With Microsoft’s Security Analyzer showing its age, it’s time for an alternative. Security these days is a constant battle between rapid patching and malicious individuals attempting to find exploits and vulnerabilities in software.
It’s not hyperbole to say that as soon as the last security hole is patched, the next one is found by hackers who produce new malware almost immediately after. These security risks have become the primary threat towards companies both large and small.
Here is our list of the best alternatives to Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer:
- ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus EDITOR’S CHOICE This on-premises package provides vulnerability scanning, patch management, risk assessment, remediation, compliance reporting, and continuous monitoring to secure endpoints, networks, and applications. Installs on Windows Server. Access a 30-day free trial.
- Paessler PRTG Network Monitor A bundle of network, server, and application monitoring tools that includes system security scanning features. Detect intruders and spot vulnerabilities with real-time system scanning.
- SolarWinds Network Automation Manager This bundle of system management tools provides protection for your devices and lets you set up activity tracking to identify threats.
- OpenVAS An open-source, free vulnerability detection system.
- Nessus The original version of OpenVAs, this vulnerability scanner is available online or for installation on-premises.
- Nexpose This tool integrates with Metasploit to give you a comprehensive vulnerability sweep.
Over the course of the last year, countless exploits have been uncovered at both the software and hardware levels. Some of these breaches are so severe they could result in the complete loss of all secure data from infected hosts. This isn’t just a concern for small or medium-sized businesses that may have lighter security than large enterprises.
Anyone can be targeted regardless of size. Macy’s had customers’ online data hacked in 2018. A third-party support partner resulted in Sears, Kmart, and Delta Airlines customers’ credit card information being stolen, a breach that affected an undisclosed number of individuals. Panera Bread, Adidas, UnderArmor, the long list of breaches taking place just in 2018 covers every sector of business across the globe.
Some estimates place InfoSec breaches due to poor security patching and routine vulnerability checks as high as 80% of all breaches. On paper, patching vulnerabilities sounds like a simple task, but when the individual patch count for any given business can reach high into the thousands, the problem becomes readily apparent. Manually managing software, hardware, and configuration vulnerabilities is a nigh-impossible task that will inevitably fail.
Enter the MBSA
Even the most bare-bones security setup will include this simple tool developed by Microsoft to ensure Microsoft products are brought up-to-date and provide strong security against the most recent software exploits. Available for over a decade on a range of Microsoft products, Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer can quickly scan Microsoft hosts on a network and help patch a range of Microsoft products with the latest security releases to mitigate the chance of a breach.
Unfortunately, this tool is extremely limited, and will only assess the status of Microsoft software. Most organizations will be running tools developed by various developers, and relying solely on MBSA for vulnerability assessment is akin to laying out the red carpet for would-be hackers.
Everything from SQL databases to improperly configured switches can be the preferred method of entry for those seeking to steal sensitive data or negatively impact a given network. The limited scope of MBSA’s tool kit provides zero protection from far too many potential entry points.
The need for a more robust vulnerability solution
As a network grows in size, it quickly becomes apparent that manual solutions are going to fall flat at scale. While there’s no replacement for skilled, knowledgeable staff, supplementing personnel with additional tools to help spot potential vulnerabilities goes a long way towards a more secure premise.
Vulnerability scanners come in a wide range of functions, specifications, and design goals. Some may feature detailed system configuration scans aimed at spotting weaknesses in networking equipment configurations that can be exploited to gain access to a network. Others may take a focused look at known software vulnerabilities, spot potential SQL inject sequences, or identify software versions that have known security windows. Real-time threat intelligence is becoming increasingly important as a tool for intrusion detection and prevention.
What your organization needs will vary from business to business. Certain sectors will require the absolute maximum amount of information security. Every switch, router, and endpoint in the network will need every possible door closed, even at the expense of potential usability. A good example of this is any organization that deals with financial information, or research and design firms that demand the utmost secrecy and security.
Anytime “the absolute maximum” amount of security is needed, there is going to be something of a trade-off in network usability. The easier it is for people within the organization to access information, the potential for intrusion is going to be higher.
Many vulnerability scanners will rate identified vulnerabilities on a scale. While this differs from software to software, the idea is the same. Each vulnerability check is given a rank to help administrators determine which flaws must be closed and which flaws can potentially be left open. Closing every single hole in a network is almost impossible, and even if it were possible the severely hampered usability of the network is likely not worth “perfect security.”
