Active Directory (AD) Security Groups play a crucial role in managing permissions and access control within Windows-based IT environments. These groups streamline administration by organizing users, devices, and resources, enabling efficient management of access rights to files, applications, and systems. By assigning permissions to a group instead of individual users, organizations save time, reduce errors, and maintain consistent security practices.
Security groups in Active Directory can be configured to grant or deny access to specific resources, define roles, and enforce policies across a domain or forest. There are two primary types of security groups: domain local, used to assign permissions for resources within a single domain, and global groups, which can span multiple domains for broader access management. Another commonly used type is the universal group, ideal for multi-domain environments requiring cross-domain permissions.
Active Directory (AD) is a prime target for cybercriminals because it is the central hub for managing user identities, permissions, and organizational resources. By compromising AD, attackers can escalate privileges, move laterally across the network, and access sensitive data or critical systems. Common attack methods include password spraying, exploiting misconfigurations, and leveraging phishing schemes to gain initial access.
To counter these threats, organizations must enforce strong security measures such as multi-factor authentication, regular privilege audits, and automated monitoring of AD activity. Implementing security groups effectively can enhance an organization’s overall security posture by adhering to the principle of least privilege, granting users only the access they need to perform their roles. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access or potential breaches.
This guide provides detailed insights into Active Directory Security Groups, explaining their types, uses, and best practices. It also offers tips for secure configuration, helping IT professionals manage access controls effectively in complex environments.
AD Security Groups and Permissions
Active Directory group management is the classifying and managing of users and devices across a network by bundling them together into AD groups.
AD security groups enable network administrators to manage permissions, policy settings, and group access to shared resources among a collection of users or devices all at once, rather than manually assigning permissions to individual users one at a time. For instance, if you want to grant staff in the HR department access to a specific network folder, you need to create a security group made up of staff from that unit.
This simplifies network administration by allowing you to assign permissions once to multiple users. Users can be added or removed from the group as the need arises. The change in group membership automatically takes effect everywhere.
With AD security groups, network admins can:
- Assign user rights: User rights can be assigned to a security group. This helps to control what the users within the group can or cannot do within a domain or forest. For some security groups, user rights are automatically assigned for administration purposes which in turn can be inherited by members of the group. It’s critical that you pay special attention to those automatically assigned user rights to ensure that they are within required boundaries.
- Assign permissions for resources: User permissions are distinct from user rights. Rights define the capabilities users possess, whereas permissions relate to access to resources. Some security groups are created by default and permissions automatically assigned when you create an Active Directory domain. Again extra care must be taken in managing those types of groups due to their automatic security permissions.
When assigning permissions for resources (such as network folders, printers), it is best practice to assign those permissions to a security group rather than to individual users. Members of a security group inherit rights and permissions assigned to that group in Active Directory.
Active Directory groups (including security groups) are characterized by their scope. The scope of the group determines the extent to which the group is applied in the domain tree or forest, and defines where the group can be granted permissions.
The following three group scopes are defined by Active Directory:
- Domain local: Domain local manages access permissions to different domain resources (such as files and folders NTFS permissions, remote desktop access, etc.) in the domain where it was created; and can be applied anywhere in the domain. A domain local group can include members from trusted domains or other types of members.
- Global: The global group scope is used to provide access to resources in another domain. Global groups are usually used as role-based groups; which means that domain objects (such as users and computers) are defined based on business roles.
- Universal: Just as the name implies, with the universal group scope, you can define roles and manage access to resources that are distributed across multiple domains in a forest.
AD Security Groups Best Practices
Active Directory security groups include Administrators, Domain Admins, Server Operators, Account Operators, Users, Guests, among others. A good understanding of how to manage these security groups with a best-practice mindset is key to keeping your system secure.
The following are key AD security groups best practices:
- Ensure default security groups don’t have excessive permissions: Regularly audit permissions automatically assigned by default security groups when you set up an Active Directory domain, as some of these groups have extensive permissions. Ensure that users only have just enough access rights required to carry out their daily tasks and nothing more. If higher access rights are required, it should be provided on a temporary basis as and when needed.
