Server patch management is the process of managing and deploying updates, or “patches”, to the software running on servers in a data center or other enterprise IT environment.
Server patch management tools can help automate and streamline the process, enabling administrators to manage patch deployment across multiple servers and track the status of each patch to ensure that all servers are up-to-date and secure.
Here is our list of the best Server Patch Management tools:
- Atera EDITOR’S CHOICE Cloud-based patch management software – full of administration tools and allows administrators to customize their patches or exclude software; it can integrate with third-party tools to cover Windows and Mac devices. Start a free trial.
- NinjaOne Patch Management (FREE TRIAL) Impressive tool used by IT professionals to reach devices anywhere they are. It gives complete control over any device running Windows, Linux, and macOS and over 135 commonly used applications; minimal end-user intervention is required. Get a 14-day free trial.
- ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL) This tool supports an extensive array of patches for over 500 third-party applications and comes in on-premises and cloud versions; administrators can deploy pre-tested patches to all devices – both physical and virtual – that are all monitored from insightful dashboards. Get a 30-day free trial.
- SecPod SanerNow This SaaS security package includes a vulnerability scanner and a patch manager that updates macOS, Linux, Windows, and software packages and also provides logs for compliance reporting.
- SolarWinds Patch Manager An easy-to-use yet powerful cloud or on-premises server patch management tool from a leader in the market for numerous operating systems and applications; it comes with in-house technology to make the patching experience smooth and successful.
- Vicarius Αn affordable patch management tool that protects assets in real-time and can respond to triggers set by administrators; it is lightweight and non-resource intensive and yet powerful enough to secure servers, workstations, operating systems, and applications.
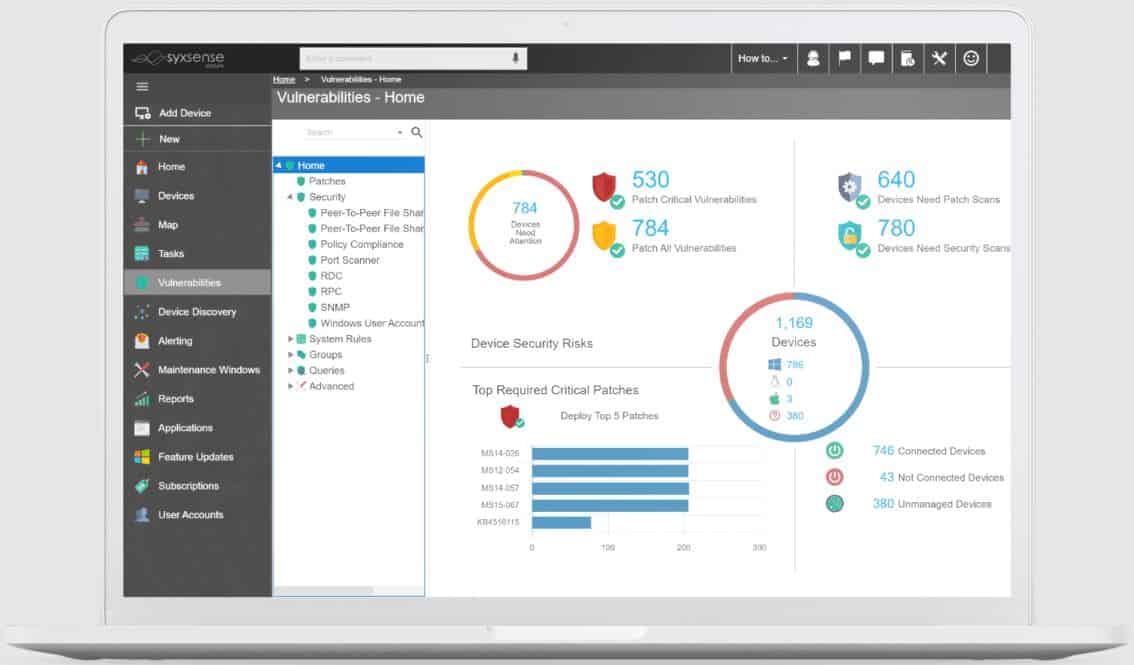
- Syxsense Manage Αn endpoint management and patching tool that covers all devices, including virtual servers; it supports patching both Windows and Linux operating systems and keeps track of devices that allow for quicker response times.
- PDQ Deploy Αpart from patch management, it can deploy scripts and make configurations with ease and accuracy; it has many ready-to-deploy third-party applications and can send out multiple silent deployments without affecting endpoint user experiences (UX).
Ok, so what is server patching?
Server patching or patching a server updates a server’s software to fix errors, update versions, or improve features and performances. The fixing of errors also involves handling security vulnerabilities and ironing out bugs that could pose a risk to a business’s data and information.
And so, we can say that there are five main reasons for server patching:
- To address a specific bug or flaw in the core processing code.
- To improve a server operating system’s – or any of its application’s – stability, features, and functionalities.
- The software and operating system makers release patches and updates whenever vulnerabilities are detected; these should be installed quickly.
- To remove bloatware – unneeded code and applications – to streamline and optimize core operating system components’ size and resource consumption.
- To enhance existing patching processes – perhaps Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) isn’t delivering or performing as expected; maybe, it isn’t working at all. A third-party patch management tool can take over the job or even out-perform such native patching services.
Adding all these points together, we can see that securing servers with the latest patches should be a critical part of any business’s cybersecurity protocols. Ignoring this process could pose a security threat to mission-critical servers, workstations, applications, and other network assets.
