Today, businesses of all sizes must be prepared for the worst. Hacking is at an all time high. The threat of ransomware attacks, trojans, and other exploits must be taken very seriously.
If you are a business owner or manager, we hope the data loss statistics listed below will serve as a reminder of why it is important to have strong cybersecurity and data recovery systems in place.
1. Security budget adequacy
In 2023, many businesses faced budgetary pressures, with over one-third of CISOs reporting flat or shrinking cybersecurity budgets. Despite this, the average cybersecurity budget grew by 6%, a decrease from the previous year’s 17% growth. Cybersecurity accounted for about 11.6% of total IT spending, showing an upward trend from 8.6% in 2020. For 2024, around 79% of organizations plan to increase their cybersecurity budgets, but only a tiny fraction expect a significant hike of at least 15%. This data, sourced from reports by TechTarget and IANS Research, reflects the ongoing challenge organizations face in balancing security needs with budget constraints.
2. 2 of 3 midsize businesses suffered Ransomware attack in past 18 months
According to the latest 2022 MSP Threat Report by ConnectWise, two out of three midsize businesses have suffered a ransomware attack in the last 18 months. This reveals the almost epidemic level that ransomware attacks have reached in the wild. What’s more, the study reveals that the size, severity, and cost of those attacks is increasing year on year.
With this in mind, high-quality backup systems that allow a business to regain access to their data and to get their systems up and running again is essential to avoid delays and a potential hit to share prices or profits.
3. 33% of folders are not protected in any way
According to the 2021 Global Data Risk Report by Varonis, on average, 33 percent of all folders used by a company are open to everyone. Don’t think that’s a problem? Put it this way: 64% of your employees have access to 1,000 or more sensitive files. In other words, there’s a solid chance that your intern can accidentally create, update, and delete vital documents without you knowing.
This is a sharp increase from the 2019 report, which found just 22% of files accessible by anyone.
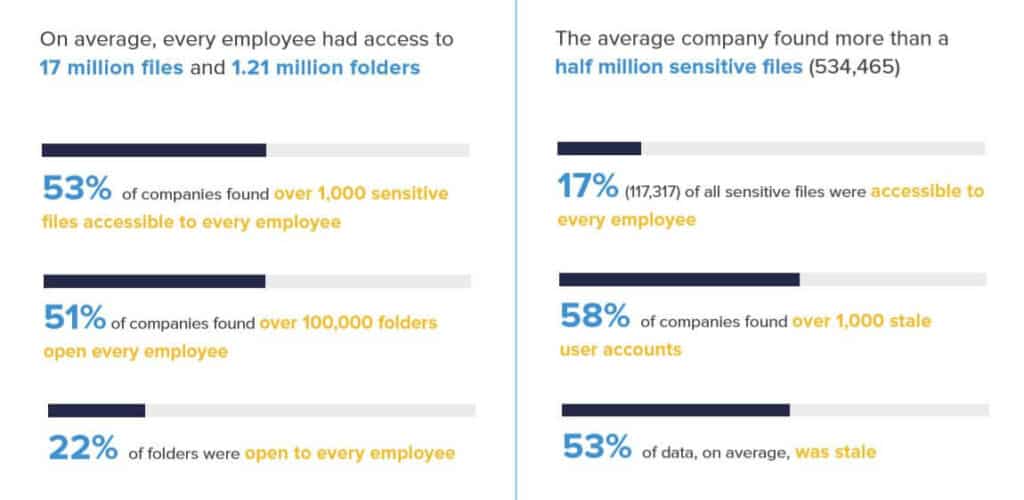
Attackers look for unsecured folders such as these. Files that are open to anyone can provide easy access to sensitive information, putting organizations at risk.
4. 28% of data breaches involve malware
Causes for data loss range from human error to physical theft. However, according to Verizon’s 2021 Data Breach Investigations Report, malware was involved in some 15 percent of data breaches, down from 17 percent the year prior (note that in the graphic below, malware attacks are included in the “System intrusion category”).