- Keep software regularly updated: Ensure that your Windows software and other third-party applications are regularly updated. Attackers often exploit or take advantage of known vulnerabilities to compromise systems. Regular patching can help minimize this risk.
- Good password policy: Implement password policies that encourage users to use passphrases they can easily remember instead of focusing on complexity rules. Complexity rules make passwords harder to remember, and most users end up writing them down, which defeats the whole purpose in the first place. It’s also recommended to set rules that lockout users after several failed login attempts. Adopt the use of Windows supported 2FA/MFA such as Windows Hello or FIDO for extra protection.
- Maintain a policy of zero trust: Zero trust means that no one is trusted by default from inside or outside the network, and verification is required from everyone trying to gain access to resources on the network. Insider threat is a risk no organization should underestimate because it can be incredibly difficult to track the source. Adhere to the principle of least privilege access to network resources and ensure that users don’t have excessive permissions.
- Audit changes to AD Security groups: Auditing helps to detect anomalous user behavior and system events. AD-related security vulnerabilities and threats can potentially be prevented through better visibility into changes that take place within the security group. Having a good auditing strategy for your AD security groups is a sure way to prevent security threats. Changes to privileged groups should be alerted in real-time to ensure that you can investigate the change and revert it if excessive permissions were created.
Here is our list of the best tools for managing AD Security Groups:
- ManageEngine ADManager Plus EDITOR’S CHOICE Centralize the administration of multiple AD domains and secure those instances from tampering with this tool that also provides reporting. Runs on Windows Server, AWS, and Azure.
- ManageEngine ADAudit Plus (FREE TRIAL) Ude this package to enforce system security by tracking user activity, preventing AD tampering, and enforcing standards compliance. Available for Windows Server
- SolarWinds Permissions Analyzer This system will help you to identify the permissions structure that you have for each device by displaying each record with a list of statuses. Runs on Windows Server.
- Quest Recovery Manager for Active Directory A backup service for Active Directory that can quickly reverse accidental or malicious changes. Runs on Windows and Windows Server.
The Best Tools for Managing AD Security Groups
Our methodology for selecting AD security group management tools
We reviewed the market for tools to manage AD security groups and analyzed options based on the following criteria:
- Display of groups and members
- A search facility
- A display of inheritance
- A cross-reference to device permissions for each group
- The ability to view multiple domains
- A free trial for a no-obligation assessment opportunity or a free tool
- A paid tool that offers value for money or a free tool that is worth installing
With these selection criteria in mind, we looked for a range of AD security group management systems that include simple free tools and more complex paid systems that have wider AD management capabilities.
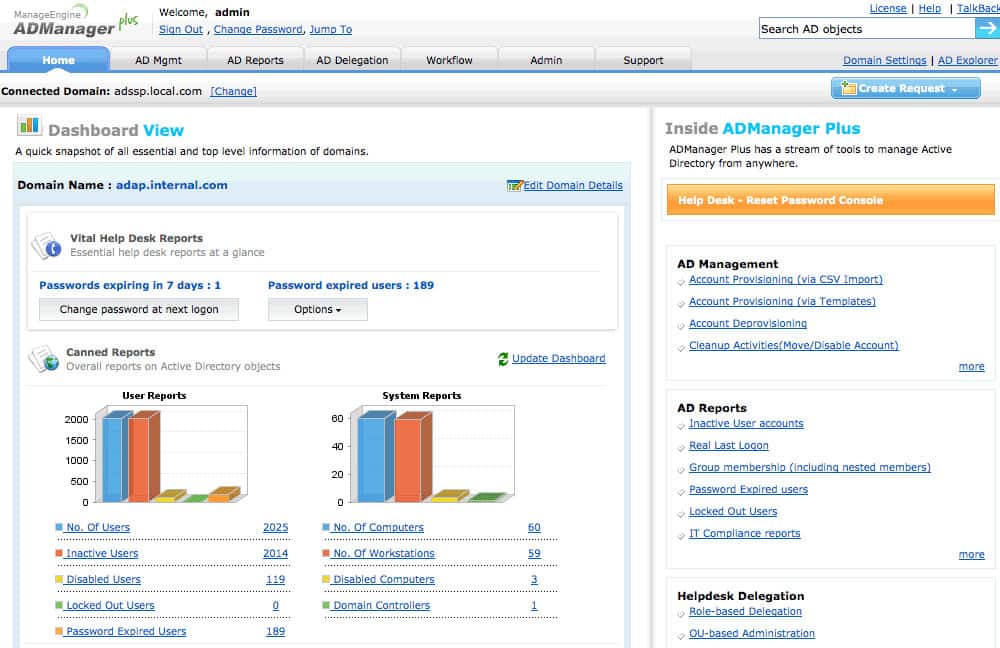
1. ManageEngine ADManager Plus (FREE TRIAL)
ADManager Plus is a web-based AD management and reporting tool that provides centralized administration and management of Windows Active Directory. It allows IT admins to manage AD objects and groups from one central location via a user-friendly GUI.