The best alternatives to Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer
Our methodology for selecting alternatives to Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer
We reviewed the market for vulnerability scanners like Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer and assessed the options based on the following criteria:
- A service that is able to check on third-party software not just Microsoft products
- A patch manager linked to a vulnerability scanner
- Process automation that gets vulnerabilities patched quickly
- Nice to have a network configuration manager bundled in
- Every action logged for compliance auditing
- A free trial for a no-cost assessment period or a free tool
- A system that is worth the money because it will cost less than the damage it will prevent
1. ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus (FREE TRIAL)
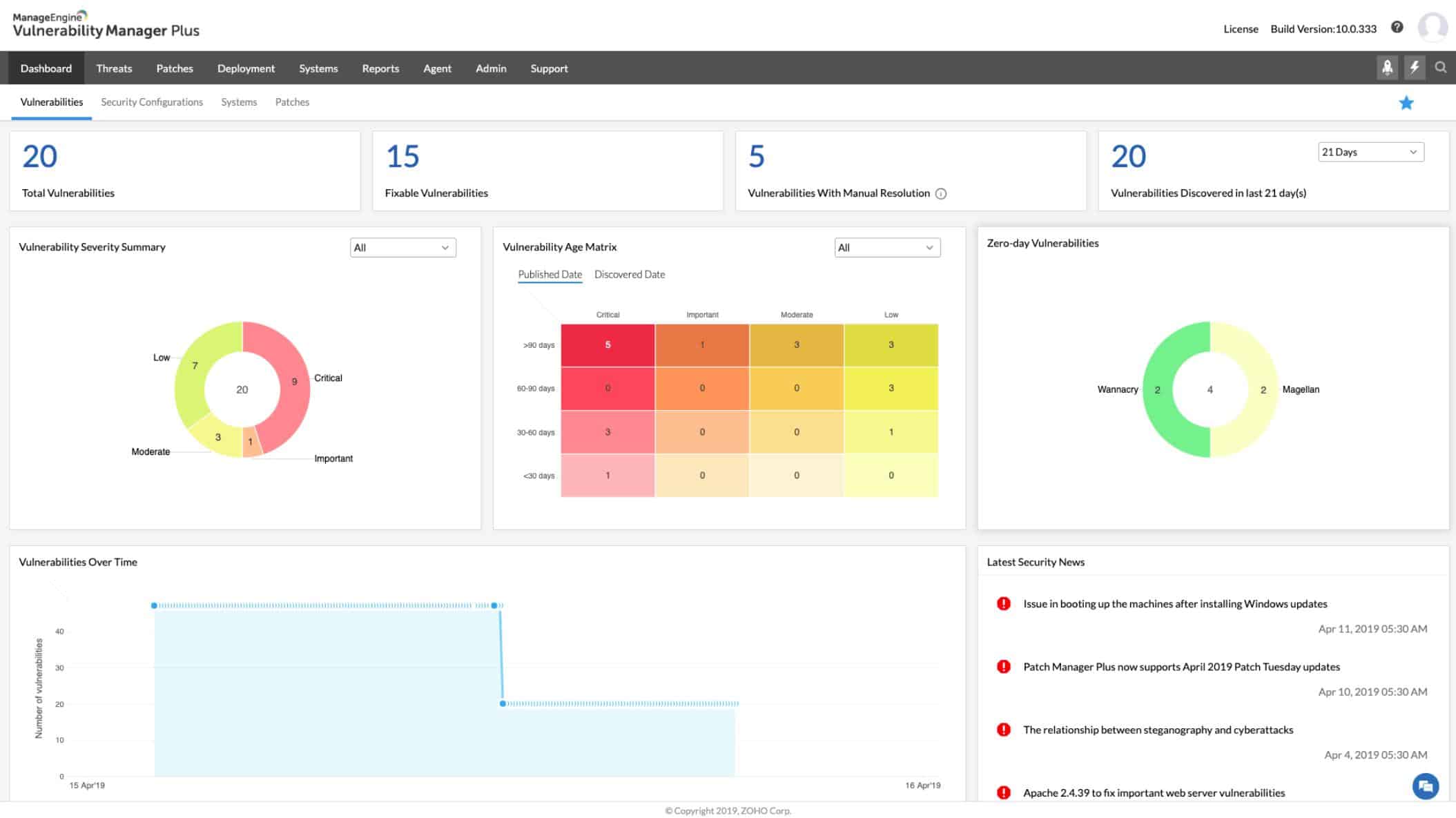
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus combines a patch manager and a vulnerability scanner. This package enables you to prevent vulnerabilities from occurring, spot those that exist, tighten exploits, and harden your system.
