Have you ever accepted a permission requested by a website that you later regretted? Maybe you’re getting bombarded with notifications or feel uncomfortable about a website knowing your location. Although you can’t take back any data you’ve already handed over to a website, it is possible (and advisable) to revoke any unused or unnecessary website permissions granted on your browser.
In this article, I’ll show you how to find and remove site permissions on the desktop versions of Chrome, Safari, Edge, and Firefox. The mobile versions of these browsers will have similar options.
In most cases, permissions granted will remain in place until you revoke them. Revoking permissions helps to secure your privacy and prevent websites from collecting personal data that can be shared with third parties or used to identify you. It can also prevent annoying website notifications and certain cyber attacks.
Chrome
Here’s how to revoke website permissions in Google Chrome:
- Click the three dots in the top right corner and select Settings
- In the Privacy and Security section, select Site Settings
- Under the Recent activity section, click View permissions and data stored across sites
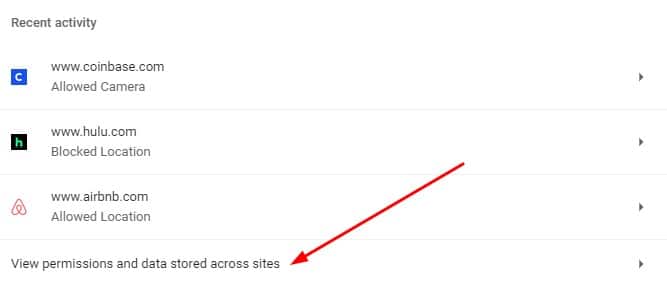
- Here you can change permissions across all sites visited or a specific site. We’ll do the latter. Find the website whose permission you want to revoke and click on it.
- You’ll see any subdomains housed under the site’s entry. You can revoke permissions for all of them, but the top one is usually the main site.
- You are now presented with a list of permissions for the site and their current settings. Adjust them how you wish. In the example below, I’ve disabled notifications from Facebook.
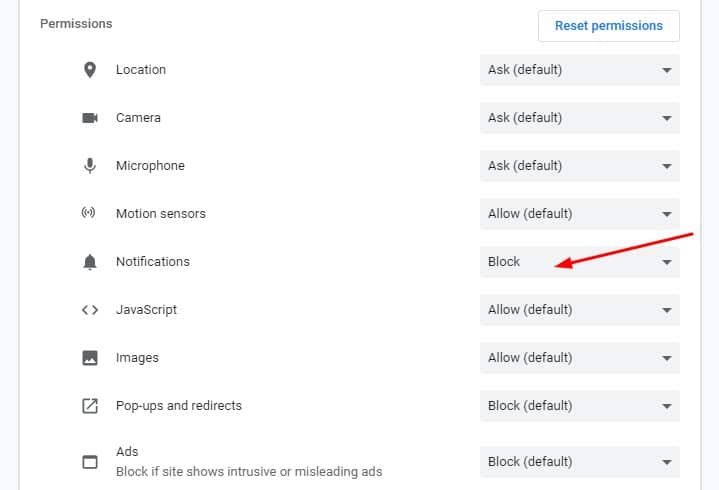
You can also click the “reset permissions” button to restore all of the permissions to their default settings.
Firefox
Here’s how to revoke website permissions in Mozilla Firefox:
- Open Firefox and click the three lines icon in the top right. Select Preferences.
- On the left sidebar, select Privacy & Security.
- Scroll down to Permissions. Click Settings… next to the permission you wish to adjust.
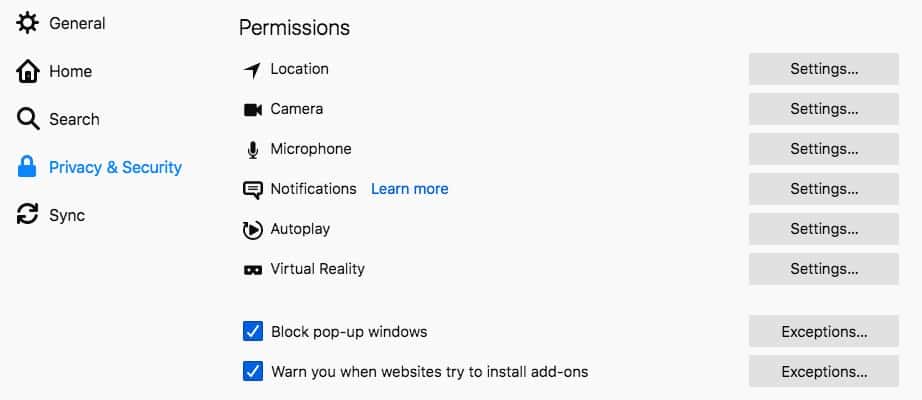
- A list of websites that you’ve set the given permission on will appear. Use the dropdown menu next to the site you want to restrict and set it to block to revoke the permission.