What is patch management?
Patch management oversees the distribution and application of updates to server operating systems and application software solutions.
System and network administrators use patch management tools, some of which we will see, to perform these tasks.
How to choose the best server patch management tools
For a patch management tool to be considered as being the best on the market, it needs to meet several criteria, including:
- Ease of use Working with server patch management tools should be effortless; minimal effort should be put into its installation, management, and troubleshooting.
- Multiple operating systems support It should cover more than one version of any, or all, of the major operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- The ability to deploy to the whole network Should reach servers on-premises, on a WAN, in the cloud, or a hybrid combination of all three architectures.
- High integration A good tool will integrate well with the current hardware and software environments with ease and without creating conflicts, bottlenecks, or crashes.
- Non-stop scanning The time between a vulnerability occurring and patched should be minimal; therefore, the tool should continuously monitor the network to spot vulnerabilities as early as possible.
- Quick identification, proper patching Once a vulnerability has been detected, it is up to the server patch management tool to quickly find the correct and latest version of the remedial patch.
- Tiny footprint The patching process shouldn’t hog bandwidth, storage space, or any other resources; on the contrary, it should be unobtrusive and appear seamless to any user on the network.
- Detailed reports The tool should have insightful, thorough, and comprehensive information that shows statuses of patches, deployments, and issues or warnings; it helps to have reports stored for later reference and audits or shared among stakeholders for a collaborative understanding board.
And so, we, too have tested and compared solutions to come up with the seven best server patch management tools on our list.
The Best Server Patch Management Tools
Our methodology for selecting a server patch management tool
We reviewed the market for patch management systems for servers and tested tools based on the following criteria:
- A selection that includes both on-premises systems and cloud-based services
- Automated systems that run unattended
- Completion reporting that shows failed patches
- The option to launch a patch on demand for one or many servers
- A central repository of available patches
- A free trial or a free tool so users can trial the system before committing money
- Value for money from a patching system that saves time and money
Let us delve straight in and have a look at the seven best server patch management tools:
1. Atera (FREE TRIAL)
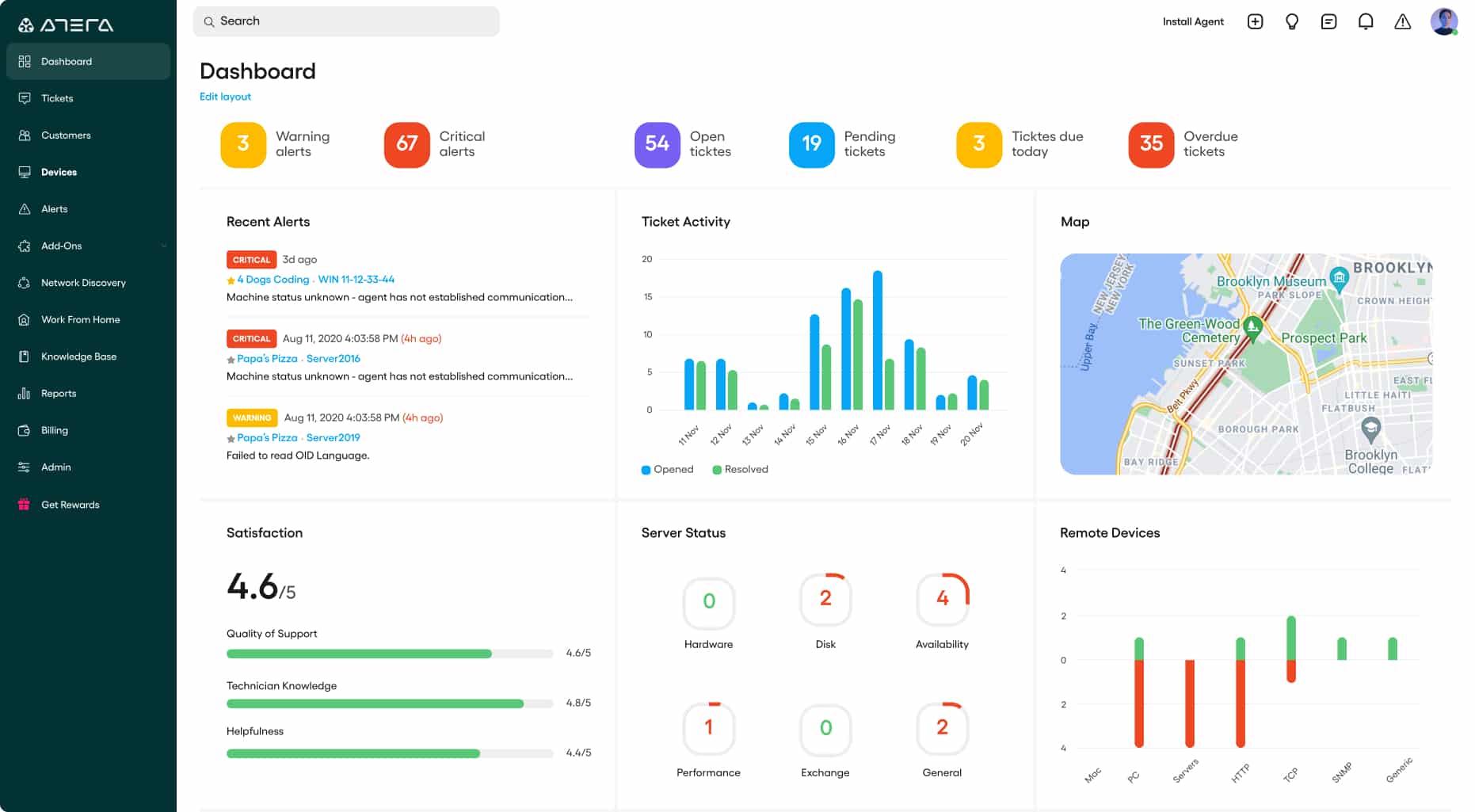
Atera Patch Management Software is a cloud-based server patch management software. It is a powerful integrated solution for IT departments and administrators alike. It is chock-full of features like Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM), Professional Services Automation (PSA), billing, helpdesk, and ticketing services, as well as patch management.
