Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies are becoming more popular, especially since the shift to remote work during the Covid-19 pandemic.
The introduction of BYOD allows employees to use their personal devices such as smartphones, tablets, desktops, or laptops to access internal websites and systems typically only available via a work-issued device. While it may sound fantastic to use a device you prefer over some ancient relic your business may have issued, it has security, cost, and regulatory implications that may dissuade some companies from adopting such a policy.
To understand where BYOD is headed and the uptake over the past decade, check out some surprising and interesting BYOD statistics from 2018 and beyond.
1. Data leakage was the biggest concern about BYOD practices in 2020
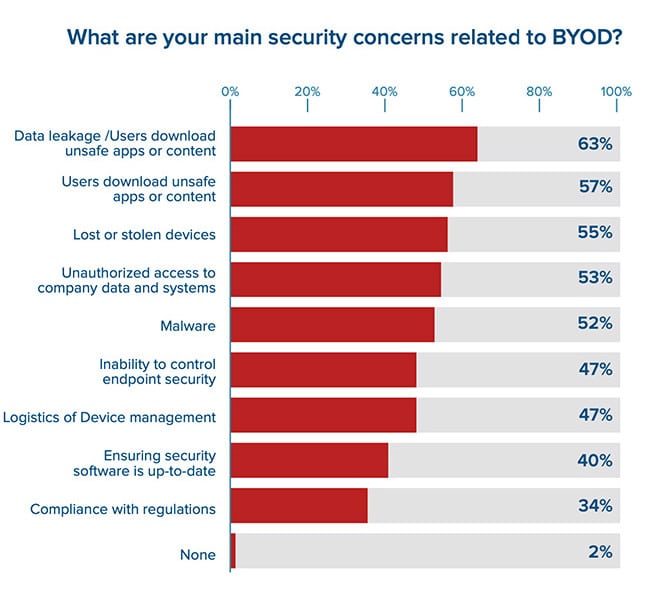
With the increase in remote working uptake due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Helpnet security reported that data leakage was the biggest concern among employees, with 63% of respondents highlighting it as the top concern. The next biggest problem was downloading unsafe apps or content, taking 57% of responses.
2. Most employees prefer separate devices for work and personal use
A report from Beyond Identity found that 80.7% of employees prefer to use a separate device for work (calls, computing, etc.) rather than a device for personal and business use combined.
3. Employers are more likely to select the brand of work-issued devices
Beyond Identity continued, with 63% of survey respondents stating that their employer selects the brand of device they use for work purposes. While this is the more obvious choice, allowing employees to choose their preferred make and model of the device they use at work is likely to be more productive than using a device they are less comfortable with.
4. Apple is the preferred BYOD brand
32.5% of employees surveyed said they would rather use Apple-branded devices than any other brand. This was closely followed by Dell and HP devices, with 17% and 14.% respectively, Beyond Identity found.
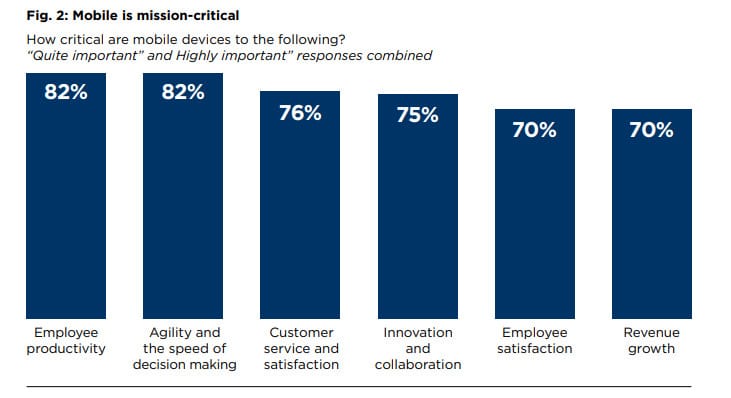
5. BYOD programs heavily influence productivity and decision making
A 2018 study by Samsung concluded that mobile is mission-critical after it asked employees what the most significant influence mobile devices had on their work ethic was. 82% of employees surveyed said mobile devices increased their productivity and the speed of decision-making in the workplace. 76% said mobiles have a positive impact on customer service and satisfaction.
6. BYOD strategies are often unregulated

In a report by Social Barrel, it emerged that BYOD programs are highly unregulated. As a result, 17.7% of survey respondents admitted they take their own devices to work, while 28.4% of IT departments actively ignore BYOD policies.