Key Features:
- Efficient Bulk Operations: Facilitates the creation and management of AD objects in bulk, significantly reducing manual effort and improving productivity.
- Password Administration: Enables administrators to directly reset passwords and manage account details, ensuring secure and timely access control.
- Proactive Inactive Account Management: Identifies and manages inactive accounts, improving security posture and operational hygiene.
- Centralized Multi-Domain Management: Provides a unified console for managing user accounts and permissions across multiple domains, enhancing administrative efficiency.
- Mobile and Application Account Management: Supports the management of mobile device accounts and integrates with platforms like Exchange Server and Microsoft 365, streamlining access and permissions across technologies.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine ADManager Plus is highly recommended for its efficient and centralized approach to Active Directory management, streamlining tasks such as bulk user creation and advanced reporting, which are essential for maintaining compliance and operational efficiency.
Network admins can use ADManager Plus to perform the following functions:
- Generate and view granular reports of users, computers, groups such as Inactive Users, Disabled Users, Users in Nested Groups, Distribution Groups, Security Groups, Inactive Computers, among others.
- Modify the existing user account properties including Exchange Mailbox and Terminal Services properties.
- Create bulk user accounts in the Active Directory with the flexibility to import properties from a CSV file.
- Create and delegate security roles for granting/revoking permissions to security principals.
ManageEngine ADManager Plus can be used to automate the report generation process. This lowers the time that would be wasted on manually navigating the Active Directory program, thereby making Active Directory more convenient.
The ADManager Plus system provides a central management console for multiple domains. Tools in the package let you create, modify, and delta user accounts in bulk and you can also allocate user accounts to groups en masse. This action can be implemented by loading in records from a CSV file.
An administrator can search for an account and rest its password directly by triggering a request to the user. It is also possible to make other changes to user accounts or groups manually and individually. The interface includes an inactive account identifier and you can spot locked accounts, which can be unlocked on demand. Accounts can also be moved between groups.
The tool can be used to manage mobile devices running iOS and Android and it will also manage accounts for Exchange Server, Microsoft 365, Google Workspaces, and Skype for Business. The system will help you manage device and resource permissions and allocate rights to groups.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideally suited for IT administrators and network managers in large organizations or Managed Service Providers (MSPs) who require a comprehensive, web-based solution for managing complex Active Directory environments across multiple domains.
Pros:
- Advanced Permission Modulation: Allows for the easy application of bulk permission changes, simplifying administrative tasks in complex Active Directory environments.
- Comprehensive Reporting Capabilities: Generates detailed compliance reports for standards such as PCI and HIPAA, facilitating audit readiness and compliance management.
- Multi-Domain Support: Excellently accommodates the needs of large, multi-site organizations with its robust multi-domain management capabilities.
- Effective Delegation Features: Empowers NOC and helpdesk teams with delegation capabilities, optimizing operational workflows and resource allocation.
- Enhanced Security Group Visibility: Offers the ability to visually inspect share permissions and security group details, promoting better access control and security management.