Key Features:
- Onsite Vulnerability Manager: Provides on-premises vulnerability management capabilities, allowing organizations to assess and mitigate vulnerabilities within their network infrastructure.
- Patch Manager: Offers patch management functionality to ensure that systems and software are up-to-date with the latest security patches, reducing the risk of exploitation.
- Frequent Scan Cycles: Conducts scan cycles every 90 minutes to continuously monitor and identify vulnerabilities in the network, enabling proactive remediation.
- Threat Intelligence: Incorporates threat intelligence data to enhance vulnerability assessment accuracy and prioritize remediation efforts based on the severity of threats.
- Robust Reporting: Provides comprehensive reporting capabilities to track vulnerability trends, measure improvements post-remediation, and demonstrate compliance with security standards.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus sweeps your network, endpoints, and software to identify configuration errors and out-of-date software. The configuration analysis module recommends changes that you can make to tighten security and the software manager automatically launches a patch manager to update operating systems and software.
The Vulnerability Manager Plus system in a software package that includes a collection of modules. The central server installs on Windows and Windows Server then each endpoint needs an agent installed on it. The agent program is available on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
The server of the package coordinates activities and reports from each distributed module operated through the device agents. This combination of services ensures that endpoints can be protected in the event of the network being damaged.
Scans occur every 90 minutes. The system includes a live threat intelligence feed and any newly discovered exploits trigger an extra search. Scans extend to network appliances, such as firewalls scan web services.
Who is it recommended for?
This is an on-premises package for Windows Server that reaches across the network to scan devices running Windows, macOS, and Linux. This is a good option for businesses of any size because it automates the actions required to fix discovered problems, such as patching. The Free edition is suitable for small businesses with up to 25 endpoints.
Pros:
- Free Version Available: Offers a free version of the software, making it accessible to small businesses and organizations with limited budgets.
- Continuous Scanning and Patching: Ideal for continuous scanning and patching throughout the lifecycle of devices, ensuring ongoing protection against vulnerabilities.
- Cross Platform Support: Can be deployed on Windows, Linux, and Mac systems, offering flexibility in implementation across diverse IT environments.
- Updated Threat Intelligence: Utilizes backend threat intelligence that is regularly updated with the latest threats and vulnerabilities, enhancing the accuracy of vulnerability assessments.
- Free Version for Small Businesses: The availability of a free version makes it a cost-effective option for small businesses looking to enhance their cybersecurity posture.
Cons:
- Complex Ecosystem: The ManageEngine ecosystem is detailed and feature-rich, requiring time and effort to fully explore and utilize all of its capabilities.
Vulnerability Manager Plus is offered in three editions: Free, Professional, and Enterprise. The free version is limited to monitoring 25 computers. The Professional edition operates on one site and the Enterprise edition caters to WANs. Both paid systems are offered on a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus is our top pick for an alternative to Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA) because it offers a more extensive and modern solution for vulnerability management and patching, while MBSA is limited to assessing system vulnerabilities. One of the key advantages of Vulnerability Manager Plus is its ability to perform more in-depth vulnerability assessments. Unlike MBSA, which primarily focuses on identifying missing security patches and configurations, Vulnerability Manager Plus scans for a wider range of vulnerabilities, including those in applications, third-party software, and operating systems. This enables businesses to have a more holistic view of their security posture. Another reason we recommend Vulnerability Manager Plus is its built-in patch management capabilities. It allows organizations to not only identify vulnerabilities but also automatically deploy patches to remediate them, streamlining the process and reducing the risk of exploits. This feature is particularly valuable for businesses that need to patch systems quickly and efficiently to minimize downtime and security threats. Vulnerability Manager Plus provides detailed compliance reporting, helping organizations adhere to industry standards and regulations, something that MBSA lacks. The tool also supports continuous monitoring, ensuring that newly discovered vulnerabilities are promptly identified and addressed.