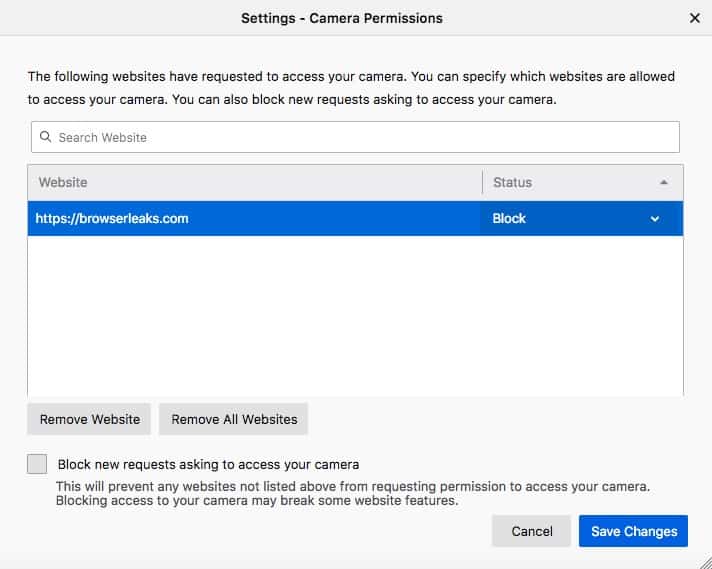
You can use the checkbox at the bottom to block all future requests for that permission. Removing websites will switch them back to the default setting, which is typically to ask the user when they next visit the site.
Safari
Safari’s permission settings are not as granular, nor are they centralized into a single menu, so you’ll need to make adjustments in a couple different places.
Here’s how to revoke website permission in Apple Safari:
- Open Safari and use the top bar to navigate to Safari > Preferences.
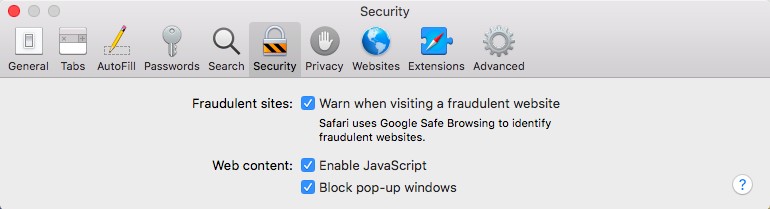
- Under the Security tab, you can enable or disable JavaScript and pop-ups. Note that these settings affect the entire browser and not specific sites.
- Under the Websites tab, you view what websites have access to each of the eight available permissions. Unfortunately, you can only view websites by permission, not permissions by website.
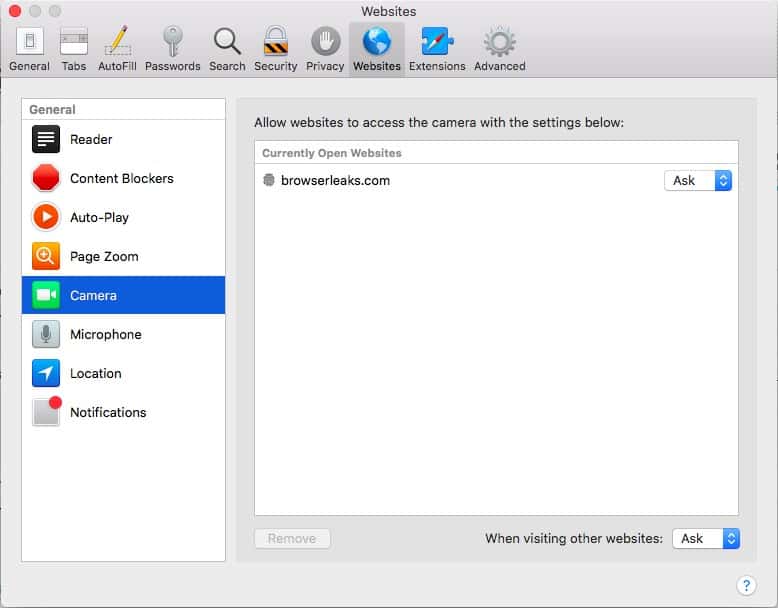
- By default, most permissions are set to Ask. Click the dropdown menu next to the site on which you want to change permissions. Select “Deny” to revoke that permission entirely.