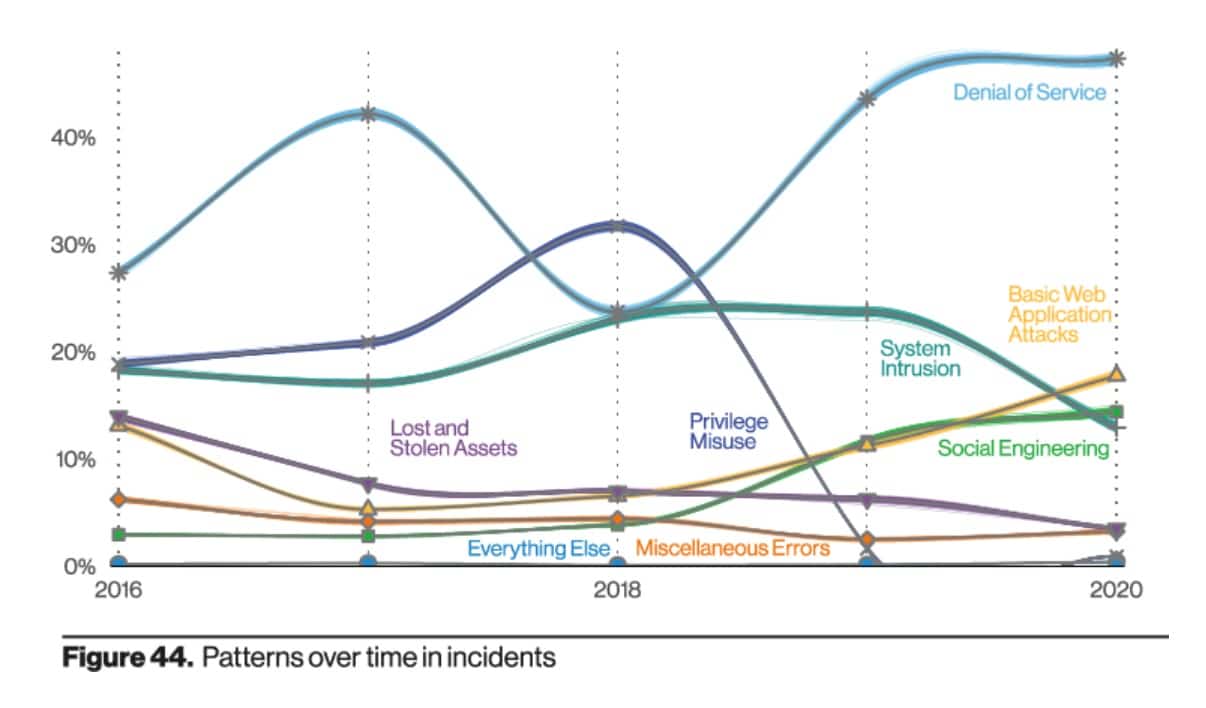
The number of mobile malware infections may have decreased year on year but needless to say, it’s important to use quality, up-to-date antivirus software to help prevent data loss caused by malware.
5. 82% of breaches involve human error
According to the 2022 Verizon Data Breach Incident Report, 82% of breaches are caused by attack vectors that involve human error. This includes, social engineering attacks, phishing, spear phishing, errors, and misuse/transgressions.
This is a reminder of how important it is to engage in training and monitoring to ensure that employees in need of further education regarding cyber-threats are singled out.
It is also a reminder of the importance of hierarchical systems with access privileges. This ensures that employees only have access to the parts of the network they require, and that important data and systems are properly segregated so that attacks cannot easily move laterally through the company network.
6. 85% rise in dark web data dumps
According to the Palo Alto 2022 Unit 42 ransomware threat report businesses saw an 85% rise in incidents that involved employees having their names and personal data dumped publicly on the dark web. The security company explains that these data leaks are used to coerce victimized companies into paying up.