Download: Get a 30-day free trial
Official Site: https://www.manageengine.com/vulnerability-management/download.html
OS: Windows Server
2. Paessler PRTG Network Monitor (FREE TRIAL)
A leading network management solution with security feature options, Paessler PRTG has a unique take on both pricing and deployment. PRTG monitors networks on a “per-sensor” basis, with each component of a given asset representing a single sensor. Monitoring the port on a switch for traffic, for example, would be a single sensor. Pricing for PRTG is based on the total number of sensors deployed, giving a flexible amount of scalability to those who use PRTG.
Key Features:
- Network Monitoring: PRTG monitors network devices such as routers, switches, servers, and endpoints to ensure they are operational and functioning within predefined thresholds.
- Security Monitoring: While not primarily a security tool, PRTG can monitor security-related parameters such as firewall logs, antivirus status, and intrusion detection system (IDS) alerts to provide insights into potential security issues.
- Performance Monitoring: PRTG tracks performance metrics such as CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, and network bandwidth to identify performance bottlenecks and issues that may impact security.
- Alerting and Notification: PRTG sends alerts via email, SMS, or other methods when predefined thresholds are exceeded or when security-related events are detected, allowing administrators to respond promptly to security incidents.
- Reporting and Analysis: PRTG generates reports and provides historical data analysis, enabling administrators to identify trends, track changes over time, and assess the effectiveness of security measures.
Why do we recommend it?
Paessler PRTG Network Monitor supervises endpoints and software as well as networks. The tool can be used to identify rogue devices because of its continuous device polling processes. This enables you to tighten up network breaches. You can use the port scanner in the tool to list open ports on all devices.
These sensors can provide a range of functions, and when deployed in the right locations can give administrators a solution for many different networking areas. Sensors can be deployed on a given asset that track application updates, for example, to ensure up-to-date patch status on the asset.
These sensors can also be deployed on network ports to monitor traffic. The software can actively track for unusual traffic or system behavior and report this back to the system’s administrator, helping to stop intrusions in their tracks.
Who is it recommended for?
PRTG is a good package for general system monitoring. It provides automated processes to track system performance through a series of thresholds that trip when responses dip or resources run short. The package contains many sensors and if you only activate 100, the system is completely free to use.
Pros:
- Customization: PRTG allows users to customize monitoring parameters, thresholds, and alerting rules based on specific security requirements and organizational policies.
- Scalability: PRTG is scalable and can monitor networks of all sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises, making it suitable for organizations with diverse network infrastructures.
- Integration: PRTG integrates with various third-party systems, security tools, and protocols, allowing for seamless integration into existing security workflows and environments.
- Active Development: PRTG is actively developed and maintained by Paessler GmbH, with regular updates and new features released to address evolving security challenges and requirements.
- Drag and Drop Editor: Offers a user-friendly drag and drop editor that simplifies the creation of custom views, dashboards, and reports, allowing users to tailor the monitoring interface to their specific needs.
- Powerful Freeware Version: Provides a robust freeware version with essential monitoring capabilities, making it accessible and cost-effective for small-scale deployments or evaluation purposes.
Cons:
- Limited Security Focus: Primarily focused on network performance, not dedicated security vulnerability scanning.
- Complexity for New Users: Due to its comprehensive feature set and various monitoring methods, PRTG Network Monitor can have a learning curve for new users, requiring time and effort to fully understand and leverage its functionalities.
This impressive flexibility makes PRTG a good solution for small or medium-sized businesses that want a versatile network vulnerability service that does more than just look for holes in the network. PRTG Network Monitor is available on a 30-day free trial.
Start 14-day Free Trial: Paessler.com/PRTG-download
Paessler PRTG Network Monitor is our #1 choice for replacing the Microsoft Baseline Analyzer because it offers a more comprehensive approach to infrastructure monitoring. The combined capabilities of PRTG with its 3-in-1 application, server, and network monitoring features help identify system security weaknesses. A complete system monitoring solution!
