
The internet has sparked numerous technological revolutions, leading to innovations like smartphones and Wikipedia. The “Internet of Things” (IoT) is a recent advancement among these. IoT refers to interconnected devices that gather information, often automating processes and enhancing user experiences. This includes smart home devices like Google Home and Amazon’s Echo, smart refrigerators, hospital equipment, and various sensors monitoring public services.
In essence, IoT aims to connect virtually everything to the internet. Cisco defines IoT as “the point in time when more “things or objects,” are connected than people, a milestone they say was reached around 2008-2009. The field has grown significantly over a decade into the IoT era, especially with more devices connected to the web than people (over 4.95 billion web users as of January 2022), leading to a wealth of intriguing data and statistics.
IoT at a glance
Considering IoT is primarily about the number of devices connected to the internet, these stats demonstrate how large the Internet of Things has grown.
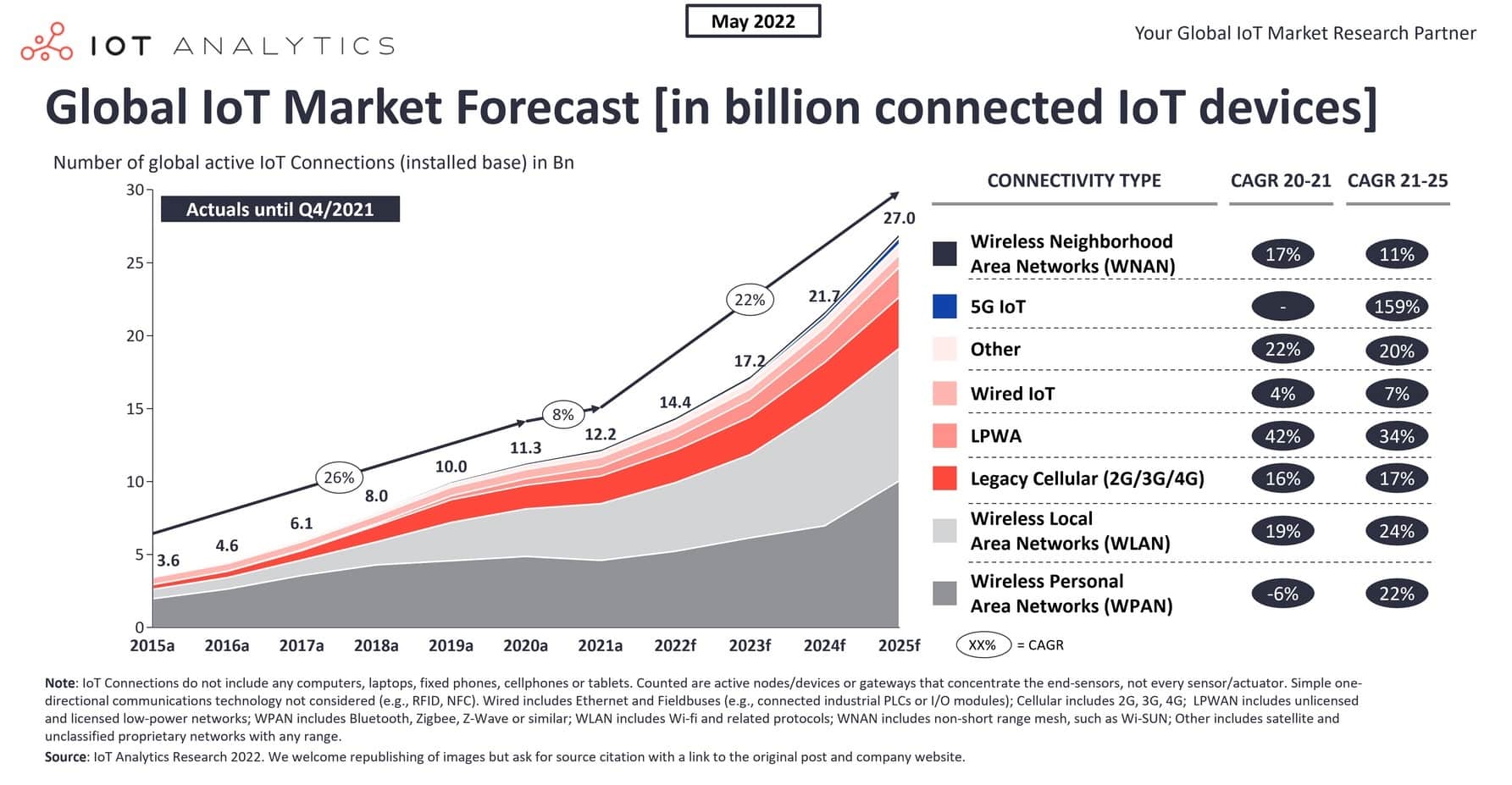
- As of 2023, guess what? According to IoT Analytics, there are about 16.7 billion IoT devices worldwide. That’s a huge jump from the 12 billion devices we had in 2021. A big part of this growth is thanks to some cool tech advancements like Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Cellular IoT (including the fancy 5G), and the coming together of LPWAN technologies. These tech upgrades are making IoT gadgets easier to use and super efficient in various ways.