Along with the added pressure that hackers are putting on victims, Palo Alto noted a 144% increase in the average ransom demanded. This reveals that while attacks are are on the rise, the cost of those attacks is also increasing – making ransomware a serious problem for the massive number of companies being targeted.
7. An incident response team can drastically reduce the cost of a data breach
The Ponemon Institute’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2021 puts the average cost of a data breach at $4.24 million, with healthcare being the most costly industry ($9.23 million). The average time taken to identify and contain a data breach is a whopping 287 days.
As expected, the shorter the lifecycle of the breach, the better. A breach lasting under 200 days costs 30% less than one with a lifecycle longer than 200 days.

8. Hard drive failure rates remain (relatively) stable
As many of us have found to our cost, hard drives can and do fail. According to Backblaze, the average failure rate for hard drives in 2021 was 1.01%, a slight increase from 2020’s overall average of 0.93%.
You can protect yourself from losing data in such an event by having a reliable data backup solution. For many, this may entail having a backup hard drive in a physical off-site location or storing files on the cloud.
See also: Best data recovery software
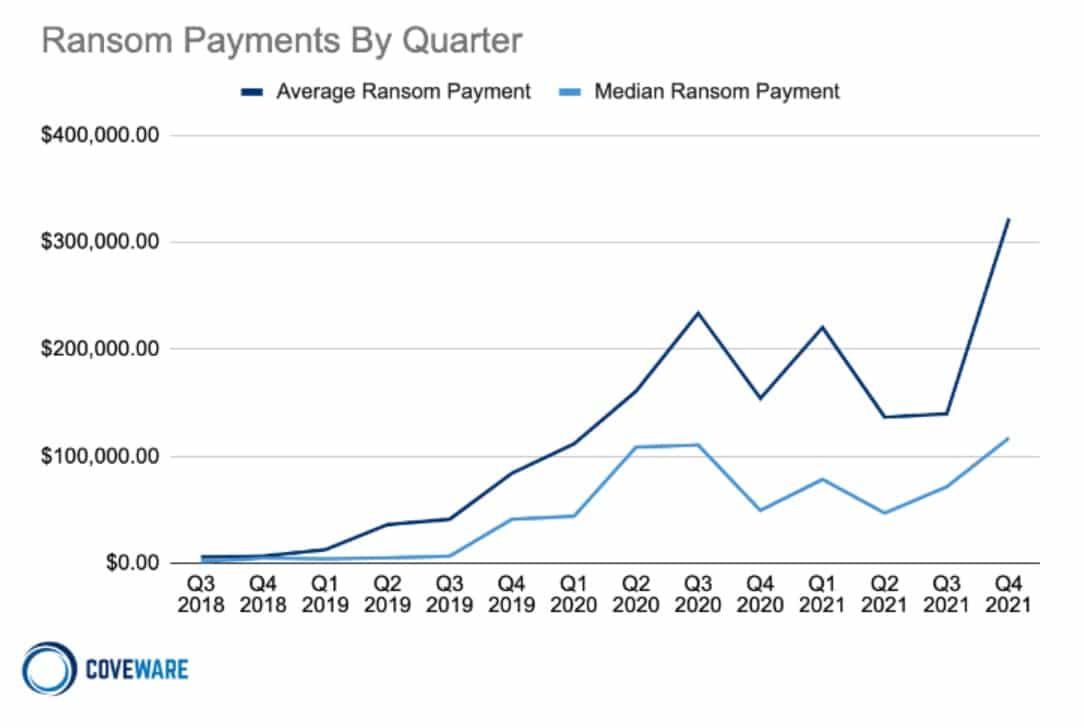
9. Ransomware attacks cause an average of 16.2 days of downtime
Ransomware makes files on the target system unreadable without a decryption key (held by the attacker). Typically, ransomware works by encrypting select files, then forcing the victim to pay up in order to decrypt them.