OS: Windows Server 2012 or later
3. SolarWinds Network Automation Manager
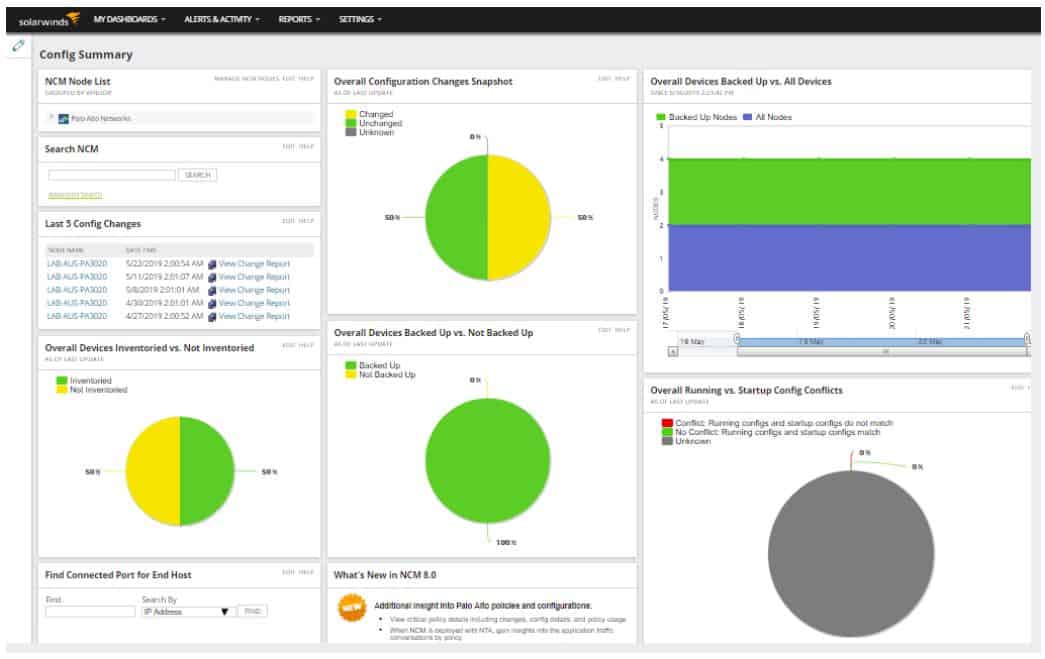
The SolarWinds Network Automation Manager is a combination of SolarWinds systems that can all be bought individually. SolarWinds designed these modules on a common platform, called Orion, so they all slot together and you access them all through one dashboard. The package provides all of the tools that you will need to monitor and manage networks and they provide warnings for suspicious activity, which gives you security tracking as well.
Key Features:
- Network Monitoring: Provides comprehensive network monitoring capabilities to track performance metrics, detect anomalies, and ensure optimal network health.
- IP Address Management: Offers IP address management functionality for efficient IP allocation, tracking, and detection of rogue devices on the network.
- Device Configuration Protection: Ensures the security of device configurations by implementing protection measures to prevent unauthorized changes or tampering.
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Network Automation Manager gives you all of the tools that you need to run your business. They will help keep your system running at peak performance with minimum manual effort. The package also tracks user activity and spots rogue devices, which will help with compliance auditing.
The bundle combines the following SolarWinds products:
- Network Performance Monitor (NPM)
- Netflow Traffic Analyzer (NTA)
- User Device Tracker (UDT)
- VoIP & Network Quality Manager (VNQM)
- Network Configuration Manager (NCM)
- IP Address Manager (IPAM)
- SolarWinds High Availability
To get a full match for the functions of Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer, you should also add on the SolarWinds Patch Manager. This is also built on the Orion platform and it will fit into the system dashboard along with all of the features of the Network Automation Manager. If fact, with this combination you get a package that beats the MBSA because the SolarWinds solution gives you constant performance monitoring as well as security tracking.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is ideal for a company that is just starting up or one that has assembled its system monitoring tools in a haphazard way and wants to scrap it all and start again. The bundle provides an integrated approach to system management, performance optimization, and security protection.
Pros:
- Endpoint Security: Enhances endpoint security through patch management capabilities, ensuring that network devices are up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates.
- Centralized Management: NAM offers a central platform to manage all your SolarWinds network monitoring tools. This eliminates the need to switch between separate interfaces for different functionalities.
- Automation Capabilities: Automate repetitive tasks like configuration changes, report generation, and basic troubleshooting steps, freeing up your IT staff for more strategic endeavors.
Cons:
- On-Premises Package: The tool is an on-premises solution, which means it requires local installation and management. Some organizations may prefer a cloud-based (SaaS) option for flexibility and scalability.
The Network Automation Manager and the Patch Manager run on Windows Server. You could also consider using the SolarWinds Security Event Manager for threat detection and that system also runs on Windows Server. You can try out the Network Automation Manager bundle with a 30-day free trial.