Key Features:
- PSA Tools Include a Ticketing System: Help Desk system is included in all plans
- RMM Tools Include a Patch Manager: Included in all plans
- Automated Software Deployer: Part of a software management service
- Scheduled Maintenance: The scheduler can automatically launch scripts as well
- SaaS Package: Priced per technician
Why do we recommend it?
Atera is a remote monitoring and management package. This bundle is delivered from the cloud and can reach any site anywhere in the world. The package includes a patch manager that is able to patch Windows, Linux, and macOS and it will also update the software that runs on top of those systems.
The tool automates the critical patch management process and uses a remote agent to track vulnerabilities that may occur in endpoints.
There’s more:
- This tool gives complete control over the patching of operating systems, software, and hardware from a central location – the cloud.
- Apart from automation, it can be used to plan and schedule tasks for single or collections of applications – like installing Java updates; it can create custom configurations for Microsoft updates and unique automation for each endpoint user.
- Administrators can add custom patches to IT automation profiles or create software bundles to install or update at scale for each customer. Alternatively, they can exclude specific software from the patches to meet unique requirements.
- They can set and automate patching for Windows and macOS devices using third-party integrations like Chocolatey for Windows and Homebrew for Mac devices.
- The tool’s powerful reporting helps administrators stay on top of all patches, deployments, vulnerabilities, and every agent at all times, ensuring complete control and airtight security; they can share these insightful reports with their clients or other stakeholders.
- Atera has a Shared Script Library – driven by the managed service provider (MSP) community – with hundreds of scripts that can be cloned, customized, and automatically added to IT automation profiles; these scripts are all tested by the in-house team and tuned to enhance the patch management process.
Who is it recommended for?
The Atera platform is available in a version for IT departments and another for managed service providers. There are four plans in each version and all of them include the patch manager. Subscriptions are levied per technician, which makes the package accessible to all businesses.
Pros:
- All-Inclusive Package: Provides hosting and storage space for metrics as well as the software
- Automated Software Management: A single console for software deployment and updating
- Manages Endpoints: Patches Windows and macOS operating systems
- Stores Statistics: Activity logging for compliance reporting
- Improves Technician Productivity: Extensive task automation
Cons:
- Network Discovery is an Add-On: Costs extra
Try Atera on a free trial!
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Atera is our top pick for a server patch management tool because it offers an all-in-one, cloud-based solution that simplifies and automates the patching process for IT environments of any size. Unlike traditional patch management tools that often require complex configurations or additional software, Atera provides a streamlined and user-friendly platform that allows IT teams to manage patches, monitor server health, and ensure compliance; all from a single dashboard. One of the main advantages of Atera is its automation capabilities. It enables businesses to automate patch deployment for a wide range of operating systems, applications, and software packages. This reduces the need for manual intervention, saves time, and minimizes the risk of human error. Additionally, Atera offers flexible scheduling options, allowing patches to be applied during off-peak hours, ensuring minimal disruption to business operations. Atera’s comprehensive reporting and alerting features are also attractions. IT teams can easily track patch status across all devices and receive real-time notifications of missing patches or potential vulnerabilities. This proactive approach helps prevent security risks by ensuring that systems are always up to date with the latest patches and fixes. In addition to the patching services of Atera, buyers get automated system monitoring, remote access, and maintenance task automation. The package also includes a Help Desk ticketing.
Download: Get a 30-day free trial
Official Site: https://www.atera.com/signup/
OS: Cloud based
2. NinjaOne Patch Management (FREE TRIAL)
NinjaOne Patch Management is a quick, efficient tool for IT professionals looking for solutions that will help address user issues by securing their devices. The cloud-native patching solution makes it easy to patch devices anywhere in the world – all that is needed is an Internet connection. Drawing from G2’s repeated recognitions, it’s evident that NinjaOne holds a solid standing in RMM and Endpoint Management.
Key Features:
- Endpoint Management: Patches Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Automated Action: Lines up patches and applies them without manual intervention
- Compliance Reporting: Stores activity reports
- SaaS Package: Hosted on the cloud
Why do we recommend it?