Note that you can set the default permission for all other websites using the dropdown menu at the bottom.
Edge
Here’s how to revoke website permissions in Microsoft Edge:
- Click the three dots icon in the top right corner and select Settings.
- In the left sidebar, select Cookie and site permissions.
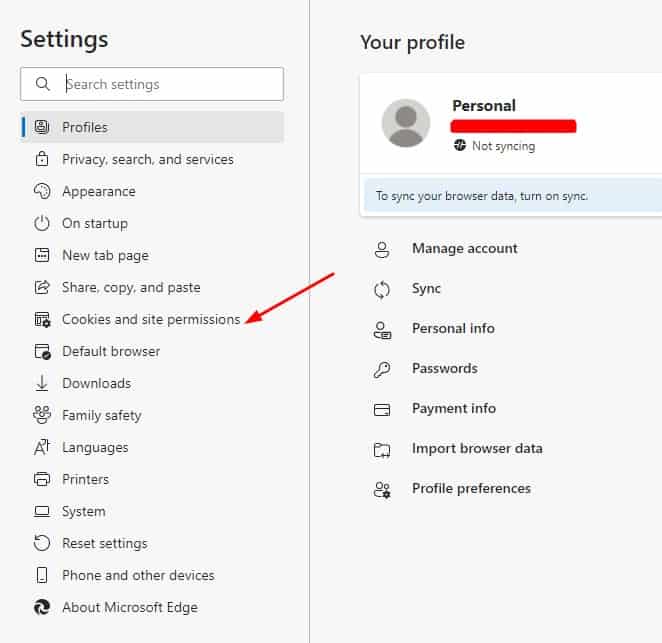
- Under Site permissions, click All sites.
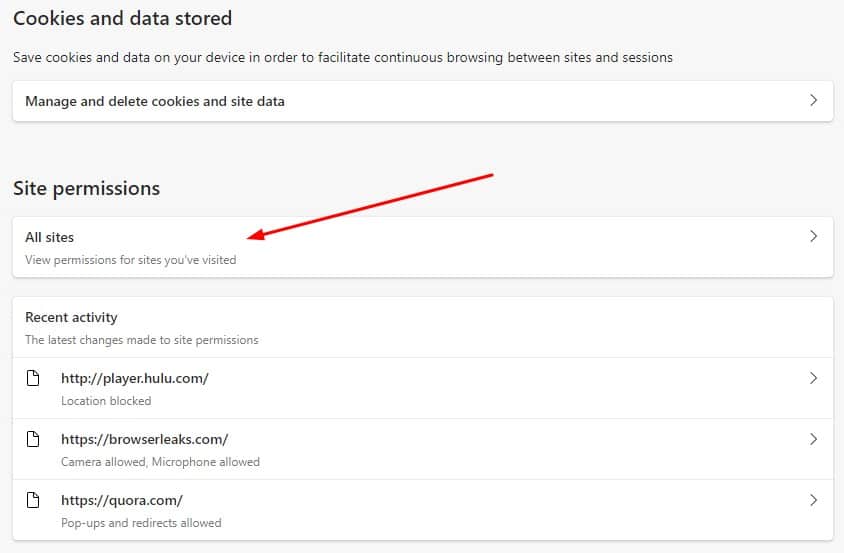
- Here you can adjust permission settings for all sites visited or a specific site. We’ll do the latter. Click the arrow next to the site for which you want to change permissions.