7. Less than 1 in 4 devices can be erased remotely
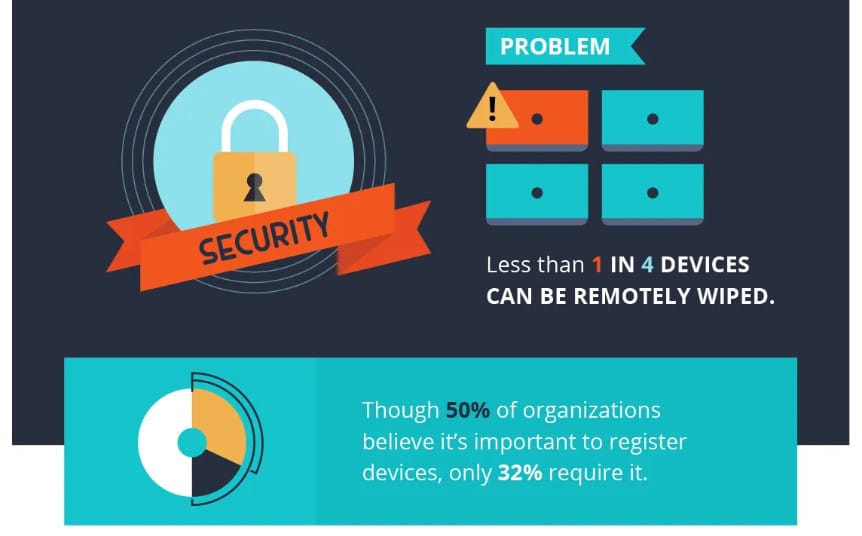
Social Barrel continued, stating that the ability to wipe BYOD devices remotely is unreasonably low, based on feedback from survey respondents. 50% of businesses recognize the importance of registering devices, yet only 23% of businesses have a policy in place to enforce it.
8. BYOE (Bring your own Enhancement) set to rise by 30% in 2023
Gartner predicts that BYOE, the concept of augmented employees, is set to rise in 2023 thanks to the advances in wearable tech. For context, human augmentation is an emerging technology that enhances employees’ ability to perform their jobs. This is most prevalent in oil and gas, healthcare, automotive, and retail industries. Common types of physical augmentation include smartwatches, smart glasses, augmented-reality glasses, and smart gloves.
9. 96%% of devices connecting to corporate networks are personal
A report by Dimensional Research showed that almost all devices connecting to an enterprise network are non-work issued devices. The figure is concerning as without proper regulation, significant security vulnerabilities may be present.
10. The worth of Bring your own Device (BYOD) is forecast at USD 366.95 Billion
Global Market Insights predicts that the BYOD market is set to soar by the end of 2022. For context, the BYOD market worth was 94.15 billion USD in 2014, which will have more than tripled in under a decade if predictions are correct.
11. Uptake of BYOD usage in the US has risen by 80% since 2018
Statistics provided by Frost and Sullivan paint a picture of how accepted BYOD policies are becoming across the US. However, the figure doesn’t clearly indicate device limitations, i.e., the company may provide laptops and desktops, but employees may be allowed to use their personal smartphones.
12. BYOD usage increased by 58% during the Covid-19 pandemic
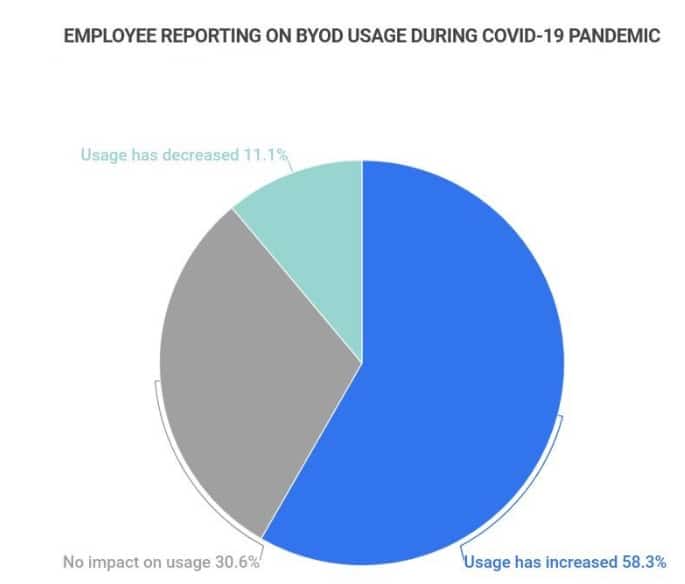
Zippia reports that BYOD usage since the 2019 pandemic has increased by 58.3%. 11.1% of businesses reported a decrease in BYOD usage for the same period, while 30.6% said the pandemic had no impact on BYOD usage.
13. BYOD has grown in popularity, with 83% of companies having a BYOD policy
Zippia’s report continued, stating that some business-use policies offer their employees a BUD (business use device), and some give employees the option of using a personal and business device. At the same time, some don’t issue a device at all.
14. 51% of employers have security practices in place for BYOD programs
11.1% of employees state they’re unsure if their business employs a security policy for BOYD, though worryingly, 37.9% of employees say their employer has nothing in place to secure business-user devices.
15. The number of employees storing work passwords on BUDs has risen by 35%
A survey by Ontech reports that more employees are saving their work passwords on business-issued devices (smartphones, to be precise). This is concerning, considering small business employees have an average of 85 passwords each, while larger business employees have 25 passwords.