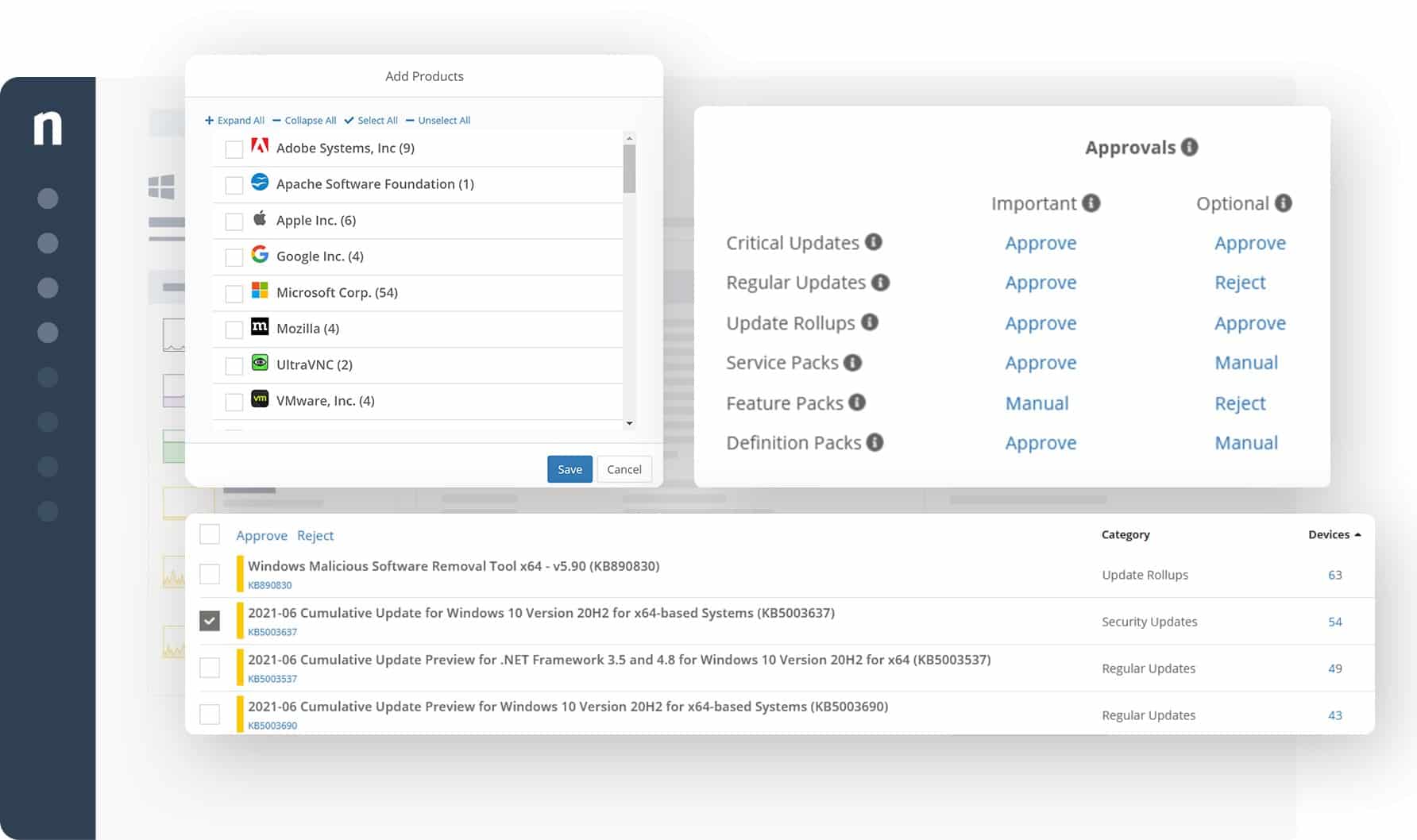
NinjaOne Patch Management is part of a cloud platform of services that implements remote monitoring and management. This patching system is part of the endpoint management tools in the package. The system is able to patch devices running Windows, macOS, and Linux. It will patch the operating systems and also the software packages running on those endpoints.
But, there’s more:
- A higher rate of patch compliance – and user experience – can be achieved with this tool simply because endpoints don’t have to be on a domain (or use a VPN) for the patching process; they just need to be online.
- It is cost-effective because there is no need for patching servers – which could be expensive to set up, run, and administer.
- NinjaOne is the ideal tool for complex network architectures as it offers cross-platform patch management for Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems; this is further enhanced with patch policies that optimize and automate patching processes at scale, as well as ad-hoc management that makes it quick and easy to deploy sudden critical updates.
- It facilitates patching by giving complete control over the process using patch identification, approval, and deployment schedules.
- Administrators also have complete visibility and control over applications on the endpoints – even when they are offline, they can patch over 135 such typical applications without the need for users’ input or intervention.
- Apart from deployment and patching, administrators can use a catalog of applications to remove or blacklist applications they may deem unnecessary or pose security risks.
- Everything is done from one central console – whether it is insights into health, vulnerabilities, or patch management reports – and there is no need for infrastructures or costly overheads.
Who is it recommended for?
This system is designed for use by managed service providers but it can also be used by IT departments. The monitoring service in the Ninja One package detects all endpoints connected to a network and logs them in an inventory, which forms the basis of the patching service.
Pros:
- Automated Software Maintenance: Offers hotfixes for in-use devices as well as patching
- Software Management: Updates more than 100 third-party applications
- Remote Monitoring: In addition to remote endpoint management services
- Scalable Pricing: Charges based on a device count
Cons:
- Not a Standalone Service: Part of a full RMM package
Experience all the power of NinjaOne with this full-featured interactive demo. You can also register and try the package on a 14-day free trial.
3. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL)
Patch Manager Plus is another tool from a leader in the software and server monitoring and management software market. It is used for automated patch deployments for Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems.
Key Features:
- Endpoint Management: Patches Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Updates Third-Party Applications: More than 850 systems
- Unattended Rollout: Give the patcher a maintenance schedule
Why do we recommend it?