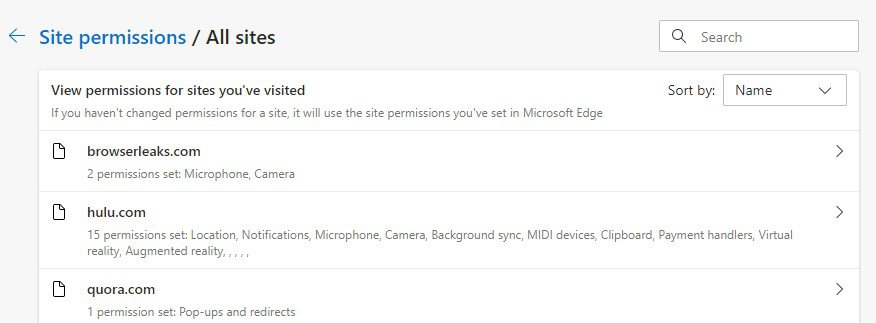
- You are presented with a list of all the permissions available to the site. Adjust them as you please. In this example, I’ve blocked JavaScript from running on Hulu.
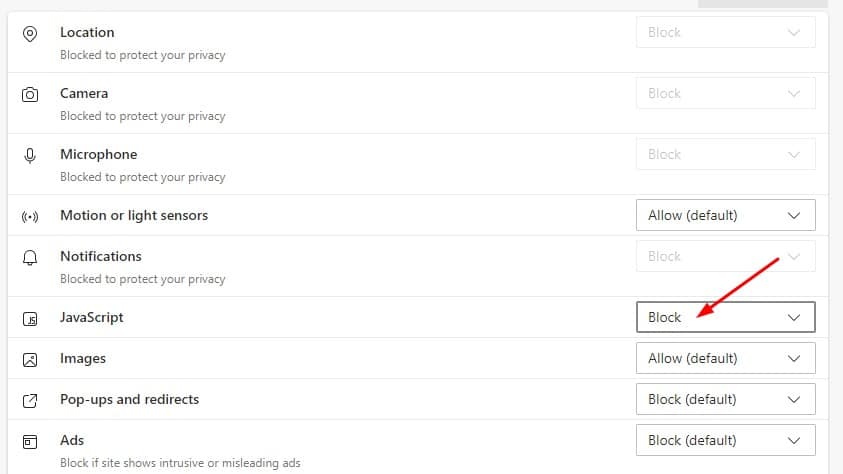
You can also click the Reset permissions button at the top to restore all of a site’s permissions to default.
Which website permissions should I revoke?
Here are a few of the more important permissions to consider revoking:
- Notifications – Probably the most requested permission on websites today. Block it to get rid of pesky website notifications
- Location – Tells websites where you are. This may be used to improve your experience using the site but, more often than not, location access is mostly used to serve you targeted adverts.
- Camera and microphone – You definitely don’t want websites to unnecessarily be able to record audio and video of you. This is particularly the case when using a VPN, as they can allow for WebRTC leaks. However, bear in mind that blocking these will reduce the functionality of some sites. For example, voice recognition on banking apps won’t work if you block audio recording.
- Ads – Advertisements aren’t just annoying to look at. They are usually fed into a website from a third-party source that wants to track you. Ads often place tracking cookies on browsers and the more malicious ones can launch attacks on your device. In practice, it’s easier to use an ad-blocker rather than revoking permissions on individual sites. You may want to accept adverts for your favorite sites as these normally fund their upkeep.
- Automatic downloads – A definite no-no if you want to keep your device malware-free
- Clipboard – Copying something with CTRL+C stores that content in your device’s clipboard. Allowing a website to copy text to your clipboard could open you up to clipboard hijacking attacks, or allow a site to spy on existing clipboard content
- Pop-ups and redirects – These introduce adverts and direct you towards more adverts and/ or malicious sites.
- Scripts (JavaScript) – This one is debatable. JavaScript is necessary for many websites to function, but is also used in a huge range of cyberattacks. If you don’t want to revoke it completely, consider using a script blocking browser extension like NoScript, ScriptSafe, or uBlock Origin. These will enable you to allow or deny scripts on an individual basis
- Motion Sensors – Allows sites to use your mobile device’s light and proximity sensors, as well as the accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer. These – together with other data – can be used for browser fingerprinting, which is a way of identifying unique browsers and tracking online activity. It’s a good idea to block access unless the site specifically needs motion sensors to function.
- MIDI and USB Devices – Be wary of allowing websites access to connected MIDI and USB devices. The last thing you want is an app spying on the contents of a connected hard drive or flash drive