A European Union digital COVID certificate serves as proof that the holder has been vaccinated against COVID-19, received a negative test result, or has recovered from COVID-19. The documents allow EU citizens and non-EU nationals to freely travel to other EU member states, and in some cases to access events or venues.
A desire to travel combined with vaccine avoidance among some EU residents and visitors has created a demand for fraudulent COVID certificates. That demand is being met by the dark web, where vendors sell vaccine certificates to individuals who wouldn’t otherwise qualify.
Comparitech researchers delved into several dark web marketplaces to find how much COVID certificates cost, who is supplying them, and how the scheme works.
COVID certificate prices on the dark web
The median price for a EU Digital COVID certificate on the dark web is US$109, with prices ranging from $75 to $600. Prices vary by vendor but are otherwise fairly consistent across countries and vaccine types.
How does it work?
Healthcare workers are the main source of fraudulent COVID certificates. Although national health authorities oversee the distribution of certificates, certificates are issued by staff at hospitals and test centers.

Every EU Digital COVID Certificate contains a QR code with an embedded digital signature to prevent falsification. Authorities can scan the QR code to ensure the signature is valid.
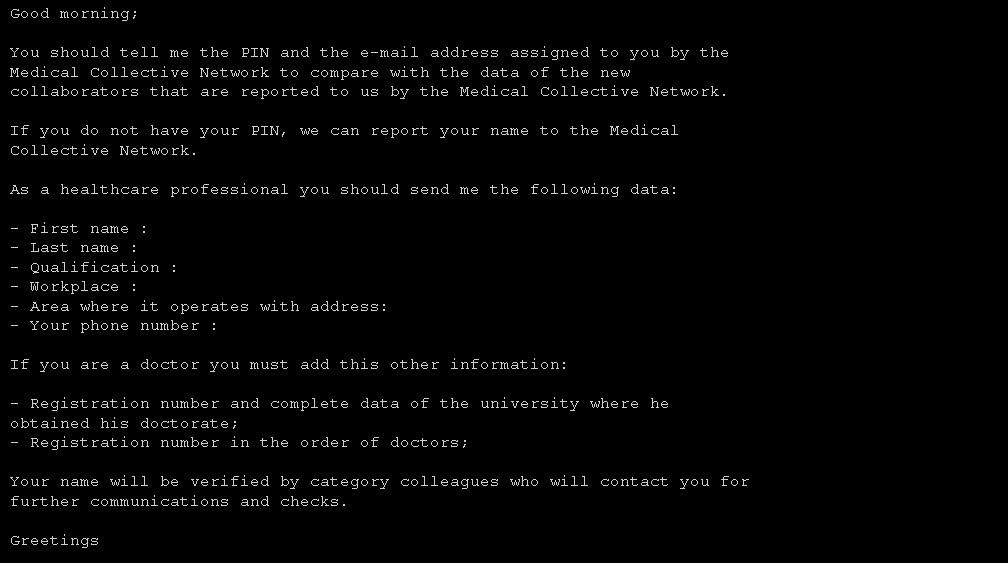
When someone buys a fraudulent certificate, they must first sign up for their country’s respective COVID vaccination database. They send their name, PIN number, and other necessary info to the vendor. A doctor or other healthcare worker marks that person’s record with confirmed vaccination. The buyer’s QR code then becomes valid. It takes just a few hours for the process to complete once a purchase is made.
Certificates were available on the dark web from the following federal programs:
- NHS (UK)
- TousAntiCovid Verif (France)
- Swiss Covid (Switzerland)
- Covid Free Gr (Greece)
- CovidSafeBE (Belgium)
- VerificaC19 (Italy)
- Irish HSE (Ireland)
- “Der grüne Pass” and ELGA (Austria)
- Diya (Ukraine)
- Check DCC (Romania)
- Green Pass (Slovakia)
- CDC VAMS (US)
- Australian Immunisation Register (Australia)
- SUS (Brazil)
- Gosuslugi.ru (Russia)
- Vaxicode Verif (Canada)
In one case, we found an advertisement recruiting doctors who can issue COVID certificates. In a text exchange with our researchers, the vendor explained that 75 percent of the profits go to the vaccinator (the person who administers the vaccine), 10 percent to the medical network, and 15 percent to the vendor.

In addition to full vaccination status, vendors on the dark web also sell negative COVID tests. The average price for these was $99. These can also be logged and verified in an EU digital certificate, but the validity only lasts 72 hours before travel is once again restricted.
Vaccines for sale
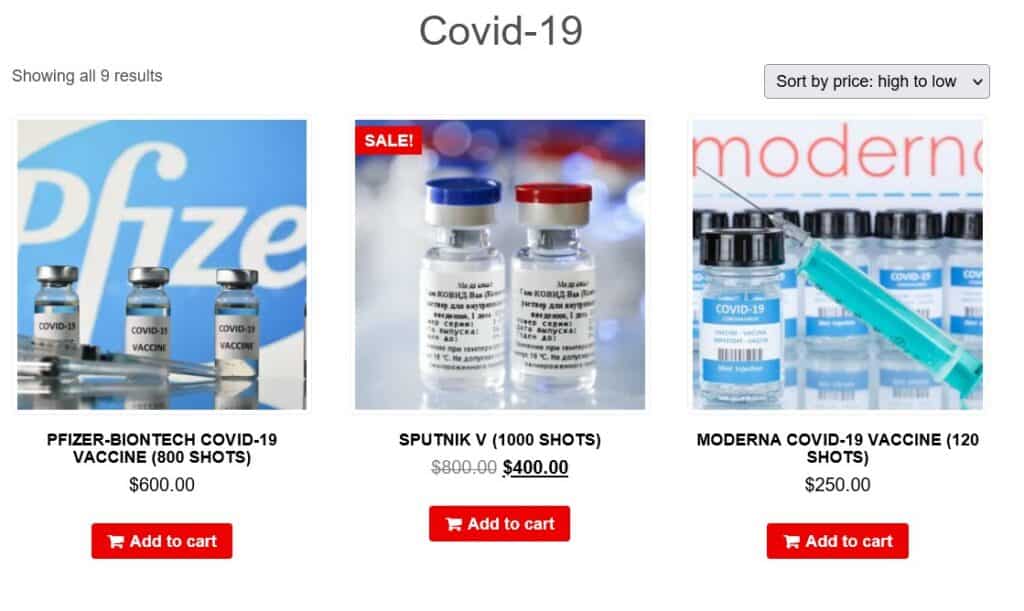
In addition to certificates, we also found actual vaccines for sale. We’re not certain where these doses came from, but one theory is that they’re sold by the same people selling fraudulent certificates.
Whenever someone buys a fraudulent COVID certificate, the vendor must record the specific dose and lot number for the vaccine used. That leaves vendors with leftover vaccine doses that are unaccounted for. This allows vendors to cash in on the leftover unused vaccines.
Comparitech researchers found listings on dark web marketplaces for up to 100,000 doses. You can see a price breakdown for different vaccines below:
Methodology
Comparitech researchers gathered listings from four different dark web marketplaces where EU COVID digital certificates were listed for sale. For each listing, we recorded the country of issuance, price, type of certificate, and vendor name.
In some cases, we directly communicated with vendors to learn more about the process.
We have elected not to share the names or URLs of vendors or marketplaces publicly, so as not to encourage fraud.
We did not make any purchases during the course of our research, so we cannot determine the legitimacy of listings. Some listings could be scams.