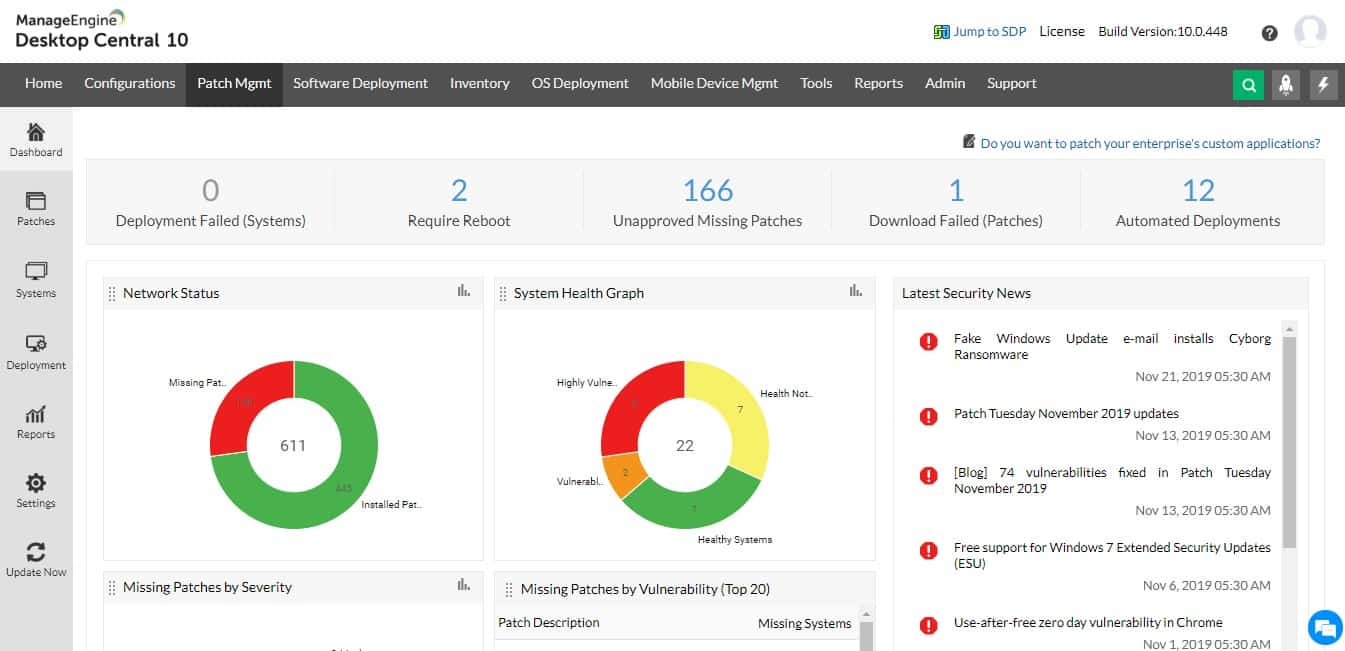
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus provides patching for Windows, macOS, and Linux, plus more than 850 third-party software packages. The service maintains a library of available patches on the ManageEngine cloud server, which are tested and approved. So your installation just has one place to check for patch availability.
It offers patching support of over 900 updates for over 500 third-party applications and is available as both on-premises and cloud versions.
Looking at more features, we get:
- It can scan endpoints to detect missing patches, test patches pre-deployment, automate the deployment process, and then report on the results and current status.
- This way, the tool mitigates deployment risks to operating systems and third-party applications. Finally, it gives in-depth insights via reports and dashboards that can also be used as references for audits and proof of compliance.
- Patch deployment can be done seamlessly – from a single interface – and across desktops, laptops, servers, roaming devices, and virtual machines.
- The tool makes it easy to view complete details of patches relevant to a network; a patch overview also shows those installed or missing on the platform, which helps administrators see the current overall compliance and security status.
- They can see how many systems are missing patches – by patch count and severity – on the whole network.
- Meanwhile, the systems view shows the health status (which is calculated based on patch severity and the number of missing patches) of systems in the environment and concerning the system health policy; they are rated “healthy,” “vulnerable” or “highly vulnerable” accordingly.
- Administrators can further narrow their data search using filters that help to analyze multiple tables, and view patch statuses or compliance data in various combinations and comparison reports.
- They can keep track of the progress of patch deployments and reboots to see if the patch application process has been done in an effective manner.
- Then, the patch summary dashboard is browser-based, interactive, and can be accessed from anywhere and at any time.
- Automated vulnerability assessment and patch deployments ensure systems’ compliance with the latest version of installed, licensed software; automatic email alerts support this in case of new updates, missing patches, or failed deployments.
Who is it recommended for?
The software for the package installs on Windows Server. However, it is also available as a SaaS platform in the cloud. A free edition will manage up to 20 workstations and five servers. The base paid package is within the budget of small businesses. The top package will operate on multiple sites.
Pros:
- Manages Operating Systems on Multiple Sites: Available in the top plan
- Deployment Options: Available as a SaaS platform or for on-premises installation
- Constant Vulnerability Scanning: Automatically triggers the patch manager
Cons:
- Won’t Install on Linux: The on-premises version is only available to run on Windows
Try ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus – cloud or on-premises – for FREE.