A 2021 Coveware study reported that the average downtime for businesses as a result of a ransomware attack was 20 days in Q4 2021. This was down 10% from Q3 2021 — a small but nonetheless welcome improvement.
Aside from suffering the costs of downtime, companies are having to fork over larger ransoms than ever before. After a period of stabilization in Q3 2021, the average price spiked again in Q4. The average ransomware payment more than doubled to $322,168 during this period.
10. 97% of data is recovered after a ransomware attack
It’s true that when you pay the fee demanded by ransomware, there’s no guarantee that you’ll receive a working decryption key. And even if you do get a key, you still may not recover all of your data. In fact, Sophos’ 2021 State of Ransomware Report found that, even after paying, only around 8 percent of victims recover all of their data. The average ransomware victim loses around 35 percent of their data.

Note that even if you manage to decrypt all of your files, there’s nothing to stop the criminal from maintaining copies. Information could be stored and used in subsequent crimes, for example, in fraud or spear-phishing attempts.
11. The average cost of downtime is $1,410 per minute
According to Veeam’s 2022 Data Protection Report, the average cost of downtime is $88,000 per hour or $1,467 per minute. Naturally, this figure is skewed by larger organizations reporting higher sums, but small and medium business are still significantly impacted.
12. Iran-nexus adversaries a growing threat to US and Israeli businesses
According to the 2022 CrowdStrike report, hackers working in Iran stepped up their operations targeting businesses in the US, Israel, the Middle East and North Africa.
According to the report, these attacks often involved the use of Ransomware with a “lock-and leak” attack method that uses data leaks as a way to coerce victims into paying.
Those methods involve the use of hacktivists and criminal hacking groups to create a veneer of deniability for state sponsored activities; often leveraging dedicated leak sites, social media, and messenger platforms to leak data via “actor-controlled personas or entities”.
13. 93% of small businesses store data or backups in the cloud
According to promising results from a Unitrends’ 2019 survey (PDF), 84 percent of all businesses store data or backups in the cloud, with a further eight percent planning to do so within the next year.
Small enterprises have a higher adoption rate of cloud technology, with 93 percent of companies using it. This is compared to 82 percent of mid-sized businesses and 81 percent of large businesses.
A follow-up report from 2021 found that the number of organizations that rely solely on cloud-based solutions is expected to rise 70% by 2023. Not a huge surprise given cloud backups offer a number of advantages including ease of access and affordability.
The caveat? According to the 2022 CrowdStrike Global Threat Report, state sponsored actors began “regularly targeting cloud service providers
to exploit trusted relationships and supply chain partnerships.”
14. 96% of businesses experienced an outage in a 3-year period
A 2019 LogicMonitor study reported that the huge majority (96 percent) of organizations have experienced at least one outage in the past three years and 95 percent had experienced at least one brownout.
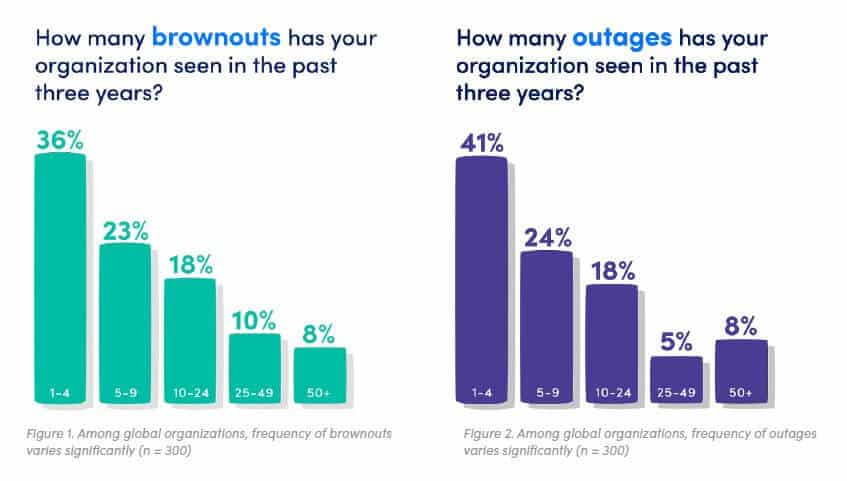
A large portion of companies (55 percent) experienced five or more outages during that period. The same report reveals that IT decision-makers believe that 51 percent of outages and 53 percent of brownouts are avoidable.