Cons:
- Optimized for Scale: Primarily designed to cater to the needs of larger organizations, MSPs, and environments with multiple domains, which may not be as beneficial for smaller setups.
ManageEngine ADManager Plus is available for download on a 30-day free trial. It is licensed on an annual subscription based on the number of domains it would manage. We recommend this product to anyone looking to make Active Directory Management more convenient as well as those who want to benefit from a high-quality report function.
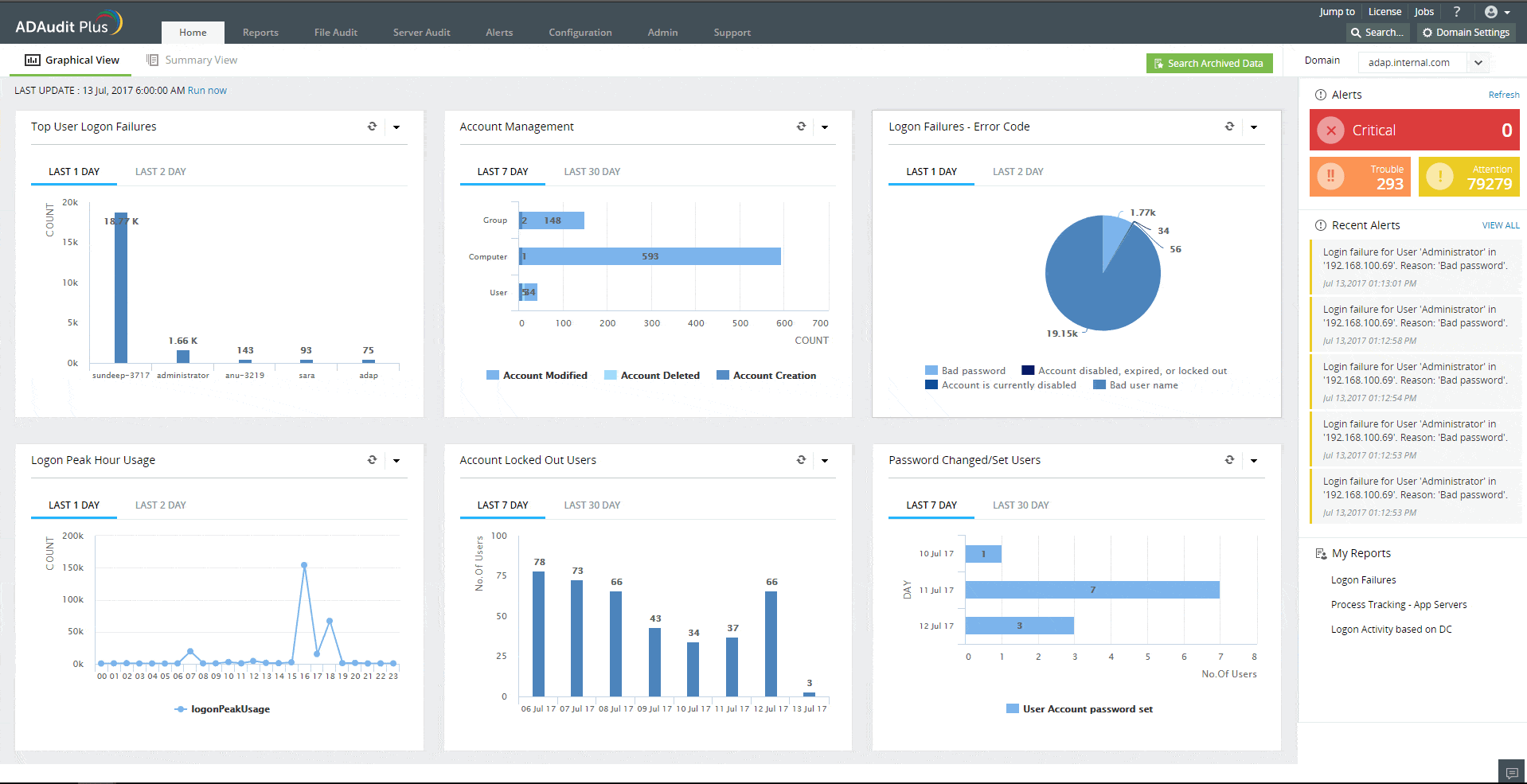
2. ManageEngine ADAudit Plus (FREE TRIAL)
ADAudit Plus by ManageEngine is an AD auditing tool that allows network admins to audit active directories, login and logoff records, file, and Windows server data, and generate real-time user activity reports.