4. SecPod SanerNow
SecPod SanerNow CyberHygiene Platform is a cloud-based system that installs agents on a local network and its endpoints. The network agent is first installed on one device through the cloud-based console. The program scans the network and discovers all servers, workstations, and network devices. Information on these is uploaded to the SecPod cloud server. The SanerNow system then installs an agent on each endpoint. The agent is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux and it provides a software scan for its device, which is also uploaded. SecPod also provides agents for cloud systems.
Key Features:
- Automated Inventory Creation: Software management
- Vulnerability Scanning: Triggers the patch manager
- Patching for Windows, macOS, and Linux: Also third-party software
Why do we recommend it?
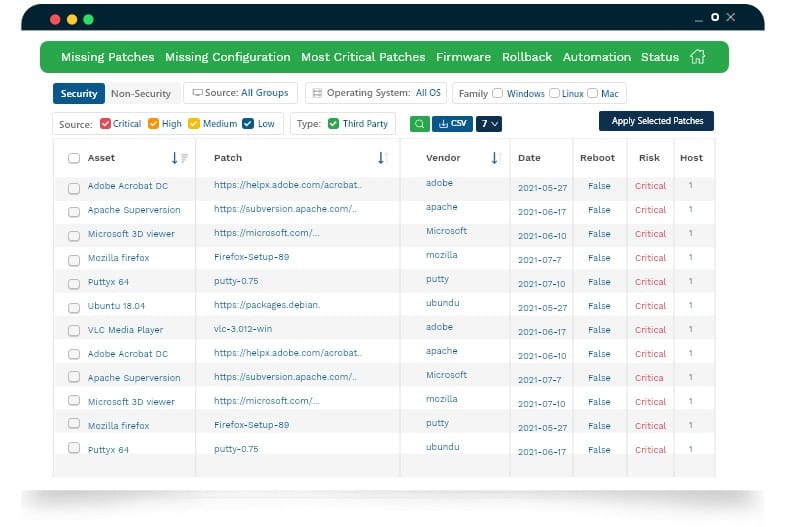
SecPod SanerNow is a cloud platform that provides security services for a business through agents that are installed on the site. The units in this package include a vulnerability scanner and a patch manager. When the scanner identifies outdated operating systems or software, it sets up the patch manager to fix the problem.
More features of SecPod SanerNow are:
- A software inventory that records the version numbers and patch statuses of all installed operating systems and software packages.
- A centralized console that can manage endpoints on multiple networks in one account.
- Posture management for cloud platform, which provides vulnerability scanning.
- Vulnerability scanning for 160,000 known vulnerabilities.
- A central library of verified patches for operating systems and more than 400 software packages.
- Automated unattended patch rollout occurring at pre-defined maintenance windows.
- Full system documentation for compliance with HIPAA, PCI DSS, NIST 800-53, NIST 800-171, and ISO.
Who is it recommended for?
This package will update computers running Windows, macOS, and Linux and the software that runs on those devices. Other features in the bundle include intrusion and malware detection. It also provides compliance management. This package is particularly interesting for large businesses running multiple operating systems.
Pros:
- Guards Hybrid Environments: Vulnerability scanning for on-site and cloud-based resources
- Rapid Patch Deployment: Set up a maintenance calendar
- A Central Library of Verified Patches: Covers more than 400 software packages plus operating systems
Cons:
- Won’t Patch all Software: Only packages that are on the SanerNow list
Get free access to the SanerNow CyberHygiene Platform with a 30-day free trial.
5. SolarWinds Patch Manager
This is a server patch management tool from SolarWinds, one of the leading server and network management and monitoring tools. It is available in both cloud and on-premises versions.
Key Features:
- Adapts WSUS and SCCM: Patching for Windows, Microsoft, and third-party applications
- Updates Software: Scans for patch availability
- Unattended Operations: Automated operations
Why do we recommend it?
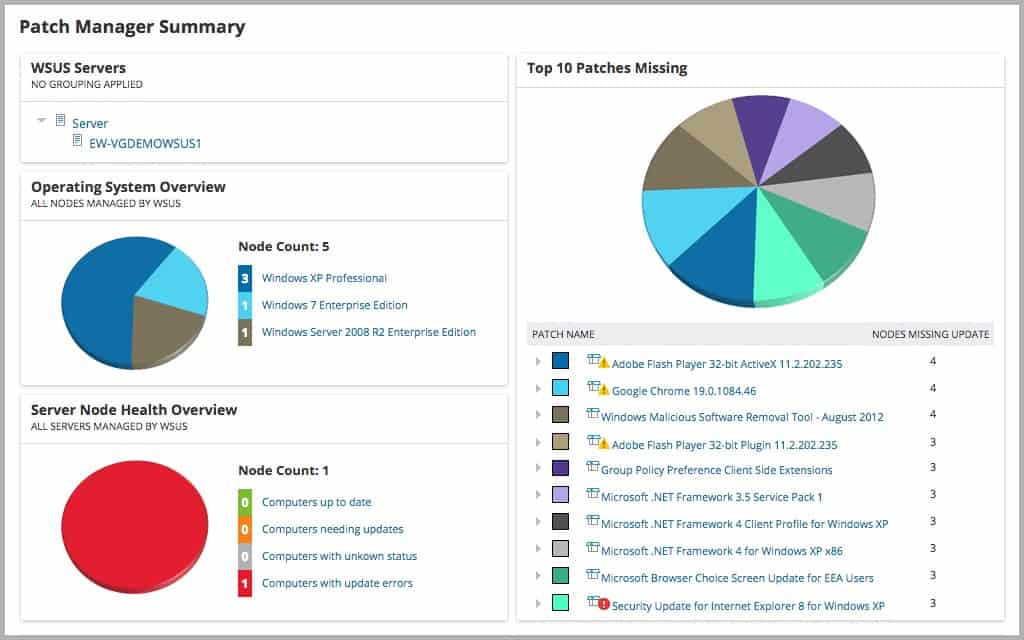
SolarWinds Patch Manager is an on-premises package that runs on Windows Server. The system will patch many endpoints across a network. However, it is only able to patch computers running Windows. The service can update software packages as well as operating systems. The tool is able to order patches according to dependencies.
