
ThreatLocker Storage Control is a cloud-based service that installs an agent on each enrolled endpoint. This agent allows an administrator to control the USB ports on the protected device. The system can protect endpoints on multiple sites within a single account.
Key Features:
- Cloud-based endpoint protection
- Zero Trust USB strategy
- Detailed device logging
- Granular storage policies
- Compliance with HIPAA
Why do we recommend it?
ThreatLocker Storage Control is part of a Zero Trust strategy, which blocks everything by default and then allows access on a case-by-case basis. It starts by refusing all USB devices and then the administrator allows some USB devices to be used by named users. Controls can be taken to categories of data.
The service operates its USB port locking procedure for the purposes of data loss prevention. Although a major reason for controlling the use of USB devices is usually a consideration for malware prevention, this isn’t an issue for computers protected by ThreatLocker. This is because another module in the ThreatLocker system blocks all software unless it is named in an allow list. So, malware won’t be able to run even if it gets onto the computer.
When it is installed on a computer, the ThreatLocker agent scans the device and identifies all of its USB ports. This information is relayed to the console in the cloud and remains a permanent record of the computer’s hardware. The ThreatLocker server then sends out locking instructions and the USB ports become unusable.
There might be legitimate reasons why a user needs to access a USB device and in these cases, that person should file a request with the system administrator. A specified user will then be permitted to use a specific USB device on one computer. This permission can be revoked and the user should be made aware that all file movements on and off the device will be logged.
The activity logging service in ThreatLocker also covers file activity on the hard drives of protected endpoints. These logs can be used for compliance auditing and they can also be forwarded to a SIEM tool.
Who is it recommended for?
Businesses that manage sensitive data can apply controls to specific types of data and specific users. So, employee A can move files on and off a USB stick for work but employee B can’t; employee C is the only person that can access or move sensitive data.
Pros:
- Unifies the controls of endpoints on any site
- Blocks USB ports by default
- Provides a mechanism to enable a specific device for deployment by a specific user
- Logging for file movements on and off a USB device
- Blocks to prevent unauthorized software from running
Cons:
- Doesn’t include an access rights manager
ThreatLocker can be assessed by watching a demo.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
ThreatLocker Storage Control is our top pick for a USB locking tool because of its ability to protect systems from unauthorized access and potential threats, ensuring consistent data security across all endpoints. Its precision, ease of use, and advanced features make it the ideal choice for organizations prioritizing endpoint protection. This system provides granular control over USB and other external storage devices. It enables administrators to define specific policies regarding who can use USB devices, what data can be accessed, and when or where access is permitted. This level of customization ensures that only authorized devices and users can interact with sensitive systems, reducing security vulnerabilities. By locking down USB access, ThreatLocker prevents common attack vectors such as malware injection, ransomware deployment, or unauthorized data exfiltration. Unlike traditional tools, it doesn’t just block devices; it actively monitors and audits all attempted connections, providing an extra layer of protection against both internal and external threats. Despite its advanced capabilities, ThreatLocker Storage Control is incredibly user-friendly. Its centralized management console simplifies policy creation and enforcement, making it easy for IT teams to deploy, update, and monitor settings across an entire organization. This reduces operational complexity and boosts efficiency. The tool provides comprehensive visibility into all device interactions, logging detailed usage data. This ensures compliance with regulatory standards and offers actionable insights into potential vulnerabilities.
Download: Get FREE Demo
Official Site: https://www.threatlocker.com/book-a-threatlocker-demo
OS: Cloud-based
2. Endpoint Protector by CoSoSys (FREE DEMO)
Endpoint Protector is a robust DLP platform that offers USB port locking and granular device control for large networks. Users can secure their network with Endpoint Protector through a combination of device control, DLP, and data recovery.
Key Features:
- Granular USB control
- Content-aware security scanning
- Enforces USB encryption
Why do we recommend it?
Endpoint Protector by CoSoSys uses exactly the same strategy as that of the ThreatLocker system. All USB sticks are blocked. When an employee connects a device a pop-up facilitates a request to allow it. The administrator can permit or allow that device and also compile a list of permanently allowed devices.
The platform offers many different ways to manage and lockdown USB ports. For example, users can whitelist devices based on vendors’ ID, hardware ID, serial number, or integration into a permission system such as Active Directory.