Key Features:
- AD Insights: Offers comprehensive auditing of Active Directory environments, ensuring every user action is tracked and recorded.
- File Surveillance: Monitors Windows and NAS file servers to track access and changes, safeguarding against unauthorized modifications.
- Server Oversight: Extensive Windows server auditing capabilities to maintain security and operational integrity.
- Workplace Monitoring: Keeps an eye on workstation activities, enhancing security across all endpoints.
- Azure Scrutiny: Provides auditing solutions for Azure AD, ensuring cloud services are securely managed.
- Compliance Ready: Equipped with predefined reports for SOX, HIPAA, GLBA, PCI-DSS, and FISMA compliance, simplifying regulatory adherence.
Why do we recommend it?
ADAudit Plus shines due to its exceptional capacity to ensure compliance and security within Active Directory environments. Its effortless click-through reports make it invaluable for organizations navigating the complex waters of industry regulations.
With this tool, you can keep track of which employees did what, when they did it, and who did it on Windows and File servers. You can get reports on domain controllers and file servers and export the reports to CSV, PDF, XLSX, and HTML formats. Network admins will be able to block or prevent legitimate users from abusing their access privileges.
One of the key benefits of this solution is its inherent support for industry-specific regulatory compliance. It is bundled with pre-configured standards compliance reports, which follow the SOX, HIPAA, GLBA, PCI-DSS, and FISMA standards. So, you won’t need to customize the system or set up your own reports in order to demonstrate compliance.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for medium to large organizations that require robust auditing capabilities across Active Directory, Azure, and Windows file systems, particularly those in industries with stringent compliance requirements.
Pros:
- Regulatory Alignment: Excellently addresses compliance demands, aiding in adherence to specific industry regulations.
- Click-Through Reports: Features ready-to-use compliance reports, offering insights into compliance status effortlessly.
- Versatile Environment Support: Compatible with AD, Azure, and Windows file systems, ensuring broad applicability.
- Automation Excellence: Supports powerful automation and scripting, streamlining administrative tasks.
- Intuitive Dashboards: The user interface includes detailed dashboards and visuals for at-a-glance insights.
Cons:
- Small Network Suitability: May not be the optimal choice for smaller network environments due to its extensive feature set.
ADAudit Plus is available in three editions: Free, Standard, and Professional. A 30-day free trial and an online demo which includes all features of Professional Edition are all available. Overall, ADAudit Plus’ great dashboard and analytics makes it a powerful tool to gain insights and visibility into your AD environment.
3. SolarWinds Permissions Analyzer
One of the common challenges with the Microsoft Active Directory program is that it offers poor permissions management. This is where SolarWinds Permissions Analyzer stands out. SolarWinds Permissions Analyzer enables network admins to gain better visibility into user and group permissions, check permissions assigned on Active Directory objects, browse permissions by a group or user, or analyze user permissions based on group membership and permissions even in multi-domain Active Directory Forest.
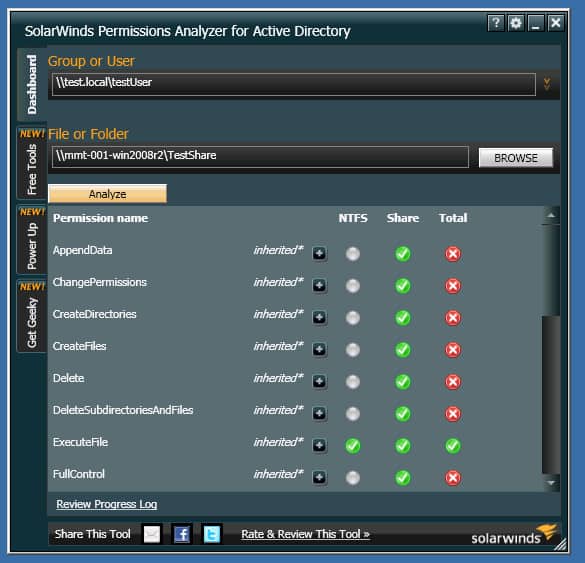
Key Features:
- Permissions Inheritance Visualization: Offers a clear mapping of how permissions are passed down through user and group hierarchies.