4. OpenVAS
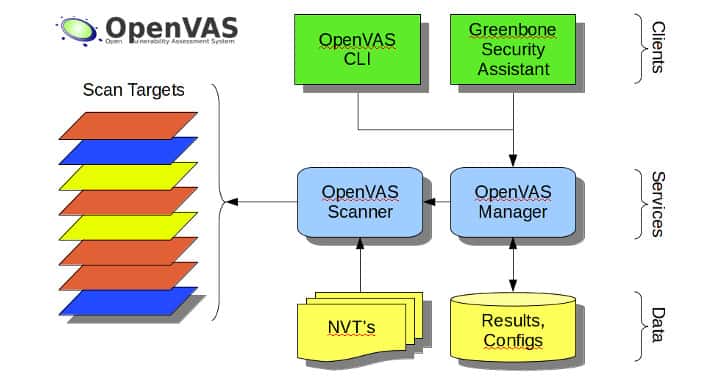
One of the premiere open-source vulnerability scanning applications currently available, OpenVAS has a strong track record for vulnerability detection that goes through constant improvement and community testing. As an open-source project the source code is freely available and can be tweaked by ambitious administrator’s to fit their needs.
Key Features:
- Vulnerability Scanning: OpenVAS conducts comprehensive vulnerability scans of networks, hosts, and applications to identify security weaknesses, misconfigurations, and potential threats.
- Extensive Vulnerability Database: OpenVAS leverages a continually updated database of known vulnerabilities, including CVEs, to detect and report security issues in scanned systems.
- Network Discovery: OpenVAS automatically discovers and maps network assets, including devices, services, and open ports, providing visibility into the organization’s attack surface.
- Threat Intelligence: The tool incorporates threat intelligence capabilities, allowing users to identify and assess potential security threats and vulnerabilities within their systems and networks.
Why do we recommend it?
OpenVAS is a highly-respected vulnerability scanner – VAS stands for Vulnerability Assessment Scanner. This tool is free to use and there is a paid alternative. The package was created as a fork of Nessus (see below) and it runs through a list of about 50,000 Network Vulnerability Tests (NVTs).
As is common with other open-source softwares, the free nature of the product means that official product support is lacking. There is something of a learning curve when using OpenVAS, and getting the most from the software will require some time to learn how it works. There’s an extensive knowledgebase and significant community support that can help new users tailor scanning profiles to fit their needs and ensure a high degree of vulnerability identification and reduce the number of false positives. Even with this community support, the lack of any official training or product support can be a frustrating downside for some users.
That being said, OpenVAS does have a good track record as a vulnerability scanner, and is used by many organizations as their primary means of securing their networks.
Who is it recommended for?
OpenVAS is a mainstay of penetration testing. So, it is used by professional security consultants. The tool doesn’t have a very good interface, so it isn’t the type of system that infrequent users or untrained technicians would use. A paid alternative offered by the company that manages OpenVAS is called Greenbone Enterprise.
Pros:
- Free to Use: OpenVAS is an open-source vulnerability scanning and management tool that is freely available for use, making it accessible to a wide range of users and organizations.
- Community Support: OpenVAS is backed by a dedicated community of developers and users who contribute to its development, support, and improvement, ensuring ongoing updates and enhancements.
- Open-Source Transparency: Being open-source, OpenVAS offers transparency regarding its codebase and functionality, allowing users to audit and customize the tool as per their requirements.
Cons:
- Lack of Paid Support Option: Unlike some commercial tools, OpenVAS does not offer a paid support option, which may be a concern for organizations requiring dedicated technical support and assistance.
- Basic Interface: The user interface of OpenVAS is described as bare-bones and lacking default quality-of-life features found in more polished commercial solutions, potentially impacting user experience and efficiency.
- Skill Requirement: May require experienced staff or security professionals within an organization, as navigating and fully leveraging the tool’s capabilities may require a certain level of expertise.
5. Nessus
Developed by Tenable and the original code base for OpenVAS, Nessus is another software with a long track record of vulnerability identification. It offers strong product support and many of the strengths of its cousin OpenVAS.
Key Features:
- Vulnerability Scanning: Nessus performs thorough vulnerability scans of network assets, and web applications, to identify security weaknesses and potential threats.
- Vulnerability Database: Extensive vulnerability database with a vast array of checks for various operating systems, applications, and devices.
- Severity Ratings: Provides severity ratings for identified vulnerabilities to prioritize remediation efforts.