The platform leverages content-aware scanning to vulnerable identity data and understands the context of an attempted file transfer. For example, a user trying to move photos onto an endpoint would be much less suspicious than a user trying to move multiple database files. This process makes onboarding easier and helps the system learn more over time the longer it is monitoring the network.
Organizations can automatically enforce USB encryption across both company-owned devices and BYOD environments. Encryption enforcement is a simple policy user can set globally or based on the characteristics of the file. Encryption requires the end user to enter a password to decrypt the data, causing minimal interference in their workflow.
Who is it recommended for?
The USB port management unit of the Endpoint Protector system is called Device Control. This is part of a Zero Trust strategy that applies those blocks on software on endpoints. That renders all malware inoperable and only software listed as approved can run. This is useful for all types and sizes of companies.
Pros:
- Custom security policies can be based on the user rather than the machine
- Automatically assesses risk based on vulnerabilities found on the endpoint
- Can alert to improper file access or insider threats (Acts as a DLP solution)
- Prevents data theft and BadUSB attacks through device control settings
Cons:
- Would like to see a trial version available for testing
Endpoint Protector protects USB locking through highly customizable DLP and device control settings. Similar to our top choice, Endpoint Protector is designed for use in a business environment. You can test out Endpoint Protector by requesting a demo.
3. ManageEngine Device Control Plus (FREE TRIAL)
ManageEngine Device Control Plus provides USB locking capabilities alongside numerous other control features designed to work in a business environment and scale with the network as it grows.
Key Features:
- Supports BYOD and company devices
- Flexible USB locking options
- Advanced Data Loss Prevention
- Zero Trust data security approach
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine Device Control Plus is a data loss prevention system that operates a Zero Trust strategy in a very similar way to that implemented by ThreatLocker and Endpoint Protector. That is, all USB devices are blocked by default and then selectively allowed for specific users on specific computers for operations with specific data categories.
The platform is flexible enough to support BYOD environments and company-owned devices in the same forum through separate policy groups. Administrators can get started right away through numerous integrations and simple templated policies that make onboarding much more accessible than some other enterprise tools.
Device Control Plus offers a range of USB locking options. Sysadmins can choose only to allow read-only access or shut down ports completely for non-authorized USB drives. When a policy needs to be challenged for a staff member to work, they can request one-time access to unlock the port. This allows the users to get access to their USB drive for a set amount of time and logs all the data transfer details to ensure the network is still protected.
Organizations also looking for Data Loss Prevention (DLP) will likely find the tool a good fit. DLP features prevent data leakage and identity the early stages of an insider attack based on behavioral patterns and metrics such as the type of data accessed and the transfer size.
The platform takes a zero-trust approach to data security, allowing sysadmin to start from scratch when building their whitelist. For example, users can specify permissions groups, device IDs, and serial numbers when selecting authorized devices. In addition, endpoint agents can collect a list of devices already installed, making it easy to collect authorized hardware already in use.
ManageEngine Device Control Plus goes above and beyond a simple port-locking tool, great for work environments. However, home users will likely choose a different option as Device Control Plus is designed for professionals.
Who is it recommended for?
Device Control Plus is designed for use by businesses that manage sensitive data. This is particularly necessary for large organizations that have too many employees to monitor manually. However, ManageEngine also makes this tool appealing to small businesses by offering a Free edition to control up to 25 computers.
Pros:
- Designed to work right away, features over 200 customizable widgets to build unique dashboards and reports
- Leverages autodiscovery to find, inventory, and map new devices
- Uses intelligent alerting to reduce false positives and eliminate alert fatigue across larger networks
- Supports email, SMS, and webhook for numerous alerting channels
- Integrates well in the ManageEngine ecosystem with their other products
Cons:
- Is a feature-rich tool that will require a time investment to properly learn
You can test out ManageEngine Device Control Plus through a free 30-day trial.
4. Gilisoft USB Lock
Gilisoft USB Lock provides more functionality than BuduLock but is still designed for small networks and home users. The platform comes in a sleek black interface that allows users to prevent data leakage by controlling access to programs, devices, and USB ports.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive resource control
- Customizable blocking presets
- Detailed access attempt reports
- Suitable for small networks
Why do we recommend it?
Gilsoft USB Lock is a system for Windows that can control access to resources on a computer and the peripheral devices that attach to it. The system lets the user block access to specific websites and it will block programs from running. The device control system lets you block all USB devices from connecting, which you can modify by whitelisting specific devices.