- Permissions Navigation: Simplifies the exploration of permissions assigned to users and groups across the network.
- Group Membership Insights: Analyzes and displays the permissions impact of group memberships, enhancing security oversight.
- Multi-Domain Management: Enables permissions analysis across multiple Active Directory domains, facilitating comprehensive coverage.
- Complimentary Access: Available without any cost, providing powerful tools for permissions management to organizations of all sizes.
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Permissions Analyzer is highly recommended for its robust capabilities in enhancing visibility and control over permissions within Active Directory environments. Its ability to swiftly analyze and display permissions structures makes it invaluable for security and compliance efforts.
Imagine an insider threat scenario where an employee gains excessive rights to key company resources and suddenly begins to carry out malicious activities from the inside. You observe that this employee has access to all sorts of key company groups, shared network folders, and files; but nobody is fully sure what and how much.
This could be a major security issue for your organization, so you need to get to the root of what’s going on quickly. One way to investigate this is to use PowerShell if you have the skill and experience to do it, but the reality is that not everyone does. That’s where SolarWinds Permissions Analyzer comes into play. With this tool, network admins can easily identify which members of their team have access privileges to sensitive data.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is particularly beneficial for network administrators and IT security professionals managing medium to large-scale Active Directory environments, who need to regularly audit and oversee permissions to prevent insider threats and ensure compliance.
Pros:
- Enhanced Permissions Insight: Delivers detailed visibility into the Active Directory permissions architecture, aiding in effective management.
- Inherited Permissions Clarity: Visualizes how permissions are inherited, making it easier to understand and manage access rights.
- Continuous Monitoring Capability: Supports ongoing surveillance of account and permissions changes, crucial for security and compliance.
- Inside Threat Detection: Ideal for identifying potential internal security risks and unauthorized access attempts, and safeguarding sensitive information.
- Cost-Effective Solution: Being free, it offers a significant value for comprehensive permissions analysis and management without financial investment.
Cons:
- Optimized for Large Environments: Primarily designed to serve the complexities of larger Active Directory setups, which may limit its utility for smaller organizations.
Best of all, SolarWinds Permissions Analyzer is available for download free of charge.
4. Quest Recovery Manager for Active Directory
Human error, hardware, and software crashes do occur. AD objects can often be mistakenly modified or even deleted; and faulty scripts can overwrite attributes. This can result in a corrupt Active Directory or Group Policy data, unplanned system downtime.
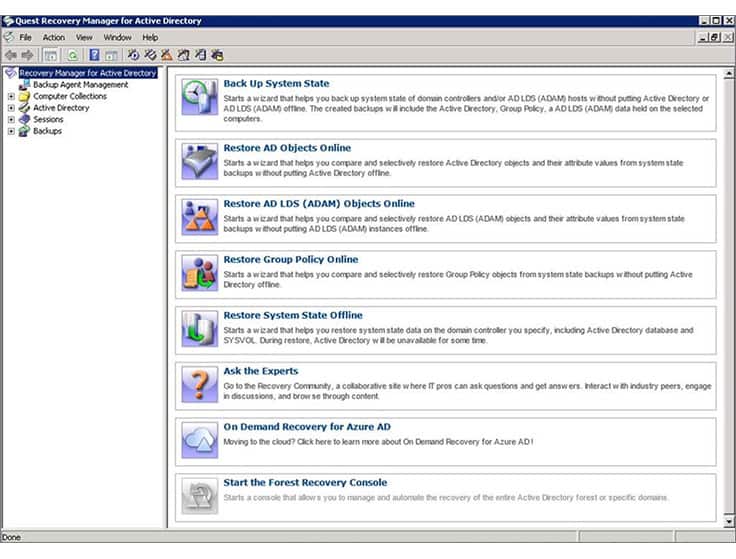 Recovery for Active Directory is a third-party AD tool that enables network admins to pinpoint changes to their AD environment at the object and attribute level, and quickly recover entire sections of the directory (both on-premise AD and Azure AD), selected objects, or individual attributes without taking the AD controller offline. In reality, when an object is lost in Active Directory you have to restart the Domain Controller to recover it. Recovery Manager for Active Directory eliminates this inconvenience by allowing you to recover objects without going offline.