- Policy-Based Scanning: Nessus allows users to define custom scanning policies based on specific requirements, compliance standards, or industry best practices, enabling tailored assessments and targeted vulnerability detection.
- Credential-Based Scanning: Nessus supports authenticated scanning, allowing it to perform deeper assessments by logging into target systems and conducting more thorough checks for misconfigurations, missing patches, and other security issues.
- Integration and Automation: Nessus integrates with SIEM systems, ticketing systems, and other security tools, enabling seamless workflow integration and automation of vulnerability management processes.
Why do we recommend it?
Nessus is a network vulnerability scanner and it dates back to 1998. While originally a free tool, the system is now a paid package. There is a free version for home use, called Nessus Essentials. Two paid versions are Nessus Professional and Nessus Expert, which are very expensive. The producer of Nessus is called Tenable.
Nessus features both active and passive network scanning and can be used to scan both cloud and local assets. It has a long list of standard scanning profiles while still offering a breadth of customization in security scanning rules. Vulnerability prioritization gives administrator’s the information they need to quickly assess security risks and take the appropriate steps to fix them.
The Nessus licensing model is flexible and allows for deployment based on assets instead of individual IPs. Tenable offers both a cloud-based SaaS scanning solution and an on-premise software deployment, giving administrators welcome deployment options. Further customization in the software’s dashboard gives Nessus the flexibility to fit wherever it needs to.
For those who like the features found in OpenVAS, but are seeking a more professionally supplemented solution with full product support, Tenable’s Nessus provides an attractive choice.
Who is it recommended for?
Tenable tends to push its higher plan for vulnerability management, which is called Tenable and is available in on-premises and cloud SaaS versions. The Nessus system is priced beyond the budgets of small businesses and universities tend to use OpenVAS on cybersecurity courses, so qualified penetration testers tend to use that system instead of Nessus.
Pros:
- Deeper Scans: Nessus offers far more comprehensive vulnerability scans than MBSA, identifying a wider range of security weaknesses.
- Scalability: Can handle large and complex networks effectively.
- Severity Assessment: Helps prioritize vulnerabilities based on their potential risk, allowing you to focus on the most critical issues first.
- Ease of Use: Nessus features an intuitive user interface, streamlined setup process, and automated workflows, making it accessible to users with varying levels of technical expertise.
- Extensive Templates: With over 450 templates supporting a wide range of devices and network types, Nessus provides users with a comprehensive library of scanning configurations.
Cons:
- Steeper Learning Curve: Nessus offers more features and flexibility, but this can come with a steeper learning curve compared to MBSA’s basic functionality.
- Expensive Enterprise Solution: The paid version of Nessus is positioned as an enterprise-level solution, which may be more expensive and less suitable for smaller networks with limited budgets looking for basic scanning capabilities.
6. Nexpose
Nexpose is a vulnerability scanner developed by Rapid7, the makers of the Metasploit framework. The software’s main selling point is its ability to easily integrate with Metasploit for real, live vulnerability testing within a closed framework. This gives Nexpose users a powerful way to accurately test their systems for risk exposure and helps identify rapid solutions to potential exploits.
Key Features:
- Vulnerability Scanning: Broad vulnerability coverage across operating systems, applications, and devices.
- Continuous Monitoring: Offers real-time and continuous monitoring for proactive threat detection.
- Contextual Risk Scoring: Provides contextual risk scoring to prioritize vulnerabilities based on exploitability and potential impact.
- Reporting: Generates detailed reports with remediation recommendations.
- Integration: Integrates with various security tools for a centralized security posture.
- Suggests Fixes: The tool not only identifies vulnerabilities but also suggests possible fixes or remediation actions, streamlining the process of addressing security issues within the network.
Why do we recommend it?
Nexpose is an on-premises vulnerability scanner. It is produced by Rapid7, the creators of Metasploit, which is a penetration testing tool. Nexpose was designed as an automated version of the manual tools contained in Metasploit. Rapid7 also produces a SaaS vulnerability scanner, called InsightVM. Nexpose is fully automated and has an attractive user interface.
Nexpose features its own contextualized risk scoring system aimed at giving administrators a fast way to assess risk levels of identified vulnerabilities. These contextualized scores provide risk priorities for identified problems and help users address the deficiencies that need immediate attention.
Live and active monitoring combined with detailed remediation reporting gives a short list of actionable steps to shoring up network security. Unlike some software that simply lists vulnerabilities and their associated risk, Nexpose smartly provides a list of actual steps administrators can take to secure their systems.