- IOT Analkytics also estimates that there’ll be over 27 billion such devices by 2025.
- A large majority of the IoT is made up of smartphones. In fact, the total number of unique smartphone users was around 5.3 billion in Q4 2023. (Source: DataReportal)
- Ericsson predicts that smartphones will account for 9.2 billion internet-connected devices by 2029. Of these, just under half will be using 5G connections.(Source: Ericsson Mobility Report)
- The global IoT market grew to $662.21 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to around $3.3 trillion by 2030. (Source: Fortune Business Insights)
- Smart home devices are and will continue to be a major component of IoT. 857 million smart home devices were shipped in 2022, which was actually a slight decrease since the previous year. These are predicted to account for 1.09 billion devices by 2027. (Source: International Data Corporation)
- Around 69% of US households own at least one smart home device, with roughly 15 percent of the world expected to by the end of 2023. (Source: Smart Homes Global Market Report 2023)
- In 2023, video entertainment systems (such as Smart TVs) were the most popular IoT device, with an estimated 32.5 percent of the market. Conversely, smart thermostats accounted for just under three percent. (Source: International Data Corporation)
- “Smart cities” are a major and emerging concept in IoT. In 2018, over one-fifth of all publicly announced IoT projects involve IoT-driven “smart cities” of some kind, with most of these “smart cities” (43 percent) announced in North America. (Source: IoT Analytics)
- In 2020, security experts ranked IoT as their top concern for the next few years (Source: Gartner)
- The need for data science specialists is expected to grow far beyond the number of specialists on the market, thanks in no small part to IoT. In 2020, 18% of IoT solution providers and enterprise users said that 18% of IoT projects were not successful at all, while 40% stated they were mostly unsuccessful (Source: IoT Now)
- As of 2023, there are more than two internet-connected devices for every human on the planet. (Source: IoT Analytics)
Healthcare IoT stats
The healthcare industry has been a rapid adopter of IoT technology. This comes with many advantages and many risks. But the overall size and complexity of the market is a perfect example of the transformative power of IoT in a single, important industry.