Of course, outages and brownouts have related costs, including lost revenue, compliance failure, and lost productivity. LogicMontor found that companies experiencing frequent outages or brownouts had 16 times higher costs than organizations that experience fewer such instances.
Tips for an effective disaster recovery plan
There are a number of things that your business can do in order to prevent and prepare for a disaster, whether natural or man-made.
Here’s how to make a disaster recovery plan:
- Back up data and send it to physical off-site locations. You may also wish to use cloud storage. Either way, backups should be made on a regular basis to ensure minimal disruption should you lose data in a disaster.
- Test your disaster recovery plan. Carrying out practice drills can help determine the overall effectiveness of the plan. This way, you can modify the plan if you find anything that doesn’t work in practice.
- Establish a disaster recovery team. The team should receive regular training on how to prepare for a variety of different situations. The disaster recovery plan should also be communicated to other key staff members, ensuring it’s understood.
- Maintain up-to-date contact information. Should a disaster occur when key staff members are out of the office, you may need their latest contact details for such an emergency. Contact details should be updated on a regular, periodic basis.
- Update your plan. As businesses change and technology develops, it’s important to regularly revisit your disaster recovery plan. Potential changes may involve a new antivirus software or cloud provider, for example.
Data loss and disaster recovery FAQs
What is disaster recovery?
Disaster recovery is a form of security planning that allows a business to maintain or recover infrastructure and systems following a disaster. With good planning, a business should be able to resume normal operations by regaining access to hardware, applications, and data. This is achieved through the use of a disaster recovery plan — a set of policies and procedures to follow in the event of a disaster.
The disaster that impacts a business may be anything from a natural event such as a flood or earthquake to one that is man-made, whether by human error, a device failure, or a cyberattack. Disaster recovery involves planning for a variety of possible circumstances, allowing businesses to reduce overall downtime and save time, money, and customer trust.
Related post: Best Data Loss Prevention Software Tools
How does disaster recovery work?
The disaster recovery process involves a lot of planning and testing. First, risk assessment and business impact analysis needs to be carried out. Security vulnerabilities must be identified in order to draft an effective disaster recovery plan. Even when a disaster recovery plan is created, it must be tested and revisited on a regular basis.
Naturally, plans differ based on the type of disaster they’re addressing, each offering varying immediate, intermediate, and long-term responses with specific responsibilities assigned to select staff members. Aside from offering corrective measures in the event of a disaster, a disaster recovery plan should also have preventive measures in place as well as detective measures that help discover events that may otherwise be missed.
What causes data loss?
You can’t get enough of data – well unless you’re talking about data loss. Accidental deletion, hardware failure, software glitches, viruses and malware, and natural disasters: these are just some of the many possible causes of data loss.
Accidental deletion is king when it comes to data loss – think one extra keystroke here or a wrong mouse click there. Now that the deed is done, your file is usually gone for good unless you have a backup! So it pays to be doubly cautious.
Hardware failure can also wreak havoc on our precious files. Don’t be too sure of its dependability because hard drives can fail before you know it. Don’t fall into the trap of assuming your files are safe forever – always have backups ready!
Software glitches aren’t new either – bugs in a program or software conflicting with each other can cause unexpected flaws that may result in data loss. Make sure to troubleshoot your programs regularly for possible issues.
Of course, who else could be responsible but malicious software like viruses and malware? Sometimes, they might even silently delete or corrupt your all-important files without you noticing it until it’s too late. That’s why having an antivirus and keeping all your software up to date is essential in protecting yourself against potential data loss due to malicious software attacks.