Nexpose’s unique take on remediation reporting and easy integration with Metasploit make Nexpose a flexible option for both new and experienced security professionals.
Who is it recommended for?
While penetration testers favor Metasploit, network managers would be better off opting for Nexpose. This system is an on-premises package for Windows Server and Linux. The cloud alternative, InsightVM is a very similar service but you don’t have to host it. So, any business interested in a Rapid7 vulnerability manager should assess both options.
Pros:
- Based on Metasploit: Nexpose leverages the capabilities of Metasploit, a well-known penetration testing framework, to enhance its vulnerability scanning and assessment functionalities.
- Free Version: Offers a free version with limited features (scan frequency, number of assets).
- Intuitive Dashboards: Nexpose features highly intuitive and customizable dashboards, allowing users to visualize and manage vulnerabilities effectively, enhancing decision-making and prioritization.
- Supports Vulnerability Lifecycle: From discovery to remediation, Nexpose supports the entire vulnerability lifecycle, providing users with tools and features to manage vulnerabilities comprehensively.
Cons:
- Complexity: Compared to MBSA’s basic functionality, Nexpose offers more features, which can introduce a steeper learning curve.
- Focus on Vulnerability Discovery: While Nexpose excels in vulnerability discovery and assessment, it may not be the best option for users looking specifically for patch management functionalities or comprehensive security solutions beyond vulnerability scanning.
Making your tools work
The most important, and far too often neglected, step in good security auditing is the proper configuration of scanning profiles and focused vulnerability testing. It’s enough to warrant its own dedicated section in this article as a reminder to administrators. Vulnerability scanners and security software will often come with their own default or preset scanning profiles designed as generic scanning solutions that can be used “out-of-the-box.” Customizing these scanning rules is critical to proper auditing of any network or platform. Likewise, doing your own closed tests on vulnerabilities themselves can help you gain insight into determining which vulnerabilities need immediate attention.
Picking the right MS BSA Alternative
Deciding which vulnerability scanner to use can depend on a range of factors:
Type of Business: As stated above, security needs will vary from business to business. Evaluate what your security goals are based on your organization’s structure, sector(s), and size. Also, address if any specific branches of the organization need heightened security over other branches.
Identify Assets: Take note of how many assets need to be monitored and evaluated for vulnerabilities, their locations, their individual functions, and importance to overall operation. Certain applications are more geared towards specific assets. It’s important to take note of both hardware and software assets, as each may have their own specific security concerns or risks. Public-facing assets, such as a web server are more vulnerable to exploit attacks than well-protected office systems.
Identify Existing Security: Understanding the security practices and implementations already in place is obviously a critical step in adding a new layer of security checks. If you already have a robust security solution from a certain vendor, for example, it may be prudent to use solutions that integrate well with your existing security.
Assess Security Risk and Desired Level of Security: Some organizations will inherently need a higher level of security than others. They may be more likely to be targeted by malicious intrusions, or naturally, have a much more public-facing. Assessing both the potential risk of being targeted and the desired level of security needed will determine what kind of vulnerability management software to implement.
Once you’ve taken stock of what your organization will need in a security solution, it’s time to start researching the potential options. The list presented here will give a brief overview of trusted solutions in the information security industry, but doing your own in-depth research is critical when selecting the right solution. Even a well-reviewed piece of software with critical acclaim from multiple sources may not be the right fit for your organization. Using the above checklist combined with a careful look at each potential software choice will give you the tools you need to pick the right software.
Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA) FAQs
Can patches and updates be excluded from a scan?
Yes. If you use Microsoft Software Update Services (SUS) you can manage which updates and patches will be skipped in that environment. When running an MBSA scan check the Use SUS Server box and enter the address of that server. When the scan runs, it will only look for patches and updates that are approved in SUS.
Does version 2.3 of MBSA work with Windows 10?
Version 2.3 of MBSA does not work with Windows 10 or Windows Server 2016.
How do I remove Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA)?
To remove Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA) Use the Add/Remove Programs feature in the Windows Settings system.
- Go to the Search programs and files box in the Start menu (Windows 7) or on the Taskbar (Windows 8 and 10) and type uninstall a program. In Windows 7, you will see an Uninstall a program option, and in Windows 8 and 10, select Apps and Features.
- Scroll through the list of presented programs to find MBSA. Click on that entry.
- Click on the Uninstall button.