SolarWinds Patch Manager offers a comprehensive list of updates for operating systems as well as numerous business applications. These updates are categorized as critical, security, definition, third-party updates, and service packs and cover multiple software solutions common in most business environments.
Some more features include:
- Patch Manager is the perfect tool for extending Microsoft WSUS and Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (MECM) capabilities for updating third-party applications.
- Its PackageBoot technology helps smooth out application patch management. It creates the right pre-and post-installation environment for successful patching; it then controls the deployment itself, thus reducing security risks. This helps in clearing the path for the most complex installation scenarios and which, in turn, curbs patching processes from failing.
- It comes with reports that give insights into vulnerabilities – straight out of the box; administrators can leverage dashboards and manage exposures from a central location starting from the minute installation is over.
- And soon after, they can also start monitoring the status of ongoing patches and quickly spot any unsuccessful patch installations, which can then be handled accordingly.
- Next, they can go on to control when and where updates are performed with advanced scheduling features.
- Looking at more distinct tasks, administrators can discover systems that run versions of Java with known vulnerabilities; this offers excellent help because, even if they could somehow manually track all Java applications and then patch them, there’s still a chance for employees to fail that could leave desktops and servers vulnerable to attacks. With this tool, nothing is left to chance.
- Similarly, administrators can start by viewing device statuses to find vulnerabilities in their domains or platforms. Then, with the help of Patch Manager, they have the luxury of deploying pre-tested patches to implement security solutions quickly.
- The tool’s web UI displays important patch data, alongside other SolarWinds products’ data, to create a standard, integrated console; among other things, administrators can view the latest available patches, the top ten missing patches, and the general health overview of an environment based on the patches that have been applied on them.
Who is it recommended for?
This system is suitable for use by large businesses that run only Windows endpoints. The system provides automated operations, which is a great time and cost saver for companies that have many endpoints to look after. The tool is able to run overnight unattended and it can wake up endpoints for patching.
Pros:
- Extends the WSUS Process: A customized SolarWinds feature
- Pre and Post-Patching Environment Settings Updates: Implements patch installation requirements
- Compliance Reporting: Logs all patching activities
Cons:
- Doesn’t Patch Linux or macOS: Only Windows
You can test SolarWinds Patch Manager with a fully functional 30-day free trial.
6. Vicarius
Vicarius is a comprehensive, cloud-based vulnerability management tool. It can take care of a catalog of servers, workstations, operating systems, and applications – without breaking the bank.
Key Features:
- Vulnerability Management: Includes AI processes
- Automation Options: Apply patches manually or on an automated schedule
- Constantly Active: Scans for patch availability
Why do we recommend it?
Vicarius TOPIA is a vulnerability manager that has an integrated patch manager. This package provides an IT asset management service, automatically creating hardware and software inventories for your business. The vulnerability scanning and patching functions are part of the system’s asset management processes. This is a cloud-based service.
Looking at more of its features:
- It protects assets in real-time, and its rich, integrated features quickly pinpoint and remediate the most significant risks to infrastructure with the help of efficient automation features and precise contextual analysis capabilities.
- Administrators can test and deploy patches manually; alternatively, they can fully automate the process and patch en masse or run the patching process when events cause triggers to fire.
- This patch management tool allows administrators to select specific endpoints or applications or respond to specific triggers and at any scale.
- Servers and virtual machines alike are protected from downtime and loss of bandwidth during patching, thanks to this patch management system being lightweight with a small digital footprint.
- And then there is the fact that TOPIA can be used to schedule the patch deployments to be sent out during off-hours or planned downtimes – no man-hour is wasted during patch deployments.
- Accurate, rich, and detailed reports can be extracted using the events and actions that the tool keeps track of. It deploys and manages patches across the network; these reports can be used as audit reports to gauge the overall patch management process.
Who is it recommended for?
This service is very accessible to all businesses and it will particularly appeal to small businesses. This is because its dashboard is easy to understand and its management options can be implemented without technical knowledge. Getting asset management, vulnerability scanning, and patching all in one package is a great cost saver.
Pros:
- Provides Manual Controls: A fully automated patch manager with options for manual actions
- Focus Options: Target an endpoint or sweep the whole fleet
- Runs on a Schedule: Unattended out-of-hours patching
Cons:
- Dark Screens Can be Hard to Read: Stylish but not very practical
Try Vicarius FREE for 30 days.
7. Syxsense Manage
Syxsense Manage is an endpoint management solution that can manage all assets inside and outside a network with coverage for all major operating systems and platforms – including Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Key Features:
- Endpoint Management: Patches Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Microsoft Patching: Update Windows applications
- SaaS Package: Hosted on the cloud
Why do we recommend it?