Natural disasters such as floods and fires are not just catastrophic events; they can also destroy physical hard drives, leading to data loss if precautions aren’t taken beforehand. So do consider having off-site backups stored away safely in case a major disaster happens unexpectedly.
Who is responsible for implementing a disaster recovery plan?
When it comes to safeguarding against data loss, having a well-crafted disaster recovery plan is an absolute must. Usually, a business’s IT or Operations department is responsible for developing and implementing such plans to minimize the risk of any data loss.
However, this should by no means be the limit. All employees should be made aware of the company’s disaster recovery plan and their respective roles in ensuring that it works out flawlessly when (or inevitably if) something goes wrong. This helps build resilience as every single staff member can chip in to aid with disaster preparedness.
For example, staff members should be given specific instructions on which procedures must be followed in case of a data breach or what steps they will need to take when there is an unexpected glitch or system failure leading to potential data loss. In addition, everyone should know how to correctly log incident reports and how exactly backups are stored away safely at scheduled intervals. If such incidents happen, downtime can be kept to a minimum, and operations resumed quickly using the least disruption possible.
Having all employees familiar with not just the disaster recovery plan but also their own roles in executing it properly gives businesses more peace of mind knowing that their staff members are equipped with the right knowledge and skills to responsibly handle potential incidents related to data loss.
How often should a disaster recovery plan be tested?
An essential part of any successful disaster recovery plan is to ensure that it is regularly tested – at least once a year, with more frequent tests if there are marked changes to the company’s operations or IT infrastructure. This will help ensure that the plan is always up to date and effective in case an incident occurs.
It’s important to review your disaster recovery plan annually to ensure that it continues to meet the needs of your business and its respective stakeholders. During these reviews, have an experienced expert look for gaps that may have been overlooked or even new scenarios that weren’t included before. Any changes or additional points should also be properly documented and included in the official Disaster Recovery Plan document.
Beyond this, conduct regular testing of certain components of the disaster recovery plan; this usually involves simulating events such as data breaches or system failures in a controlled environment so that you can determine how your staff members would respond when faced with such scenarios in real life. During these tests, it’s beneficial to record how staff members reacted during these incidents and note any blunders that could be potentially avoided if better preparations were made ahead of time.
Regularly testing your disaster recovery plan gives everyone involved peace of mind knowing that every possible precaution has been taken into account, and should an incident occur, they can rest assured that their data remains protected and secure while they handle the event accordingly.
Do regular users need to be concerned with disaster recovery, or is it the responsibility of the business owner?
Regular users need to be aware of disaster recovery plans, as it is in their best interests for the safety and security of the data and information they rely on. While it is ultimately the business owner’s responsibility to ensure that their organization has an up-to-date and well-crafted disaster recovery plan in place, there are certain steps that end users can take to help ensure that they remain prepared if anything goes wrong.
For instance, getting familiar with possible scenarios which could lead to potential data loss helps paint a clearer picture of how serious such incidents can be; understanding the importance of securely logging out of services or applications when not using them also helps reduce the risk associated with data breaches and other similar events. Additionally, regularly backing up your personal files ensures that should something happen, you have a backup version safe somewhere else.
It’s important to remember that disasters don’t always come in large waves – often, it is quite easy to overlook small but potentially hazardous scenarios which build up over time. Regular users being mindful and responsible with their accounts helps strengthen the overall resilience of businesses by having all parties constantly involved, vigilant, and taking whatever necessary precautions they can.
How does data loss impact customer trust and reputation?
It’s important to keep customer data safe and secure. When there’s a data breach and sensitive information is lost or exposed, customers can lose confidence in the organization’s ability to protect their personal data. This can lead to customers feeling uneasy about sharing their information with the affected company, which could ultimately result in a loss of loyalty and business. Data breaches can also create negative publicity that can hurt the organization’s reputation, making it harder to rebuild trust and attract new customers.