13. The healthcare IoT market is expected to be worth $534.3 billion by 2025. (Source: Grand View Research, Inc.)
14. North America was the largest buyer of IoT devices in healthcare, accounting for a third of the entire global market. The main obstacles to adoption include high initial costs, limited supporting infrastructure, and the security issues posed by IoT systems. (Source: Market US)
15. The EU had around 870,000 active healthcare IoT devices in 2016 and 6.8 million in 2021. ETNO expects there to be almost 17 million healthcare IoT connections in Europe by 2030. (Source: ETNO)

17. In 2017, Allure became the first skilled nursing facility to implement EarlySense, a remote monitoring system that tracks patients’ vital signs. This led to a dramatic 80 percent reduction in “code blue” or emergency events within six months. (Source: Allure Group)
18. 80 percent of healthcare business executives see increased innovation as the biggest advantage of IoT implementation. 73 percent pointed to cost savings, while 76 percent pointed to “visibility across the organization” as key advantages. (Source: Aruba)
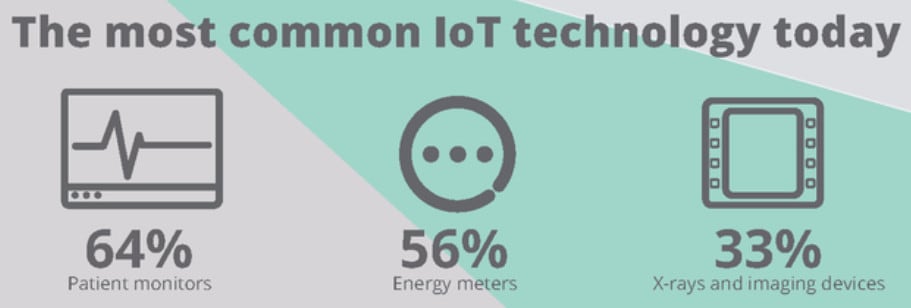
19. The most common healthcare IoT devices are vitals monitors, followed by imaging systems, respiratory devices, and implantable cardiac devices. (Precedence Research)
20. Over 70 percent of healthcare organizations that use IoT devices utilize them for monitoring and maintenance. (Source: IEEE)
21. 50 percent of healthcare IoT is used for remote operation and control, and 47 percent connect their devices to location-based services. (Source: Aruba)
22. Security breaches are a significant drawback to IoT. In 2023 alone, there were over 700 breaches that resulted in the release of 500 or more patient records. (HIPAA Journal)
23. Generally, IoT compromises happen in one of two ways: password compromise or vulnerability exploits. In the first half of 2023, nearly 98 percent of password brute-force attempts took place via Telnet. (Source: Securelist)
24. The health industry is responsible for 6 percent of global IoT projects, with 55 percent of those occurring in the Americas. (Source: IoT Analytics)
25. According to Scand, IoT devices can save healthcare companies a combined $100 billion per year by reducing inefficiencies. (Source: Scand)
26. Palo Alto Networks reports that 83% of medical imaging devices run on devices with unsupported operating systems. This figure is worrying due to the security implications of using older platforms.
Perhaps more concerning, HealthTech reports that 82 percent of healthcare professionals claim some of the organization’s devices use outdated versions of Windows. Medical imaging devices should be running on Windows 10 operating systems or later to keep up with the latest malware threats and patch OS vulnerabilities
Industrial, energy, and construction IoT stats
The manufacturing and industrial sectors are early and fast adopters of IoT technology, a trend currently known as Industry 4.0. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has a heavy focus not on people using machines, but on machine automation with minimal human input thanks to robotics.
IoT is set to allow robots to operate more intelligently in the industrial sector, with a move toward greater efficiency and cost savings. Human operated machinery is decreasing in the manufacturing and industrial sector, making automated IoT that requires a decreasing level of human input a large focus.
Meanwhile, construction is experiencing a bit of a slow adoption with new technologies such as IoT. Although technically part of the industrial sector, construction maintains a set of technological needs that set it apart, even as it shares a lot of the same technical challenges as the wider industrial sector.
There’s a lot of attention on how IoT can be used to improve worker safety in construction, which many workers and industry observers openly welcome. Given the construction industry is among the most dangerous for workers, IoT can help make it safer than ever before, so long as businesses in construction are willing to spend the money to make it happen.