The tool can allow users to charge their phone on their PC but disable the option for file transfer. In addition, administrators can restrict access to external drives, CD/DVD burners, and other portable devices. There is even an option to specify certain websites, which may help prevent data theft through cloud services such as Google Drive.
Blocking is very customizable but comes with several presets users can enable to get started right away. Copy protection can also prevent users from copying and pasting to move the text off of documents and place them elsewhere.
The reporting feature is essential and logs access attempts for USB file transfers, folder access, and blocked websites. In addition, the reports can be exported in CSV format. However, while this approach is simple for small networks, it lacks robust auditing features to aid in a forensic investigation or prove company compliance.
Who is it recommended for?
This system has many features that will appeal to small businesses but it isn’t a networked application and so it wouldn’t be suitable for large businesses. Small businesses could use the tool for a few computers and it would be suitable for home use.
Pros:
- Great user interface
- Blocks both USB ports as well as disk drives
- Offers password protection as well as full USB denial
- Can also block websites
Cons:
- Better suited for larger environments
While there is an enterprise deployment option, I feel this tool is best suited for small networks or home users who want more control options from their USB port locking tool. Gilsoft USB Lock starts at $49.95, and can be tested through a free trial.
5. URC Access Modes
URC Access Modes provides detailed deceive control, USB port locking, and administration for individual machines. The software lacks a centralized monitoring console, so URC Access Modes is best suited for smaller environments. However, if you’re looking to manage a PC in a shared area, this program can help prevent unauthorized access to files.
Key Features:
- Detailed device control
- Easy-to-use interface
- Suitable for home and small business
- Free to use
Why do we recommend it?
URC Access Modes is a free tool that works in a similar way to Gilisoft USB Lock. It can block many processes on a PC as well as controlling USB ports. For example, the tool can make it impossible for a user to open a Command Prompt window.
The software allows administrators to control access based on different zones and devices easily. Users can easily enable or disable access to things like command prompt, USB storage devices, registry editor, and group policy editor through a simple but intuitive interface. Of course, in a domain environment, this should all be controlled through Active Directory. However, homegroups can use URC Access Modes to simulate that level of control on a much smaller group with relative ease.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is very appealing for home use and for small businesses. However, any company with more than a few PCs would find it difficult to work with because it only operates on the computer that hosts it and the USBs that connect to that computer.
Pros:
- Very detailed USB lockdown options
- Can stop the theft of intellectual property
- Gathers information that can determine if an action was malicious
Cons:
- Interface could use improvement
The program is just making simple changes to the registry on the backend, but this allows fewer technical users to control their machines and enable USB port locking with little to no effort. While this isn’t the best option for larger businesses, URC secures its spot on this list thanks to its ease of use and intuitive layout.
6. Edit your registry
If you don’t want to use any tools, you can block USB port access through Windows Registry Editor. Be warned, editing the registry requires some technical know-how and severe problems if done incorrectly. Consider using simple tools before choosing this option.
This method also does not allow you to create exceptions or whitelist devices easily.
Here’s a short guide on how you can block USB ports in Windows 10. You may need local admin privileges to perform these edits.
- Press Windows Key + R to open up the Run box. Type “regedit.exe” and press enter to access the Registry Editor.
- Naviage to the following path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Services > USBSTOR
- Find click on “Start” and choose “Edits DWORD 32-bit Value”.
- To disable USB ports and drives, change the Value to 4 and then click OK.
- To enable them again, change the Value to 3 and click OK.
- Restart your computer.
You can also do this in Device Manager by doing the following:
- Click on Start and search Device Manager.
- Once inside Device Manager, find Universal Serial Bus Controllers.
- Right-click on the device or port you want to restrict and choose Disable Device.
- Enable access by right-clicking on the device and selecting Enable Device.
Keep in mind and tech-savvy users can quickly undo these changes if access to Device Manager and Registry Editor is not restricted.
Conclusion
We’ve examined some of the best USB port-locking tools on the market, but which one is best for you? For established businesses, either Mange Engine Device Control or Endpoint Protector will provide rock-solid protection from data theft, infection via USB and aid in meeting compliance standards.
Home users and smaller networks should consider Gilisoft USB Lock or URC Access Modes. Both tools provide excellent protection for individual PCs in a way that is easy to learn and implement right away.
How do you lock down your USB ports? Have you used USB port-locking tools in the past? Let us know in the comments below!