Recovery for Active Directory is a third-party AD tool that enables network admins to pinpoint changes to their AD environment at the object and attribute level, and quickly recover entire sections of the directory (both on-premise AD and Azure AD), selected objects, or individual attributes without taking the AD controller offline. In reality, when an object is lost in Active Directory you have to restart the Domain Controller to recover it. Recovery Manager for Active Directory eliminates this inconvenience by allowing you to recover objects without going offline.
Key Features:
- Live Restoration: Enables swift recovery of AD data without service interruption.
- Precision Recovery: Allows detailed restoration of specific AD objects and attributes.
- Scheduled Backups: Automates backup processes, safeguarding against data loss.
Why do we recommend it?
Quest Recovery Manager for Active Directory is highly recommended for its ability to perform live restorations and object-level recoveries without taking the system offline. This capability is crucial for maintaining continuous operation and avoiding downtime in critical environments.
Systems are primed for recovery by automated background backups. You don’t need to take your AD instances offline either to back them up or to recover them. Any object type can be recovered: organizational units, sites, groups, users, or computers. Any type of data can be restored, such as group policy objects (GPOs), object attributes, or system configurations.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideally suited for network administrators who need a reliable solution for recovering Active Directory objects and attributes. It is particularly valuable in large, complex networks where detailed sorting and filtering capabilities can significantly streamline management tasks.
Pros:
- Resource-Efficient: Functions smoothly in resource-restricted and older environments.
- Management Efficiency: Supports automated backups and centralized domain control.
- Enhanced Organization: Offers extensive sorting and filtering capabilities for large setups.
Cons:
- Dated UI: The graphical interface appears antiquated compared to alternatives.
The main issue with Recovery Manager for Active Directory is that it comes at a relatively high price. It is therefore most suitable for organizations running multiple AD domain controllers across multiple locations. A free 30-day trial is available.
Active Directory Security Groups FAQs
Why is Windows group policy important in Active Directory from an application security perspective?
Group policy lets you centralize account administration, which means fewer people are involved in controlling security. You can impose global corporate security policies instantly for all user accounts by grouping users. So, standardizing user account settings is quicker with a group policy.
How do I find out if an Active Directory security group is mail enabled?
Only security groups with Universal scope can be mail enabled. You can see whether a group is mail enabled by looking at the group’s properties. Right-click on the group and select Properties from the context menu. Open the General tab and if the Email address has a value in it, the group is mail-enabled.
How do I change an Active Directory security group owner?
You can have multiple owners for an Azure Active Directory security group so if you want to replace an owner, you just need to add a new owner and then remove the previous owner. The account that you want to make an owner much already be a member of the group.
- Log into the Azure Portal with the Administrator account and then open Active Directory.
- Select Groups and then click on the group that you want to change the owner for.
- In the menu list to the left of the group overview, click on Owners.
- Click on Add owners, which will open an overlay panel.
- In the Add Owners panel, search for and then select the user account that you want to promote. Click on the Select button.
- Refresh the main group page.
- Click on Owners again. In the Owners screen, click on the owner that you want to remove. Click on the Remove button at the top of the screen.
- Confirm the removal by clicking Yes in the popup dialog box.
What security group can only read from Active Directory?
There is a pre-created user group that only allows the members to read Active Directory and not make any changes. This is the Windows Admin Center Readers group. You just need to add users to this group.