27. Industrial manufacturing companies are the biggest investor in digital factory factory transformation, spending $318 billion per year. (Source: PwC)
28. China uses more industrial robots (many of which are internet-connected in some way) than anyone else in the world. In fact, it’s more it has more than doubled its number of industrial robot installations since 2019. (Source: IFR)
29. Asia and Australia are the biggest markets for industrial robots but the EU is another top contender. The US is the largest regional market, but has shown muted growth in recent years in most industries except automotive. (Source: IFR)
30. In 2022 alone, more than half a million new industrial robots were installed globally. This technology has seen consistent growth in all markets since 2012, though adoption in the Americas remains low compared to the rest of the world. (Source: IFR)
31. Manufacturers account for about 40 percent of all private 4G and 5G networks (Source: Mordor Intelligence)
32. Industrial data analytics may cause a few headaches along the way. Research has shown that the biggest issue us data quality management, followed by data security. (Li, Chen, and Shang, 2022)
33. The automotive industry accounted for over 80 million IoT devices in 2021, making it the biggest adopter by far. (Source: ETNO)
34. Germany is one of the top five global adopters of digital factories and accounts for 36 percent of the EU’s market share singlehandedly. (Source: IFR)
35. The manufacturing industry poured $237.59 billion into IoT in 2021 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8%. (Source: GlobeNewswire)
36. Industry 4.0 spending is expected to increase to $276 billion by 2029. (Source: Research and Markets)
37. Notably, there are 6 supporting technologies to pay attention to in Industrial IoT: Additive manufacturing (3D printing), augmented and virtual reality, collaborative robots, connected machine vision, drones / UAVs, and self-driving vehicles). (Source: IoT Analytics)
38. Contractors are much more likely to invest heavily in emerging technology than business owners. This is important given that “adoption of technology” was cited as one of the top factors that helps companies deal with disruption. (Source: KPMG)
39. In 2019, most construction CIOs believed that machine learning and AI would become commonplace in the next five years. However, in 2021, just 16 percent thought it’d be the biggest return on investment. (Source: KPMG)
40. 84 percent of construction business operators planned to invest a moderate or high amount in technology in 2022, with the remainder either unsure of their budget or planning a low spend. (Source: KPMG)
41. 45 percent of companies expected Integrated PMIs to offer the biggest return on investment. In second place was Building Information Modeling, and in third, use of advanced data analytics. (Source: KPMG)
42. In 2021, 81% of construction companies said they were planning to introduce robotic automation into their operations during the coming decade, partly in response to a growing skills crisis being experienced by 91% of them. (Source: ABB Robotics)
43. Construction IoT has the potential to vastly reduce various accidents, including backover accidents, by using RFID technology to deliver proximity warnings. (Source: Kanan, Elhassan, & Bensalem, 2017)
44. Other areas where IoT is making headway into construction include wearables to monitor worker heart-rate and temperature, concrete curing, sensors to monitor fuel consumption and vehicle wear and tear, RFID for inventory management, and GPS for equipment and personnel location tracking. (Source: Tech Bullion)
45. Research indicates that data privacy, interoperability, and flexible governance structures were among the most important factors for a company embracing IoT devices. (Source: Ghosh, Edwards, & M. Reza Hosseinim, 2020)
46. Industrial IoT makes up 17 percent of all global IoT projects. (Source: IoT Analytics)
47. Commercial drones are a major tool in industrial IoT. Over 40 percent of commercial drones are used for industrial inspection. (Source: Verizon)
Agriculture IoT stats
IoT is ripe for growth in the agriculture sector, which is indeed already rapidly adopting IoT solutions where possible. Agriculture has always been quick to adopt new technologies that make every aspect of the industry faster and more efficient, as profit margins for both large and small-scale farms can be thin and driven by sometimes unpredictable markets.
48. Precision agriculture—a form of agriculture that uses technology to make every aspect of the agriculture process as streamlined and efficient as possible— was valued at 10.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 12.8% until 2030. (Source: Grand View Research)
49. The global agriculture sensor market size was valued at $1.34 billion in 2020 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 13.6% from 2021 to 2028. (Source: Grand View Research)
50. According to the USDA, in 2019, guidance systems (e.g., GPS) had the highest rate of adoption across the agriculture industry, and in 2019, were used on between 45 and 65 percent or more of planted crop acres. (Source: USDA)
51. Farmers are also using GPS for soil mapping and variable-rate technologies (which allow farmers to vary crop inputs based on growing conditions) at a rate of around 20 percent per planted acre. (Source: USDA)
52. Most guidance systems are used for corn, with almost 70 percent of this crop planted and grown using this technology. (Source: USDA)
53. Around 35 percent of planted corn in the US is monitored with yield mapping technology, which uses GPS to map crop yields and moisture levels. (Source: USDA)
54. Automated guidance and steering systems are extremely popular for many planted crops, with over 50 percent of rice acres being planted, fertilized and harvested in the US using this technology. (Source: USDA)
55. According to IoT Analytics, Smart Agriculture accounts for just 4 percent of all global IoT projects, with nearly 40 percent of those Smart Ag. projects occurring within the Americas. (Source: IoT Analytics)
56. As of 2021, 18 percent of rural farms in the US lacked internet connectivity, down from 25 percent in 2019. This lack of connection makes most farming IoT solutions difficult to implement. (Source: USDA Farm Computer Usage and Ownership)
57. The “Smart agriculture” or “smart farming” market is predicted to be worth $25.4 billion by 2028 as farmers worldwide seek to utilize RFID, GPS, drones, sensors, and more to gather actionable data and to automate every part of the process.