Syxsense Manage is an IT asset manager that is based in the cloud. The platform includes an automated patching system that provides a scanning service, which operates a partial vulnerability management strategy. It is able to patch MacOS, Windows, and Linux and you can enroll devices in any location into the same account.
Of course, Syxsense Manage is also a tool for patch management. It allows all aspects of the patching process to be easily organized and executed.
Delving further, we find:
- A single agent and a cloud-based platform make it easy to install and start using Syxsense Manage and make it a light and non-intrusive tool as it goes about managing and monitoring endpoints.
- Endpoint servers that can be monitored include physical and virtual ones located on-premises or in the cloud and running various versions or flavors of Windows and Linux operating systems.
- The tool keeps an eye on endpoints to ensure all patches are up-to-par and that no security standards have been compromised; assets covered include operating systems, hardware, and software.
- Once scans show that there are indeed vulnerabilities, the tool prioritizes the patching process based on the threat posed by the discovered security risk; it even shows exploited vulnerabilities.
- Syxsense Manage is a versatile tool – administrators can, for example, track patching and updates for third-party software like Java or deploy Windows 10 Feature Updates; they can then see all Windows 10 versions on a single dashboard.
- It has a wide array of reports, including “Security Risk Assessment” to show the overall health of the network or the “Most Vulnerable Devices” report, which shows the endpoints that need to be patched immediately; these reports can be shared or exported and used as proof compliance to security guidelines like HIPAA.
- The tool also enhances network security by monitoring authorization issues, policy implementations, and the status of antiviruses; furthermore, it can spot misconfigurations in operating systems and compliance violations to make sure a more comprehensive security perimeter buffers the patching process.
- Traffic congestion or network bottlenecks are kept to the minimum by skipping the need for approvals thanks to Syxsense’s built-in detection logic that allows only required updates to be deployed; filters can also be applied to deploy updates that share a common value dynamically.
- Even post-patching rebooting of endpoints is tackled with care – devices that need rebooting can be specifically targeted; interaction with users can be done via custom messages and during specific times.
Who is it recommended for?
This system is able to centralize the management of scattered devices in one console. This is a good choice for SMEs that have a lot of home-based employees or roaming agents. You can include endpoints anywhere in the world into your monitoring and management account.
Pros:
- Patch Prioritization: Applies security fixes first
- Remote Operations: Manages endpoints on multiple sites
- Compliance Reporting: Documents vulnerabilities and logs remediation actions
Cons:
- Not Big on Software Updating: Doesn’t patch systems other than OSs and Microsoft products
Try Syxsense Manage FREE for 14 days.
8. PDQ Deploy
PDQ Deploy is a software deployment tool created to update third-party software solutions, deploy scripts or make system configurations quickly and accurately. It can also be used to help automate patch management campaigns.
Key Features:
- Software Deployment: An automated system
- Automated Software updater: Give it a maintenance calendar
- Cloud-Based Patch Library: A single source of verified patches
Why do we recommend it?
PDQ Deploy watches over a list of 100 applications and provides installation and update packages for them. The service lets you compose software profiles for new computers, add services to a computer, and update all monitored software. The tool also includes a script editor that lets you create task automation and run it through the deployment platform.
This tool enhances the patch deployment and management process with added capabilities to deploy multiple application patches, execute custom scripts, and remotely execute Windows system commands.
There’s more:
- PDQ Deploy performs even more tasks on top of Windows patch management or software deployment – it can be used to copy files, send notification alerts to users logged on, and even force reboots in case of endpoint users’ reluctance to do so.
- It has a Package Library of over 250 ready-to-deploy, popular third-party applications to choose from, including Adobe Reader DC or even Microsoft Cumulative Updates; these applications are tested for bugs, kept up-to-date, and made accessible at all times.
- The tools also make it easy to keep all Windows systems up-to-date with multiple silent deployments to numerous devices; schedules can be set for the updates to be pushed at certain times; it doesn’t matter if the endpoints are offline – the download commences as soon as the device comes back online.
- Administrators can collaborate on deployment and patching processes. The tool comes with multi-admin access and even a shared database; they can get notifications sent to them when successful deployments are completed.
Who is it recommended for?
This system is useful for companies that use applications that are on the PDQ Deploy watchlist. If you have a lot of customized systems or applications that aren’t stored on the PDQ deploy platform, you can still manage those packages but through scripting, which is time-consuming to set up.
Pros:
- Reliable Operations: Maintains a pre-screened library of all available patches
- Patches Windows: Also patches Microsoft products
- Will Queue Updates for Offline Endpoints: They will be applied as soon as those devices come online
Cons:
- Only for Windows: Doesn’t patch Linux or macOS
Try PDQ Deploy FREE for 14 days.
Server patch management FAQs
What is a patch management process?
Patch management is an endpoint management function that keeps operating systems up to date and up to the latest version. This is important for system security because patches are often created to close down newly-discovered exploits. Although “patching” usually only refers to updates for OSs, updates for software packages can usually be implemented through patch managers as well.
What is patching a server?
Patching updates operating systems and software to fix errors in a system that have been newly discovered by the creators of that package. A patch is made available to update software without having to uninstall it and install a new version.
What is WSUS patch management?
WSUS stands for Windows Server Update Services and it is an update manager that is built into the Windows operating system and Microsoft’s applications. It is free to use but it is only available for Windows Server and not other Windows versions.
We would like to hear your thoughts on our choices for the seven best server patch management tools. Leave us a comment below.