IoT development
IoT takes developers, and many organizations are now rolling out IoT development, both in house and using dedicated software development companies. One of the biggest focuses in IoT development is security, as developers look to not only implement stronger security measures in IoT but also to increase IoT solutions for security purposes.
58. IoT developers are primarily concerned with connectivity (52 percent), while security sits at 33 percent. Deployment and Data Collection are tied for third place, with 25 percent each. (Source: Eclipse Foundation)
59. Most IoT developers are working on developing industrial automation systems (33 percent). Smart agriculture systems (29 percent), and building automation (24%) are other major focus areas. However, public safety systems account for just seven percent of all projects. (Source: Eclipse Foundation)
60. Development in education IoT is a growing area of interest as well, as school systems look to implement IoT as part of the teaching process. (Source: Eclipse Foundation)
61. Excluding Linux, the top two IoT operating system landscapes include Windows and Android. (Source: Eclipse Foundation)
62. For devices, the top IoT operating systems include FreeRTOS, Linux, and Zephyr. (Source: Eclipse Foundation)
63. Linux is by the top Edge/Gateway operating system for IoT, comprising 58 percent of all gateways and edge nodes. However, in 2020, it accounted for over 70%, indicating that developers are open to alternatives like FreeRTOS. (Source: Eclipse Foundation)
64. Amazon Web Services (AWS) dominates the IoT market, with 41 percent of IoT developers utilizing AWS. A further 27 percent use Microsoft Azure, while just 20 percent use Google Cloud Platform (GCP). (Source: Eclipse Foundation)
65. For programmers in IoT, C is a popular language for constrained devices, while Java is the most popular for gateway and edge nodes, as well as IoT cloud applications. (Source: Eclipse Foundation)
66. Most IoT developers use Eclipse Desktop IDE (38 percent), while 35 percent use Visual Studio Code. (Source: Eclipse Foundation)
67. The two connectivity protocol used by IoT devices is 5G (44 percent) with Wifi and Ethernet tied at 38 percent. Meanwhile, while Bluetooth has dropped to just 23 percent. (Source: Eclipse Foundation)
68. 70 percent of IoT developers say that software supply chain security is important, with 36 percent saying it’s “extremely important”. Worryingly, 10 percent of those surveyed replied “what is software supply chain security?”. (Source: Eclipse Foundation)
69. IoT devices can experience their first hacking attempt just minutes aftert being connected to the internet. The improved efficiency of IoT cyberattacks is likely a result of the increased popularity of smart devices.
FAQs about IoTs
What are some examples of IoT devices?
IoT devices span many products, from traditional consumer electronics to industrial systems. Examples of popular IoT devices include:
- Smart TVs that can stream media content and be controlled remotely
- Smart speakers like Amazon Echo or Google Home
- Connected home appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, and more
- Automated surveillance systems for homes and businesses
- Autonomous vehicles such as cars, buses, drones, etc.
- Agricultural sensors used to monitor the quality of crops
- Industrial robots used in factories for automation purposes
- Medical implants that can collect data on patient health
- Smart lighting systems can be programmed to turn on and off at specific times or when motion is detected.
These are just a few examples of the many IoT devices rapidly becoming part of our lives. As technology advances, more everyday items will become connected to the internet, allowing us to control them remotely and collect data for analysis. By connecting physical objects to the digital world, we’re creating an ever-expanding universe of interconnected devices that can work together to provide greater convenience and insights into our day-to-day lives.
What are the main security challenges associated with IoT devices?
As we rely more and more on IoT devices in our daily lives, it’s essential to be aware of the unique security challenges they can pose. Some of these challenges include weak security measures, lack of regular updates, and vulnerable authentication and access control. It’s also important to remember that IoT devices often collect and transmit sensitive data, which can be intercepted or compromised if not properly secured. Since these devices are interconnected, a security issue in one device can potentially impact the entire network, causing even more problems. Unfortunately, there are no universal security standards in the IoT industry, which can make it tricky to ensure consistent security practices across devices and ecosystems.
See also:




